Introduction
Current literature describes a multiplicity of constructs related with career success. This concept is referred by Hirschi and colleagues (2018) to designate both objective success, that can be externally confirmed (e.g., finding a job after graduation) and to subjective success, which implies the evaluation about career progress according to one’s criteria (e.g., graduates’ perceptions of employability). One evidence of the diversity of knowledge produced that refer to career success is observable through the several meta-analysis published in the last years around this concept (e.g., Fuller & Marler, 2009; Ng et al., 2005; Ng & Feldman, 2014; Rudolph, Lavigne, Katz et al., 2017; Rudolph, Lavigne, & Zacher, 2017; Zhao et al., 2020). Overall, these studies identify an extensive range of predictors of subjective and objective dimensions of career success, that were organized in four major malleable dimensions identified by Hirschi and colleagues (2018) as human capital and career management resources, environment and motivation, basic dimensions of the career resources model. These four dimensions stand out for their predictive power of career success in a concise way, taking advantage of the extensive, but also fragmented knowledge so far produced and that define the framework of the career resources questionnaire (Hirschi et al., 2018). Therefore, career resources are defined by the authors as “anything that helps an individual attain his or her career goals” (p. 4).
Despite the promising results obtained by the authors in the validation study of the original version of the career resources questionnaire with worker and student’s samples, with good indicators of reliability, convergent and criterion validity, to our knowledge, there is still not diversified empirical research evidencing validity indicators in diversified contexts. Furthermore, and once the validity of the instrument has been demonstrated, it is relevant to use it to explore open issues in the career development literature. One example of that relates to the development of career resources over time and how the development of one set of resources can influence the development of others (Hirschi et al., 2018). In the educational context, the spiral effect of competencies development is well recognized since the Blooms’ taxonomy (Krathwohl, 2002), knowledge now retrieved in the literature about the 21st century skills (Allen & van der Velden, 2012; Silva, 2008). However, such information is not so clear in the career development literature, that is, there is still not evidence if there is a cumulative effect of career resources, and, if it exists, how the different resources are structured and how they are expanded over time and in which circumstances.
Another relevant issue regards the association of sociodemographic and educational attainment variables with the development of career resources. For example, parental education represents one common indicator of social and cultural background, which is theoretically expected to hamper access to the labour market among graduates from disadvantaged backgrounds (Blasko et al., 2002; Erola et al., 2016; Tomlinson, 2017). Age, is also frequently considered in the career development literature. Although, the conclusions about the relation of this variable with career outcomes are not so linear because of the difficulty to disentangle it from other variables, such as work experience, for example (Froehlich et al., 2015). A positive association between career management skills, work experiences and age has been demonstrated, based on the ability to activate and mobilize work- related skills and planning at the time of transition (Phillips et al., 2002), but also on higher levels of career maturity, career decision-making capacity and self-efficacy (Creed et al., 2007; Edwards, 2014; Van Dinther et al., 2011). This is coherent with other studies defending an increased sense of competence and understanding of the world of work from worker students (Bennion et al., 2011; Edwards, 2014; Jamieson et al., 2009; Swain & Hammond, 2011). However, other studies have also identified lower confidence from older students regarding the expected returns of education in employment prospects (Brine & Waller, 2004; Egerton & Parry, 2001). Similarly to work experience, extracurricular activities or programs have been associated with positive effects on career development, namely career exploration (Munson & Savickas, 1998; Potts, 2015), opportunity to develop experiences providing the perception of competence (Munson & Savickas, 1998), career agency (Munson & Savickas, 1998; Potts, 2015; Wu et al., 2010), soft skills development (Lau et al., 2014; Potts, 2015) and future career prospects (Potts, 2015). Nonetheless, the benefits derived from extracurricular activities’ engagement seem to result more from individual’s experience and strategic plan rather than the activity itself (Thompson et al., 2013; Tinsley et al., 1993). This can explain the non-significant or negative correlations between extracurricular activities and career-related variables and outcomes that has also been found (e. g., Monteiro & Almeida, 2015; Pinto & Ramalheira, 2017; Thompson et al., 2013).
This brief overview highlights the relevance to include individual and familiar characteristics that might influence career resources development. Gathering evidences about such features is particularly relevant to improve knowledge about how career resources develop over different sociocultural contexts. This knowledge could inform career intervention programs about what type of actions are relevant to include in each stage of higher education studies and with diversified graduates’ profiles in order to smooth the university-to-work transition impact (Monteiro, Almeida, & García-Aracil, 2020; Tuononen et al., 2019) or to foster graduates’ employability prospective (Bridgstock, 2009; Monteiro, Almeida, Gomes et al., 2020).
The main aim of this article is to present the process of adaptation for the Portuguese context of the career resources questionnaire with higher education students and to evidence indicators of reliability, construct validity and criteria validity of this instrument. Although the process of development of career resources will not yet be explored, first and later years graduation’ students will participate in this study, in order to obtain evidences of validity of the scale with a heterogeneous sample. Sociodemographic and educational attainment variables above presented, that are expected to have relation with career resources, will be considered.
Method
Sample
A total of 652 participants completed the instruments, from 3 different course fields of a Portuguese public university. The majority of the participants are Portuguese (93%), 5% are Latin American (Brazil, Argentina and Equator), 1% are African, and 0.9% from other European countries (Spain, France, Italy and Romania), with ages ranging between 16 and 59 years old (M=21.30, SD=4.98). Regarding gender distribution, around 64% are female. Average course achievement was 14.37 (SD=1.69), in a 0-20 scale. Remaining descriptive sociodemographic and academic background variables are presented in Table 1.
Procedures
The participants were higher education students from a Portuguese public university. The invitation for participation was made in person at classroom or by email, after a previous contact and approval of schools and courses directions. Data collection was divided in two moments. The first, aimed at 2nd year undergraduate students, occurred during the first semester of the academic year of 2019/2020, in classrooms, where participants accessed through their smartphones or laptops to a link for the instrument, which was made available via Google Docs. The second moment, aimed at 4th year undergraduate students, occurred during the second semester of the academic year of 2019/2020. In this case, due to the suspension of attendance classes caused by the Covid confinement measures, data was collected through the direct collaboration of course directors, who forwarded the invitation for participation to students, which included the link for the instrument made available via Google Docs. In both moments, a text describing the objectives of the study and the voluntary nature of the recruitment process was presented to participants, who then decided about their participation and, in case of agreement, signed an informed consent form. No reward was offered for participation in the study. The obtained data was analyzed with the software IBM SPSS (version 26.0) and Amos (version 26.0).
Adaptation of the instrument
The process of translation adaptation of the English version of the CRQ (student version) to the Portuguese language followed three stages: (i) translation and back translation involving three specialists, proficient in both languages, and with experience in the content of the items and with the sample under study (higher education students); (ii) item content analysis, appreciating the clarity of the items, adequacy to the study objectives and target population, by two other independent specialists, with knowledge in the field and about higher education population; (iii) a pre-test with a subgroup of 30 participants with the same characteristics (age and year of course) of the sample used in the study. This pre-test was developed both with paper and pencil and with online form available from Google Docs.
Data analysis
Descriptive statistics and correlations analysis were performed with the software IBM SPSS Statistics version 26. Confirmatory analysis was conducted with IBM SPSS AMOS 26 Graphics, using maximum likelihood estimation. As the questionnaire required a mandatory response for all items there were no missing data. To analyze convergent validity evidence, values of AVE≥.5 were considered acceptable, as suggested by Fornell and Larcker (1981). Discriminant validity was evaluated using correlational analysis and was considered adequate if AVEi and AVEj≥r ij 2 (Fornell & Larcker, 1981). Reliability was evaluated using composite reliability (CR) (Fornell & Larcker, 1981) and ordinal alpha coefficient (α) (Marôco, 2014). Values of CR and α≥0.70 were considered indicative of adequate reliability. The goodness-of-fit was evaluated using chi-square statistic and is p-value, the chi-square per degrees of freedom ratio (χ 2 /df), Comparative Fit Index (CFI), Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI), and Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA), with a 90% confidence interval (90%CI). According with Marôco (2014) and Kline (2015), the model’s fit to the data was considered appropriate when: χ 2 /df≤5.00, CFI and TLI≥0.90, and RMSEA≤0.10.
Results
The Portuguese version of the CRQ (Higher Education Form) is presented in Table 2. The instrument is composed by a total of 38 items, aggregated in twelve dimensions: (i) Occupational expertise; (ii) Job market knowledge; (iii) Soft skills; (iv) Organizational career support; (v) Job challenge; (vi) Social career support; (vii) Career involvement; (viii) Career confidence; (ix) Career clarity; (x) Networking; (xi) Career exploration; (xii) Learning. A 5-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 (completely false) to 5 (completely true), was presented for participants respond to each item.
Table 3 provides the summary measures of items to describe the psychometric sensitivity of the Portuguese version of the CRQ. All the items present kurtoses and skewness around the 0 value, which means this sample is close to the normal distribution. All the items of the scale showed factorial weights higher than .5 in its specific factor (Model 3 of 12 factors, presented in Table 4).
Construct validity
Four different models were tested to explore structure and dimensionality of the items in the Portuguese sample, as presented in Table 4. Model 1 represents a one-factor model with all items loading in a single factor. Model 2 reflects a four-factor model with all items loading onto the higher-order domains (human capital career resources, environmental career resources, motivational career resources and career management behaviors). Model 3 presents the twelve-factor model, where the items were grouped in twelve dimensions, as presented in the original version (Hirschi et al., 2018). Lastly, model 4 tested a hierarchical structure, where the twelve factors loaded onto their respective four higher-order dimension, as it was theoretically hypothesized. Although both models 3 and 4 presented acceptable values (CFI and TLI≥.90 and RMSEA<.05), model 3 provides the best fitting model, which, together with high standardized factor loadings of the items in the respective scale, presented in Table 3, support the construct validity (Arbuckle, 2008; Bentler, 1990). These results were similar to those obtained by Hirschi and colleagues (2018) in their students’ sample.
Convergent validity and discriminant validity
Correlations analysis between the twelve dimensions obtained in confirmatory factor analysis are presented in Table 5. Correlations between items composing each factor were also observed trough Average Variance Extracted (AVE) and Composite Reliability (CR). All the factors present AVE>.5 and CR>.70, which indicate an adequate convergent validity of the twelve factors. The AVE of the twelve factors is greater than the square of the correlation between factors, which, according to the criteria of Fornell and Larcker (1981) confirms discriminant validity of the factors. Correlations observed between the CRQ factors evidence that the majority of the factors are significantly correlated, with a magnitude of correlations between weak (R=.08) to high (R=.67), adopting the criteria proposed by Hemphill (2003).
Table 5 Correlation matrix between CRQ factors, Average Variance Extracted, Composite Reliability and Coefficient Cronbach’s alpha
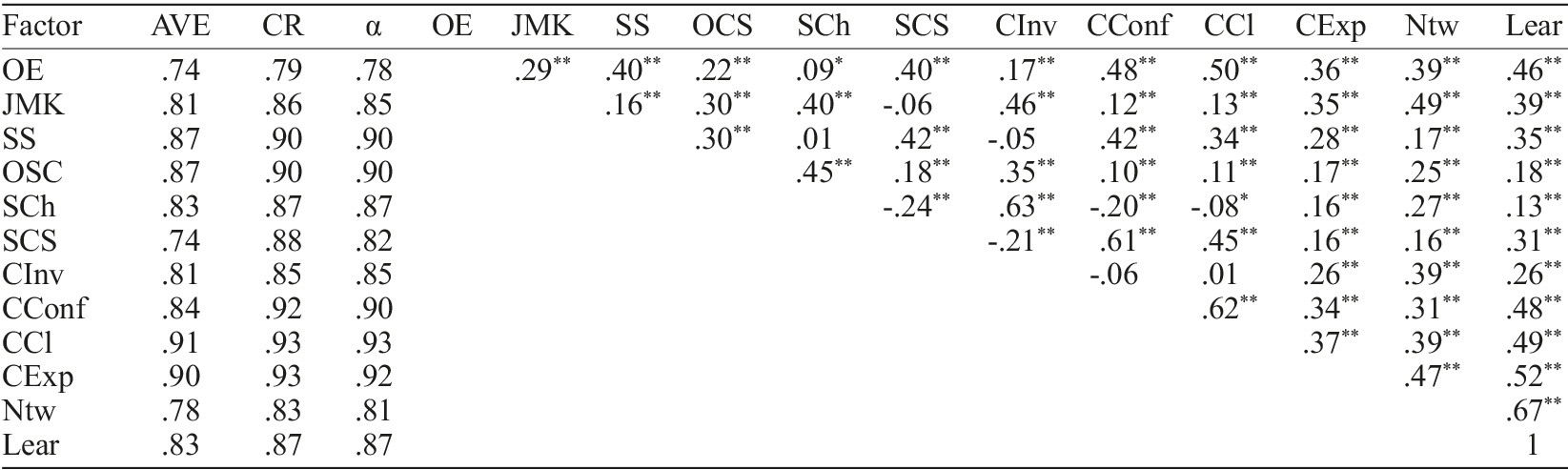
**Notes. OE - Occupational expertise; JMK - Job Market Knowledge; SS - Soft Skills; SCh - Study Challenge; SCS - Social Career Support; CInv - Career Involvement; CExp - Career Exploration; Ntw - Networking; Lear - Learning. Significant correlation at the level .01.
Reliability
Reliability assessed by Coefficient Cronbach’s alpha (α) and by the Composite Reliability (CR) and presented in Table 5 reveal that all 12 factors have good internal consistency (>.70) to excellent (>.85) (Nunnally & Bernstein, 1994).
Criterion validity
To test criterion validity, some background variables (age, parental education, work experience and extracurricular experience) and educational outcomes (course achievement and course satisfaction) were correlated with the CRQ (Table 6), on separated groups: total sample; 2nd year students; 4th year students. In a general overview, there seems to emerge more significant correlations among the 2nd year than among the 4th year students. In all the groups, age and work experience were the background variables with more significant correlations with CRQ factors. Parental education presents weaker correlations, with five of the factors of the CRQ significantly related with this variable. Regarding educational outcomes, CRQ factors are strongly correlated with course satisfaction and with course achievement. The majority of the CRQ factors are significantly correlated with course satisfaction, in the three groups, ranging between the weak (R=.08) to high (=.45) correlations, with stronger correlations among the participants of the 4rd year of graduation. Negative correlations were found between study challenge and social career support, career confidence and career clarity.
Table 6 Correlation matrix between CRQ factors and criteria variables
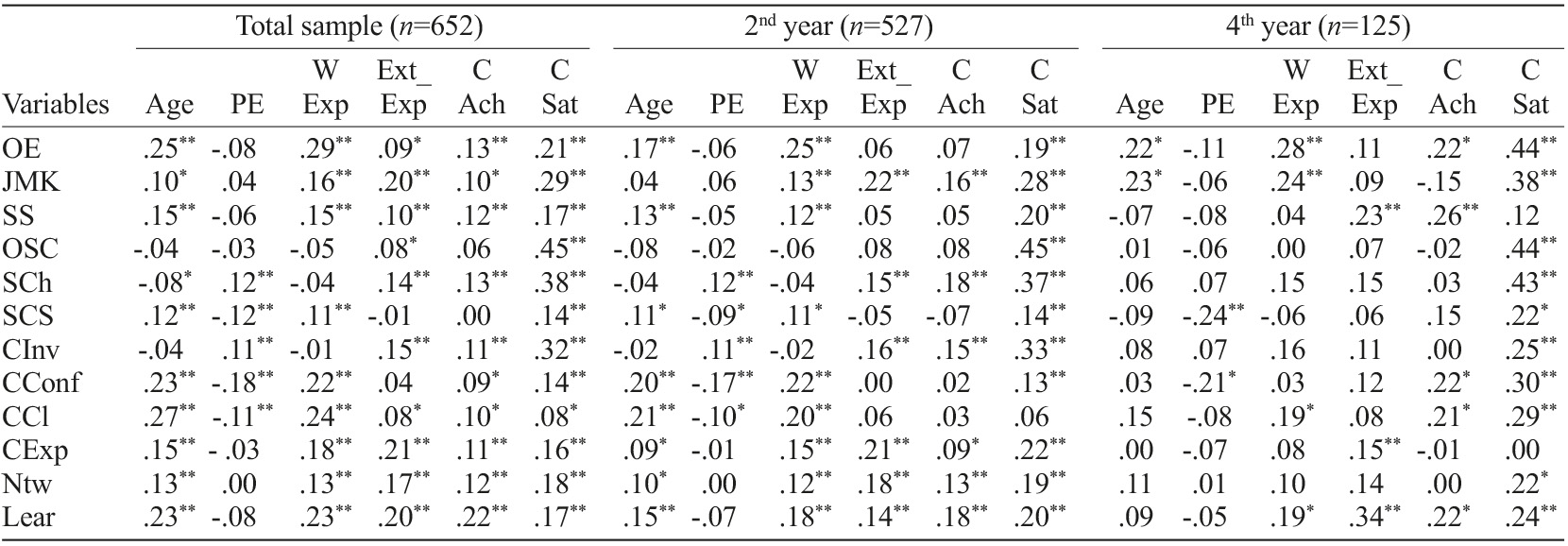
***Notes. OE - Occupational expertise; JMK - Job Market Knowledge; SS - Soft Skills; SCh - Study Challenge; SCS - Social Career Support; CInv - Career Involvement; CExp - Career Exploration; Ntw - Networking; Lear - Learning; PE - Parental Education; WExp - Work Experience; ExtExp - Extracurricular Experience; CAch - Course Achievement; CSat - Course Satisfaction. Significant correlation at the level .05; Significant correlation at the level .01.
Discussion
This study shows that the CRQ evidences robust psychometric characteristics for the Portuguese sample used in this research. These results strengthen the validation previously published by Hirschi and colleagues (2018) with a student sample, extending it to a sample from a different culture and socioeconomic context. To our knowledge, this is the first replication study regarding the psychometric properties of this instrument, and the first adaptation for the Portuguese context. Also, students from different levels of their academic degree were considered, as a first way to capture possible diversity of resources’ development and to explore different possible levels of correlations with criteria variables.
Regarding the factorial structure, the model that showed the best fit was the twelve-factor model, similarly to the results obtained in the original study. However, the hierarchical structure, with the twelve factors loading in the respective four higher-order dimension, also demonstrated acceptable fit results. Convergent and discriminant indicators of the different factors composing the CRQ, as well as internal consistency of items per factor, reinforce construct validity. These results confirm the career success framework of twelve specific dimensions, within four wider areas, as a valid model.
Correlations between the CRQ factors and external variables indicates a significant association with background variables and outcomes variables, ranging between weak to high correlations. Although, taking into account the career-related nature of the instrument, it is expected that stronger correlations and predictive power might be found with future external variables, such as employability, job and career satisfaction or work engagement, which refer to the relevance of extending this study over time. The majority of the correlations between the CRQ dimensions are positive, with the exception of the negative correlation found between study challenge and social career support, career confidence and career clarity. A possible explanation for this can be that students with higher career confidence and clarity and social support can be more demanding with regard to the level of the course they attend. Age, work experience and extracurricular experiences appear to have significant association with career resources variables, which might mean these variables can potentially interfere in career resources development. Parental education indicators manifest slighter correlations with career resources, which can have several meanings that cannot be completely enlightened in the scope of the present study. One possibility regards the fact that more disadvantaged groups being unrepresented in this study, simply because these subgroups of population do not reach higher education levels. Another possibility is the university experience to blur existing differences directly related with parental education, such as social and cultural capital
Limitations and further research
This study represents a first step for open doors for further research that might explore and develop some other aspects that this study could not address. A first issue regards the fact that the sample used in this study comes from a single university. Further studies should integrate other university contexts, which can be particularly relevant to capture higher diversity in the organizational career support dimension. A second aspect concerns the lack of longitudinal data, which could inform the predictive capacity of the CRQ with future career outcomes. Likewise, the evaluation of career resources over graduation studies also represents a relevant topic for further research. Although this sample involved students from earlier and later stages of their higher education studies, this is a cross-sectional study. This limits the extraction of conclusions that longitudinal data would allow, through evaluation of career resources in two or more different moments. Further research, with more balanced sample sizes, could fall on the model invariance across earlier and later stages of higher education studies, as a way to confirm that the same construct is being measured across these two groups.
Practical implications
The existence of a valid, concise and comprehensive scale is highly valuable for the international perspective, but also for the Portuguese context, where an equivalent measure does not exist, at least, to our knowledge. This brings a set of practical benefits, not only for the fostering of career resources research, but also for career counseling and for universities pedagogic and career services. Such instrument allows the development of evidence-based interventions that can be adjusted according to needs previously diagnosed, at the same time that the results of these interventions can be evaluated and be targeted for continuous improvement. The identification of key career resources areas, through the CRQ, can also support and inform curricular and pedagogical interventions in order to improve graduates’ satisfaction with their higher education experience and as a way to foster their employability. All these concerns become more relevant in a time where students accessing Higher Education arrive with increasingly heterogeneous profiles, which require appropriate responses from institutions.