INTRODUCTION
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (XGPN) is an unusual variant of chronic pyelonephritis in which there is massive destruction of the renal parenchyma by granulomatous tissue containing lipid-laden macrophages and multinucleated giant cells. There is an intensive inflammatory infiltration and renal fibrosis.1
XGPN is typically a disease seen in adults, and it is rare and sporadic in pediatric-aged patients, where it is often confused with neoplasms and other inflammatory processes.1 It is usually associated with recurrent urinary tract infections (UTI) and renal calculi causing obstructive uropathy.2 However, the pathophysiological mechanism is not yet fully understood.1 The most common form in children is a diffuse and unilateral XGPN, and the clinical presentation is usually nonspecific and very variable.3 The diagnosis can be done by imaging techniques, but the definite diagnosis is done by pathological assessment.1
Here, we present the case of a child with this rare diagnosis of XGPN.
CASE REPORT
We report a case of a 2-year-old girl who presented to a pediatrician with a one-year history of UTI and recurrent cloudy urine with traces of sand. There was no information about the microorganisms involved in these UTI, nor their treatment. There were no other clinical signs or symptoms, and the patient was medicated with daily prophylactic antibiotics (oral sulfamethoxazole - trimethoprim).
Otherwise, past medical history and family history were unremarkable. The patient’s physical examination only revealed a supra umbilical hernia and an abdominal distension. The weight was in the 50th percentile (13.7 kg), height in the 15th percentile (90 cm), and blood pressure below the 90th percentile (80/38 mmHg). During follow-up, several urinalyses demonstrated pyuria without bacteria growth (urine analysis: always with cloudy aspect, pH between 5.5 and 6.5, density between 1.018-1.019, proteins of 100 mg/dL, negative nitrites and sediment with countless white blood cells (highest level of 776/μL)). No crystals were observed in any urine analysis. Na abdominal ultrasound (US) was then performed with no conclusive results, describing the presence of a right kidney with bosselated contours and heterogeneous structure with the presence of some hyperechoic foci translating lithiasis without na obstructive omplement.
At this time, she was admitted to the Pediatric Nephrology unit of our hospital, and the US was repeated. The second US showed a right kidney calyceal dilatation, staghorn stones, with the largest measuring 13 mm, and hyperechogenicity of perirenal tissue. Based on these imaging features, na abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan was ordered, revealing renal enlargement, presence of obstructive calculi, parenchyma destruction and involvement of perirenal tissue, suggesting the diagnosis of XGPN (Figs. 1 and 2).

Figure 1: Abdominal CT scan, 2omplem and axial plane, revealing right renal enlargement, presence of obstructive calculi (the one of larger dimensions with 12 mm), reduction in parenchyma thickness and involvement of perirenal tissue.
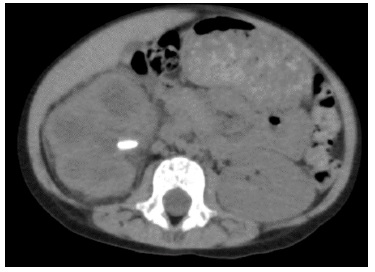
Figure 2: Abdominal CT scan, omplem and axial plane, revealing right renal enlargement, presence of obstructive calculi (the one of larger dimensions with 12 mm), reduction in parenchyma thickness and involvement of perirenal tissue.
Analytically, it should be noted that no abnormalities were observed in the blood count and in the infection parameters during clinical investigation. Serum creatinine (0.42 mg/dL, reference range of 0.30-0.70 mg/dL), urea and ompl and urine (in a random urine sample) electrolytes levels were normal and the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was 117.9 mL/min/1.73 m2 (according to Schwartz’s formula). Lymphocyte subpopulation, omplemente and immunoglobulins levels were in the normal range. Renal scintigraphy with technetium-99m dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) was performed and confirmed functional exclusion of the right kidney and the presence of cortical scarring and subacute alterations in the functional left kidney, these last ones interpreted in the context of previous UTI (Fig. 3). After diagnosis of XGPN and exclusion of the right kidney, a successful complete right nephrectomy was performed, and the histology confirmed the diagnosis. The surgical procedure was performed by laparotomy. Macroscopically abundant purulent content and extensive dilation of the pyelocaliceal tree were observed, as well as an absence of corticomedullary definition and marked decrease in renal parenchyma (measuring between 0.3 and 1.3 cm in thickness), without identified calculation (Fig. 4). Histologically, there was dystrophic calcification, extensive atrophy of the renal parenchyma, and foci of suppuration (Fig. 5). During the surgery, a voiding cystourethrography was performed, excluding the presence of vesicoureteral reflux. The surgery was uneventful, and the child was discharged seven days after the procedure with indications for follow-up in Pediatric Nephrology and Pediatric Surgery. At the time of writing this article, the patient was clinically well, fulfilling the clinical follow-up. No UTI occurred in the two years of follow-up and the renal US post-surgery only showed a vicarious left kidney (measure 102x53x52 cm).
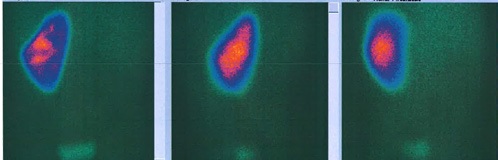
Figure 3: Posterior, left and right posterior oblique images of the renal DMSA scintigraphy, showing good uptake in left kidney and none uptake in the right kidney
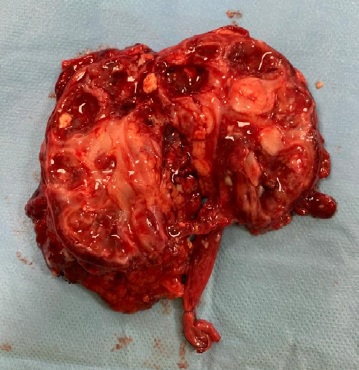
Figure 4: Macroscopic appearance of the affected kidney. Anatomical piece with 115 g and a total dimension of 9x6x5 cm (kidney dimensions: 7.5x4x4 cm)
DISCUSSION
XGPN is an unusual variant of chronic pyelonephritis in which there is massive destruction of the kidney by chronic obstructive nephropathy.1 This was first described by Schlagenhaufer in 1916 and was named xanthogranuloma by Osterlin in 1944. The term “xantho” that, in Greek, means yellow, is used due to the infiltration of lipid-laden macrophages that appear yellow in the pathological section.4 However, the first pediatric cases were only published in 1963 by Avent and Friedenberg.5 It affects mainly the adult population with a predominance in women in the sixth decade of life. It is a rare diagnosis in the pediatric population, with only a few cases having been described in this population.1,2
In children, some studies have shown a slightly higher predominance in the male gender with approximately 60%-75% being diagnosed before five years of age (the age varies between eighteen days and seventeen years, according to the cases reported in the literature).5-9 Renal involvement is usually unilateral, and some studies report a slight predominance in the left kidney.6,7 In extremely rare cases XGPN can be bilateral.1,2
The pathophysiological mechanism is not yet fully understood, but it is known that some factors may be involved. Chronic urinary obstruction by renal calculi (30%-50% staghorn calculus) or tumors, congenital urinary tract malformations, untreated chronic UTI, renal ischemia, lipid metabolism disorders, altered immune response and lymphatic obstruction are some of the factors reported in the literature.9,10 The most common pathogens seen in these cases are Proteus spp. (45%-62%) and Escherichia coli (15%-36%), followed by Pseudomonas spp. and Klebsiella spp. in some other patients.5,7,10 There is a case reported in the literature of an adolescent with XGPN with positive cultures to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, whose disease etiology was believed to be a bacterial seeding from a recently unsterile tattoo.11
The XGPN can present in two ways, a more frequent diffuse form and a less frequent focal form (less than 15% of the cases), but more common in children relative to adults (in a series of cases from Ireland with 66 patients only 8% were focal).2,5 In both forms there is replacement of renal parenchyma by granulomatous mixed inflammatory infiltrate composed of plasma cells, lymphocytes and numerous lipidladen macrophages, areas of suppuration and a dilated pelvicaliceal system with xanthomatous foamy histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells.1,2,5 In the diffuse form there is enlargement of the entire kidney, and in the focal form the disease is restricted to a renal segment or one pole of a duplex system.1 The perirenal infiltration can occur in both types and can be easily confused with renal neoplasm, such as Wilms’ tumor or other neoplasms as neuroblastoma, leukemia, lymphoma, clear cell carcinoma and retroperitoneal sarcoma, or an inflammatory process, such as renal or perirenal abscess, renal tuberculosis, focal or diffuse nephritis, sarcoidosis or Wegener granulomatosis disease.7,10
The extent of the inflammatory process can be divided into three different stages. In stage one, the inflammatory process is restricted to the parenchyma (14%); in stage two there is involvement of perirenal fat (66%), and in stage three the adjacent structures are invaded (20%), such as retroperitoneum, diaphragm and psoas muscle.1,5 In more advanced forms, there may be gastrointestinal involvement and fistulas may be created into the colon or duodenum, or even fistulas into the skin.12,13
Our patient had a stage-two disease, the most frequently observed. Clinical presentation is extremely variable and non-specific. In a series of 66 cases from Ireland, the median of symptom duration was twenty days (88% with less than 4 weeks of duration), and the most common presentations were systemic illness (62%), abdominal or flank pain (60%), fever (53%), UTI (54%), abdominal mass (39%) and hematuria (12%).5 In another case series of 17 cases, 77% of patients were below the third percentile of weight, and the most common symptoms were abdominal or flank pain, weight loss and anorexia, ranging from 1 to 24 months of duration of symptoms until the diagnosis.6 Analytically, anemia is observed in most patients (86%), of this one third with hemoglobin level below 8 g/dL and more than two thirds with polymorph leukocytosis (71%), thrombocytosis (80%) and hypomagnesemia (65%). The erythrocyte sedimentation rate is high in 86% of the patients.5 In blood tests, we also frequently observed an elevation in C-reactive protein level (until 100%), and in urinary sediment, besides hematuria, pyuria (87%) and proteinuria were also observed.5,10 Urine cultures are positive in 60%-100%, but in the case series with 66 patients mentioned above, almost half of the patients (44%) did not have any microorganisms identified.5,6,10 In some cases, cultures may show mixed bacterial growth (15%-18%).5,7 It should be noted that typically urinary tract symptoms (like dysuria) are uncommon.1 Our patient did not have any analytical changes or other abnormalities in the physical examination, making the diagnosis difficult at an early stage. However, the presence of persistent pyuria without bacterial growth had to be investigated.
Radiological features of US and CT scan, in combination with clinical signs and symptoms, enable the diagnosis of XGPN, as in the case presented herein.1 In the diffuse form, US can show multiple hypoechoic areas with perinephric collection and fatty infiltration of the kidney, and CT scan can show global enlargement of the kidney with multiple areas with round hypoattenuation and focal regions filled with pus or debris (forming the so-called “bear paw” sign). The perirenal involvement can be observed by blurring the perirenal fat and psoas muscle contour.2 Contrast CT scan or a magnetic resonance imaging can be useful in planning the surgical procedure, as it allows a better definition of the perirenal inflammation.13,14
Clinical investigation should also be carried out during other clinical situations, when the symptoms are poorly explained by the initial diagnosis, such as the case of an adolescent diagnosed with multisystem inflammatory syndrome associated to COVID-19, whose persistence of fever and abdominal pain after hospital discharge, led to the diagnosis of an abdominal mass corresponding to a XGPN confirmed after histological diagnosis.14 Obstructive cases are generally diagnosed preoperatively (82%) by their characteristic clinical and radiologic features.7 In the Irish case series of 66 patients, up to 74% of the patients were diagnosed before surgery.5
Although imaging methods are extremely useful, the definite diagnosis is histopathological.1 In pathological assessment, we can see the findings described above and also within our case report. Renal DMSA scintigraphy or renogram can be done to assess renal function (90% of patients can have less than 10% of function in the affected kidney).5
Treatment varies according to the form of the disease.1,2 In the diffuse form, generally, a total nephrectomy is performed, with or without antibiotic therapy.15 The procedure generally involves an open radical resection; however, laparoscopic intervention has been described in the literature. There is a case report of a 5-year-old girl with a XGPN with a nephrocutaneous fistula submitted to a successful laparoscopic resection, whose fistula tract was also used for specimen extraction.16
In the focal form, partial nephrectomy can be the suggested approached, but first, a cycle of antibiotic therapy can be attempted, and has been shown to successfully treat the XGPN, without the surgical procedure and with no recurrence reported.1 This was evidenced in the case of an 18-day-old female neonate, where a focal form of XGPN was successfully treated with seven weeks of systemic antibiotic therapy, without any complication or recurrence.8. It should be mentioned that a renal biopsy may be necessary in focal forms to confirm the diagnosis and exclude other conditions.17 After surgical nephrectomy, the long-term prognosis is usually excellent, without recurrence in the contralateral kidney. However, a routine follow-up should be done to monitor the single kidney.1
Concluding, this case highlights the importance of complementary tests in a child with signs and symptoms of urinary tract dysfunction, in order to exclude any pathology requiring therapeutic intervention. In our case report, the first inconclusive US made us proceed with the investigation in other to find the pathological condition that was causing the symptoms. In relation to XGPN, we should have a high index of suspicion, since clinical presentation is usually nonspecific and very variable.
















