Introduction
Reticulate pigmentary disorders include a variety of diseases that exhibit significant clinical overlap. Dowling-Degos disease (DDD), as the main representative, is a rare autosomal dominant genodermatosis characterized by progressive pigmented lesions primarily involving large body folds1. Galli-Galli disease (GGD) is characterized by the association of DDD with an acantholytic dermatosis of the spectrum Darier, Hailey-Hailey, and Grover diseases2,3. It was first recognized by Bardach, Gebhart, and Luger in 19822. Only a few patients with this disease and genetic analysis have been reported (Table 1). Herein, we report a case of a female patient diagnosed with GGD, confirmed by genetic analysis, pointing out the clinical, dermoscopy, and histopathological aspects.
Table 1 Literature review. Galli-Galli disease with genetic analysis
| Author/year | Patients (age/sex) | Clinical description | Genetic analysis | Histopathology | Dermoscopy | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voth et al. (2011)11 | 68/M | Chronic pruritic erythematous hyperkeratotic papules of axillae, neck, trunk, and groin | c. 418dupA KRT5 gene | Lentiginous changes Suprabasal acantholysis | - | Topical corticosteroids (no improvement) Topical antibiotics (no improvement) Oral antihistamines (no improvement) Erbium: YAG laser (dyspigmentation) |
| Reisenauer et al. (2014)7 | 48/F | Pruritus and hyperpigmented erythematous macules and thin papules along the flexor surfaces of her arms, her upper back and neck, axillae, and inframammary areas | KRT5 (c. 38dupG; Ser14GlnfsTer3) | Lentiginous changes Suprabasal acantholysis | - | Tretinoin cream 0-025% cream (pruritus worsened, irritation) Hydrocortisone 2 a 5% and emollients as needed (no response reported) |
| Lõrincz et al. (2018)12 | 74/M | Hypopigmented papules, hyperpigmented macules of neck, trunk, and flexor extremities | c. 418dupA KRT5 gene | Lentiginous changes Suprabasal acantholysis | Acitretin, 25 mg every other day to daily (inflammatory eruption and pigmentation improved) | |
| Rundle, Ophaug & Simpson (2020)10 | 77/F | Widespread eruptions of pruritic crusted and scaling pink papules and tan macules, which started on the thighs and later progressed to involve the neck, trunk, flexor, and extensor surfaces of the extremities | Nonsense mutation in POGLUT1, p.(Arg218*); c. 652>T | Lentiginous changes Suprabasal acantholysis, dyskeratosis | - | Topical corticosteroids (no improvement) Doxepin, 20 mg nightly (no improvement) Acitretin, 10-25 mg/d (pruritus and papular eruption resolved) |
| Current report (2023) | 55/F | Reddish-to-dark brown hyperkeratotic papules and reticulated confluent macules scattered on the trunk and upper and lower extremities | c. 3G>C, P (Met111e) mutation on POGLUT1 | Lentiginous changes Suprabasal acantholysis, dyskeratosis | Irregular star-shaped brown mottled areas and yellow-brown polygonal structures surrounded by whitish haloes | Topical clobetasol propionate 0,05% and oral antihistamines. (modest improvement on pruritus; papular eruption not resolved) |
Clinical case
A 51-year-old female patient presented to our dermatology consult with a 21-year history of a pruritic eruption starting in the flexural areas with progression to the trunk and limbs. There was no personal or family history of skin disease. Physical examination revealed reddish-to-dark brown hyperkeratotic papules and reticulated confluent macules scattered on the trunk and upper and lower extremities (Fig. 1). Dermoscopy of the lesions showed irregular star-shaped brown mottled areas and yellow-brown polygonal structures surrounded by whitish haloes (Fig. 2A). At this point, we considered the following diagnostic hypotheses: Dowling-Degos disease, Galli-Galli disease, transient acantholytic dermatosis, and Darier’s disease. Histopathological examination of a leg lesion skin biopsy revealed focal acantholytic dyskeratosis and elongated rete ridges down-growing into the dermis (Figs. 2B and D). Clinical, dermoscopy, and histopathology features were compatible with GGD. Genetic screening found the c.3G>C, p(Met111e) mutation on the POGLUT1 gene, confirming our clinicopathological diagnosis. Treatment was attempted with topical clobetasol propionate 0.05% and oral antihistamines. The patient’s pruritus decreased, but the skin eruption has not resolved.
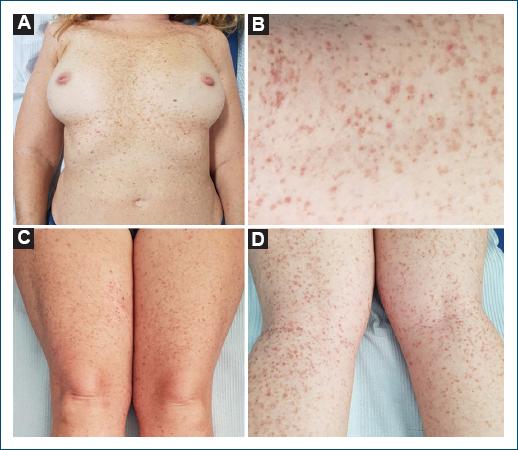
Figure 1 A: reddish-to-dark brown hyperkeratotic papules and reticulated confluent macules scattered on the trunk and upper extremities. B-D: numerous hyperkeratotic, red-brown, flat-topped papules, some with overlying peripheral crust, with a background of lentigo-like macules on lower extremities.
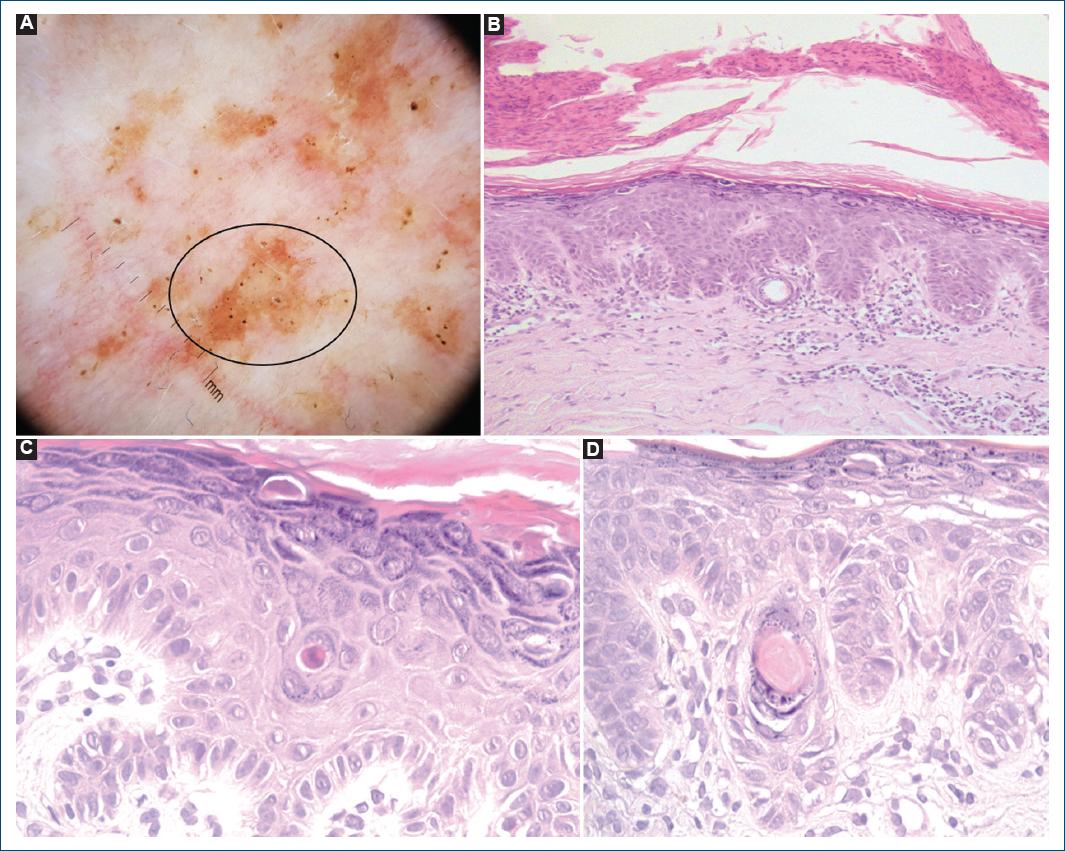
Figure 2 A: dermoscopy in polarized mode (×10 magnification) of a hyperkeratotic papule (leg): irregular star-shaped brown mottled areas (black circle) and yellow-brown polygonal structures surrounded by whitish haloes corresponding to follicular plugging and inclusion cysts; regular hairpin and dotted vessels are also visibly surrounded by whitish haloes on a pinkish background. B: histopathology (hematoxylin-eosin ×100) of a leg lesion skin biopsy revealed scattered suprabasal lacunae and a subcorneal cleft under a parakeratotic scale. Note the pattern of elongated, pigmented, finger-like rete ridge epidermal acanthosis and elongated rete ridges with down growth of filiform anastomosing epithelial strands. The dermis shows a dense infiltrate of predominantly lymphocytes. C and D: histopathology (hematoxylin-eosin ×400) of a lentigo-like macule biopsy revealed acantholysis, keratin plug formation, and dilatation of the follicular infundibulum with the focal formation of a pseudohorncyst.
Discussion
DDD is an uncommon genodermatosis; < 100 cases have been reported in the literature4. The most closely associated disorder is GGD, with both conditions being considered on the same disease spectrum3-6. GGD can be differentiated from DDD histologically, with the differentiating factor being the presence of acantholysis in GGD4-6. Thus, GGD is considered an acantholytic variant of DDD. The disease’s onset age varies, ranging from early adolescence to late adulthood6. The central genes implicated in DDD/GGD pathogenesis are KRT5 (keratin 5 gene), POGLUT1 (protein O-glucosyltransferase 1), POFUT1 (protein O-fucosyltransferase 1), and PSENEN (presenilin enhancer protein 2 gene)4,5. Our patient presented a mutation on POGLUT1, an essential regulator of Notch signaling. Mutations in POGLUT1 result in aberrations in Notch signaling, leading to abnormal pigmentation and keratinocyte morphology5. The mode of inheritance is thought to be autosomal dominant with variable penetration, but sporadic cases have also been observed, such as in our patient6.
Clinically, DDD/GGD presents with reticulate hyperpigmentation of the flexures; the main sites of involvement are the axilla, inguinal folds, submammary folds, and the neck4,6. Although the lesions are usually asymptomatic, they may occasionally be associated with pruritus4. At the physical examination, the lesions appear round-to-oval hyperpigmented lentigo-like macules3,4. Our patient presented a disseminated and pruritic dermatosis involving the trunk and extremities. Clinically, differential diagnoses include reticulate hyperpigmentation disorders such as Haber syndrome, acropigmentation of Dohi, and reticulate acropigmentation of Kitamura, that differ from GGD in clinical factors such as age of onset or location of skin lesions4-6. Haber’s syndrome is characterized by verruciformis papular lesions of the trunk and distinct facial erythema, most commonly presenting in childhood. The acropigmentation Dohi is characterized by the presence of hyperpigmented and hypopigmented pinpoints or pea-sized macules on the backs of the hands and feet. In Kitamura’s disease, breaks in palmar pits, and acral hyperpigmentation can be observed, especially on the backs of hands and feet6. In addition, the genetic background is different. The acropigmentation of Dohi is associated with mutations in ADAR1 (adenosine deaminase, RNA-specific 1) on chromosome 1, and mutations in ADAM10, encoding a zinc metalloprotease, have recently been identified in reticulate acropigmentation of Kitamura; at present, there are no genes/gene loci associated with Haber syndrome7.
Dermoscopy is not routinely employed for DDD/GGD diagnosis4. In our case, dermoscopy revealed some typical features of GGD: an irregular star-shaped brown outline on a red-brown background, follicular plugging, and inclusion cysts4,8. The dermatoscopic features may reflect the characteristic histology of DDD/GGD disease. The irregular brown star-shaped outline of color is created by the uneven distribution of inclusion cysts and follicular plugging, preventing visualization of the basal layer pigment4,8. Thus, dermoscopy may provide essential clues for diagnosing DDD/GGD when adequately integrated with clinical data. Knowledge of such in vivo features can allow an early diagnosis. Moreover, the most representative skin lesion for the histopathological examination can be taken based on a dermoscopy.
The well-defined pattern of acantholysis in GGD is a unique hallmark and a distinct histopathological feature within the histomorphologic monotony of reticulate pigmented disorders6. Histologic features of GGD include acantholysis and seborrheic keratosis-like changes, including follicular hyperkeratosis and epidermal acanthosis with down growth of filiform anastomosing epithelial strands with basal hyperpigmentation3,4. The histologic differential diagnosis for GGD includes entities characterized by focal acantholysis, namely Darier disease, Hailey-Hailey disease, and Grover disease3,4,6.
The treatment of DDD/GGD is complex, and a standard treatment strategy has yet to be established4. First, patients must be advised to avoid friction through clothing and to use sun-protective measures to prevent the worsening of hyperpigmentation. Reported therapeutic options include topical and systemic corticosteroids, topical retinoids, cyclosporine, and UVB phototherapy, although most of these interventions have shown limited success4,9,10. Intense pulsed light therapy and laser devices (Er: YAG; Q-switched Nd: YAG) have been used with acceptable results4,9,11. Ablating the pathologic epidermis and triggering regeneration of a new epidermis from the interfollicular epithelium may help resolve the clinical lesions4. Unfortunately, this condition is progressive, and most treatment modalities fail to resolve the lesions completely4,10. In our case, the patient refused treatment with oral retinoids and UVB phototherapy. The knowledge about the benign nature of the dermatosis was reassuring, and she was satisfied with pruritus control.
GGD and DDD are inherited skin diseases with variable progressive course. They are of benign and harmless behavior but esthetically annoying6. We present a rare case of GGD describing clinical, genetic, dermoscopy, and histopathological features. Clinicopathological correlation and good cooperation between dermatologists and histopathologists are essential to make the correct diagnosis of GGD.














