Case
A 68-year-old female patient with previous vertebral compression fractures from metastatic breast cancer treated with vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty presented a new incidental thoracic finding on the surveillance computed tomography (CT) scan. Venous phase contrast-enhanced CT revealed high attenuating linear intravascular material within the left pulmonary artery and its posterior, descending and lateral basal branches (Fig. 1). The patient had no respiratory or cardiovascular symptoms.
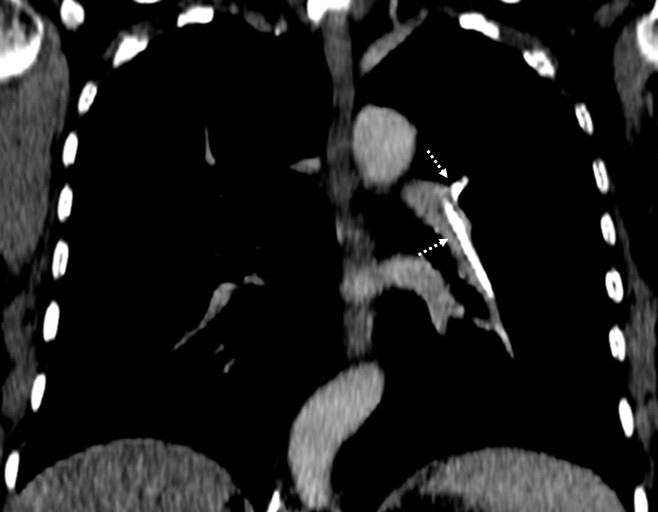
Figure 1: Reconstructed oblique coronal plane venous phase contrast-enhanced CT (mediastinum window) with high attenuating linear intravascular material within the left pulmonary artery and its posterior and descending branches (dashed arrows) consistent with bone cement pulmonary emboli.
Similar high attenuating linear intravascular material was found within the thoracic anterior external vertebral plexus at the level of T12 and the azygos vein (Fig.2, A); and within the lumbar anterior external vertebral plexus at the level of L5, the left common iliac vein and the inferior vena cava (Fig. 2, B). The vertebral bodies of T11, T12 and L5 were filled with the same high-density material (Fig. 2).
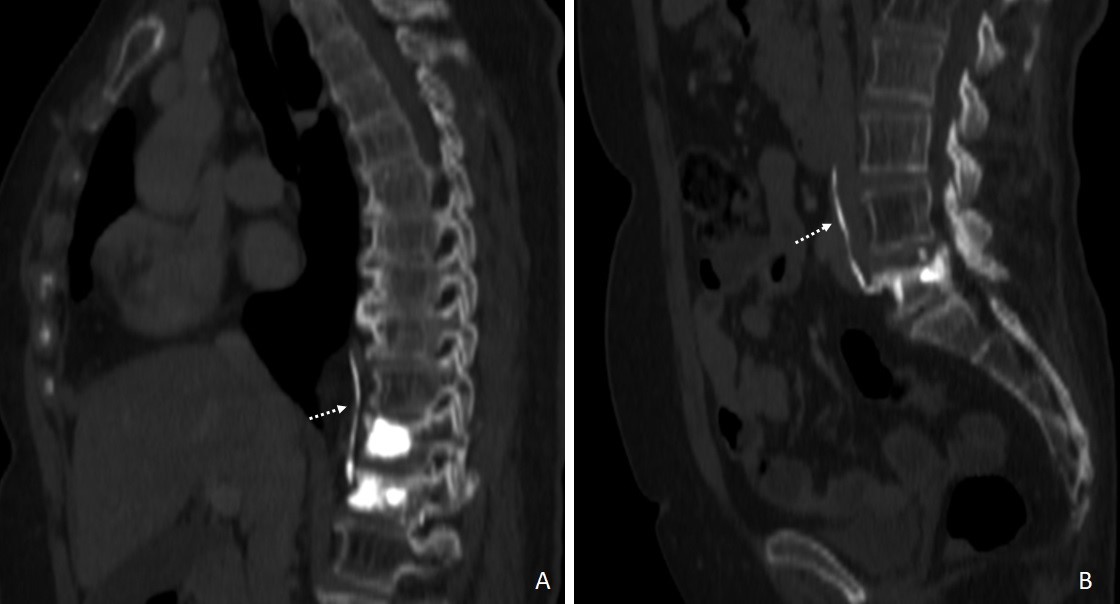
Figure 2: Reconstructed oblique sagittal plane venous phase contrast-enhanced CT (bone window) with high-density material filling the vertebral bodies of T11 and T12 and within the azygos vein (A, dashed arrow) and filling the vertebral body of L5 and within the left common iliac vein and the inferior vena cava (B, dashed arrow) indicating bone cement venous leakage.
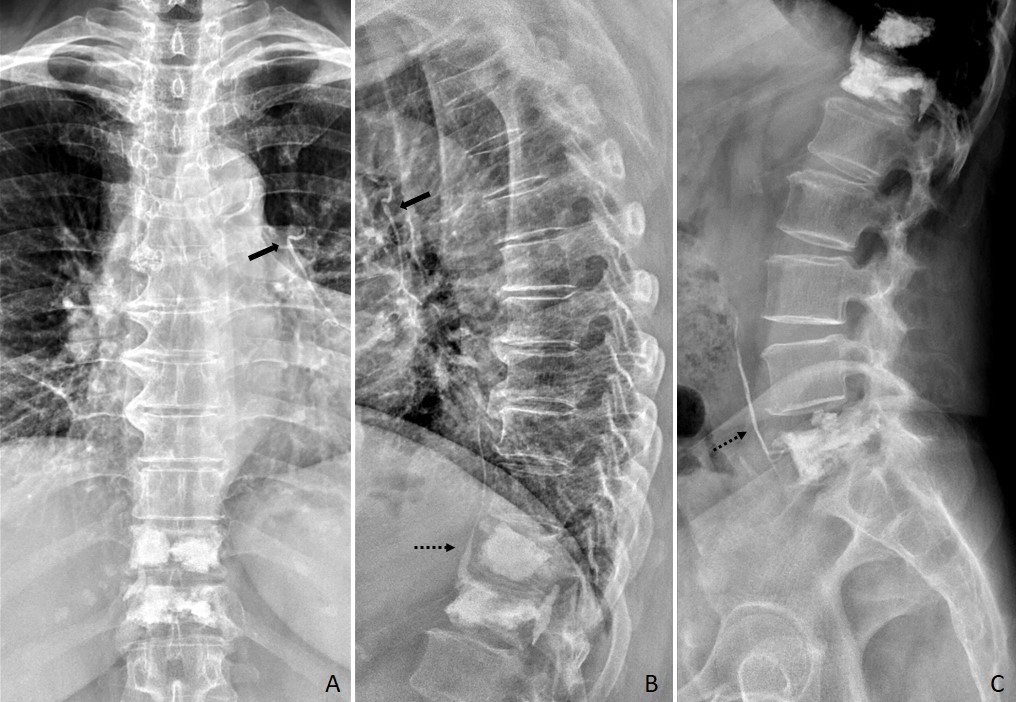
Figure 3: Postoperative thoracic and lumbar spine radiographs after vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty of T11, T12 and L5 demonstrate radio-dense linear opacities on the left peri-hilar region (arrow, A and B) and on the anterior paravertebral region (dashed arrow, B and C) consistent with leaked bone cement within the left pulmonary artery and its posterior and descending branches, the azygos vein, the left common iliac vein and the inferior vena cava.
These findings were consistent with pulmonary cement embolism after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty.(Fig. 3)
Discussion
Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty are widely used minimally invasive procedures for patients with symptomatic spinal compression fractures.1,2,3 By injecting polymethyl methacrylate cement into the vertebral body, under image guidance, it provides vertebral stability and immediate pain relief.1,3 Nevertheless, complications such as venous cement leakage into the paravertebral veins leading to pulmonary embolism are not uncommon.1,3 Compression fractures increase venous drainage of the already highly vascularized vertebral bodies3 and the risk of leakage is even higher when treating bone metastases since there is often cortical destruction.1 Furthermore, cement leakage into the inferior vena cava is a significant risk factor for pulmonary embolism.2 Most patients with pulmonary cement embolism are asymptomatic and do not develop any sequelae.1 Nevertheless, when associated with chest pain, dyspnoea, tachycardia or hypoxia, there should be suspicion of pulmonary infarction.2,3















