Introduction
In recent years nuts are gaining popularity, not only among the consumers but also among the producers. Hazelnut (Coryllus avellana L.) is the second most consumed nut worldwide, just after almond, being Turkey the biggest producer (Nunzio, 2019). Hazelnut consumption is associated with several health benefits, due to its composition in macronutrients (lipids and fibre), micronutrients (minerals and vitamins), fat-soluble bioactives (tocols, phytosterols, phytostanols and squalene) and phytochemicals (flavonoids and phenolic and hydroxycinnamic acids) (Alasalvar & Bolling, 2015; Glei et al., 2018; Oliveira et al., 2008). This dried fruit can be consumed not only as a snack food, but can also be incorporated in different manufactured food (Tunçil, 2020). Approximately, 80% of the hazelnut production is used in the chocolate industry, confectionery, pastry, ice cream and biscuits (Aydoğan et al., 2018). Nowadays, there are different hazelnut varieties, almost 400, although only 20 of them represent the basis of the worldwide production (Nunzio, 2019).
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO, 2017), in 2017, the worldwide production of hazelnut was approximately one million tonnes. In Portugal, this crop occupied an area of about 357 hectares, with an annual production of approximately 307 tons (INE, 2018). In recent years, producers in this sector have suffered a crisis, which has led to the abandonment of many of the Portuguese hazelnut orchards, mainly due to their low productivity, implementation and cultivation errors, as well as unusually low sales’ prices and great difficulties to compete in the foreign market (Correia et al., 2017a; Silva et al., 2005). However, because of the increasing demand from consumers and high health benefits, there is an interest in increasing the area of this culture (Botta et al., 2019).
This study is included in the project entitled “ValNuts: Valorisation of nuts”, which aims the implementation of good practices in harvest and post-harvest processes, as well as the development of new products that bring added value to nuts’ producers and processors.
Good harvest and post-harvest practices are essential to achieve a good product, which defines their marketability and producers’ profits (Turan el al. 2019). Therefore´, the specific main goal of this particular study was to characterize the post-harvest hazelnut sector in a sample of Portuguese producers living in the Viseu district and also in the sole Portuguese hazelnut industry.
1. Methods
1.1 Instrument
To undertake this study it was prepared a survey to access information about several issues related to hazelnut fruits, and which included the following sections: Part I - Sociodemographic data; Part II - Identification of the main varieties of hazelnut produced in Portugal; Part III - Post-harvest practices and Part IV - Distribution practices.
Part III included different questions about the post-harvest practices, such as:
How the fruits are harvested?
Total time to collect the hazelnuts
Are the harvested fruits delivered immediately? Where and under what conditions are they stored?
Main problems during the storage
How and under what conditions are hazelnuts transported?
Product disposal modalities
In part IV were included questions to address how and in what conditions the hazelnuts were distributed. It was also analysed the main problems in the distribution of nuts sector.
1.2 Data collection
It was undertaken a cross-sectional study on a sample of 10 hazelnut producers from Viseu, Portugal. The size of the sample was made according to the defined in the Project and taking into consideration the most representative producers of this sector. The survey was also applied to the sole hazelnut industry in Portugal.
The data were collected from December 2017 to January 2018, by personal interview, and all ethical issues were verified when designing and applying the survey.
1.3 Statistical analysis
For data analysis basic descriptive statistical tools were used, namely, frequency distribution, mean and standard deviation. For all data analysis was used the SPSS software from IBM Inc. (version 25).
2. Results and discussion
2.1 Sample characterization
Table 1 summarizes the demographical data for the sample studied. In this survey participated 10 producers, with an average age of 53±18 years. All of the participants lived in the Viseu district. The majority of the participants, 66.7%, had a university degree and 75.0% of them did not have studies in agriculture areas.
Table 1 Sociodemographical characterization of the sample at study.
| Sociodemographic Data | Percentage (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age group | ≤ 30y | 14.3 |
| 31y ≤ age ≤ 50y | 28.5 | |
| 51y ≤ age ≤ 64y | 28.6 | |
| ≤ 30y | 28.6 | |
| Education degree | Primary school | 11.1 |
| Secondary School | 22.2 | |
| University degree | 66.7 | |
| Studies in agriculture area | Yes | 25.0 |
| No | 75.0 | |
From the sample at study, beyond hazelnuts the participants also produced almonds (20.0%), walnuts (80.0%) and other nuts (10.0%). When the participants were asked if they dedicated themselves exclusively to the agricultural sector, 60.0% answered yes, against 40.0% that answered no. For 50.0% of them, the labour of the company was exclusively salaried, for 40.0% it was family and salaried and for 10.0% it was exclusively family.
2.2 Characterization of the main varieties of hazelnut produced in Portugal
Figure 1 shows the type of the participants’ hazelnut crop and for 80.0% of them the hazelnut plantation was in the form of an orchard, against 30.0% for which the plantation was as parcel bordering. It was also observed that only one participant, 10.0%, had his hazelnut plantation both in the form of parcel bordering and orchard. Furthermore, none of the participants had their plantation with isolated trees. For those who had their hazelnut plantation in the form of an orchard, it was observed that all of them had orchards up to 10 hectares.
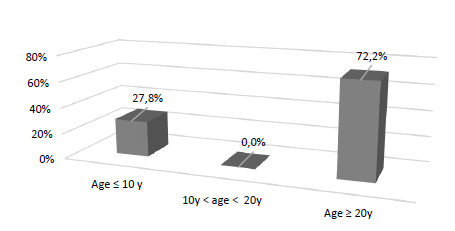
Figure 2 presents the age of the participants’ hazelnut orchards and 72.2% of the orchards were aged 20 years or more, ranging from 2 to 30 years old, meaning that the majority of the orchards were old. It was also observed that 61.1% of the orchards were characterized by dry cultivation.
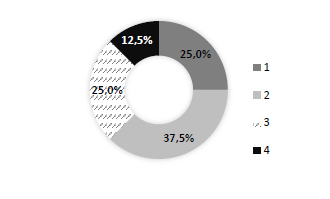
The participants were also questioned about the number of parcels of their orchards and 37.5% had two parcels, 25.0% three parcels, 25.0% one parcel and only 12.5% of the participants had four parcels (Figure 3).
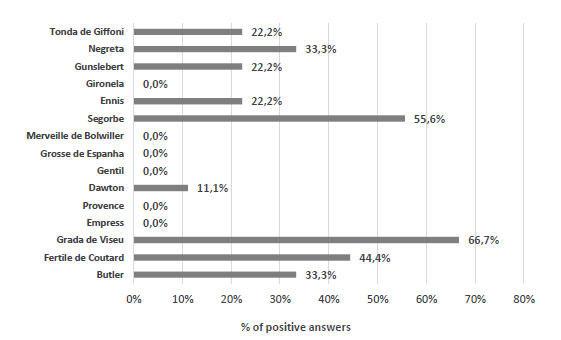
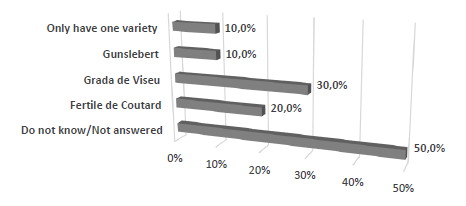
As it can be observed in Figure 4, the varieties most cultivated by the producers were Grada de Viseu (66.7% of positive answers), followed by Segorbe (55.6% of positive answers). According to the literature, the most common hazelnut varieties in Portugal are Fertile de Coutard, Grada de Viseu, Negreta and Tonda de Giffoni. There are also other common hazelnut varieties, namely Gunslebert, Merveille, Daviana, Butler and Ennis (Correia et al., 2017a; Vaz, 1999; Silva et al., 2003).
The annual quantity of production varied between 0 and 12 tons, with an average of 1.93 ± 3.71 tons.
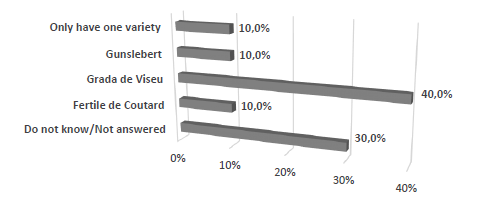
The producers were also questioned about the most important varieties in terms of production and 40.0% of them indicated that to be Grada de Viseu (Figure 5).
As for the most important variety in terms of productivity, 30.0% of the producers also answered Grada de Viseu (Figure 6).
The main problems pointed by the producers were lack of incentives and difficulties in competing with foreign market prices. These problems are not knew and effectively are the main reasons for the abandonment of many hazelnut orchards in Portugal (Ramalhosa et al., 2018).
2.3 Characterization of the post-harvest practices
The mechanized harvest allows to increase the yield of the culture and to reduce the operation costs (Bernardi et al., 2017). However in this study, it was observed that most of the participants, 87.5%, indicated that the harvest was done manually, against 12.5% who indicated that it was done mechanically. As the survey was made by personal interview, the producers mentioned that the harvesting of hazelnuts by machines brings a lot of dust, such as stones and wood, which are difficult to separate from the fruits. Therefore, the use of mechanical harvesting is almost inexistent. Additionally, according to (Bernardi et al., 2017), the use of machines to perform the harvest is dependent on terrain topography.
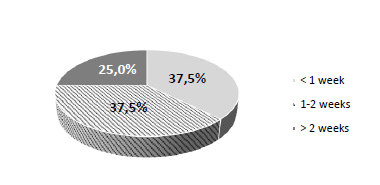
Figure 7 shows the total time that the participants took to collect the hazelnuts and 37.5% did it in less than one week, 37.5% took between one and two weeks and 25% of the participants took more than two months to collect the hazelnuts. This means that the time needed to harvest hazelnuts is long, probably due to the fact that it is not the main profession and therefore many of the producers harvest when they have time. Moreover, the harvest is also dependent on the fruits dropping from the tree.
All of the participants indicated that the harvested fruits were not delivered immediately, with 71.4% of them indicating that delivery was made between 3-4 weeks after harvest and 28.6% of the participants took more than four weeks to deliver the collected fruits. During that time, the fruits were kept in warehouses or garages, at room temperature and without relative humidity control.
After harvesting and cleaning operations, if the hazelnuts’ moisture content is greater than 8-10%, it is necessary to dry them (Correia et al., 2017b). In fact, drying is essential to guarantee hazelnuts’ quality during storage (Turan et al., 2019). From the sample at study, 87.5% of the participants indicated that they dried the hazelnuts naturally and none of them did it artificially. The fruits are harvested between August and October, relatively hot months, with a low relative humidity, thus allowing drying to be carried out naturally, by exposing the fruits to the sun. For example, in Turkey hazelnuts are also usually dried in the sun (Turan, 2018).
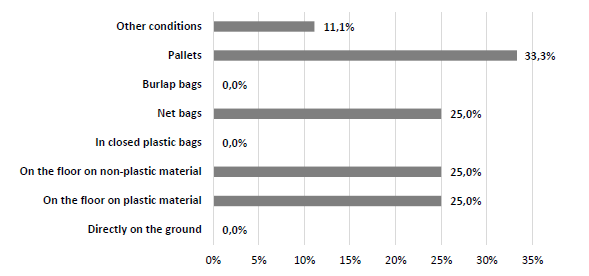
Figure 8 presents the way that the participants used to kept the fruits in the warehouse until delivery and most of them, 50.0%, kept the hazelnuts on the floor with a a covering material, 33.3% of the participants kept the fruits in pallets, followed by net bags. In a study developed by Jung et al. (2018) it was found that he ideal storage conditions or packaging method varied among cultivars due to their different moisture adsorption and physicochemical and enzymatic stability during storage.
Due to their high unsaturated fatty acid content, hazelnuts are susceptible to rancidity (Turan et al., 2019). Another danger associated with nuts is the appearance of mycotoxins (Mendes et al., 2016). Therefore, it was investigated if the participants were aware about the main problems that can occur during hazelnuts’ storage. For the global sample, as it can be observed in Table 2, the main problem identified by the participants was the loss of fruit weight (mean = 1.25 ± 0.50) and the problem considered less important was the change in the hazelnuts texture (mean = 6.00 ± 0.00).
Table 2 Main problems identified by the participants during hazelnuts storage.
| Problems during hazelnuts storage | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Loss of fruit weight | 1.25 ± 0.50 |
| Appearance of pests | 2.25 ± 1.89 |
| Development of moulds | 2.33 + 0.58 |
| Fruit rancification | 3.33 ± 0.58 |
| Change of colour | 4.00 ± 0.00 |
| Change of texture | 6.00 ± 0.00 |
Scale from 1 (most important) to 6 (less important)
The majority of the participants, 57.1%, indicated that the transport of the fruits to the warehouse/cooperative was done in net bags, 14.3% in bulk and 28.6% of the participants indicated that it was done in other ways. As for the type of vehicle used during the transport, 57.1% of the participants used an open vehicle and 42.9% of them a closed vehicle.
As for the product disposal, one participant delivered 30.0% of its production to traditional trade and 70.0% to a manufacturing company, one producer delivered 100.0% of its production to a processing company, two producers delivered 100.0% to a cooperative, one producer used all of its production for self-consumption, one of them delivered 95.0% of its production to packers and one of the producers disposed 50.0% of its product in direct sale and the remaining 50.0% to a cooperative. Two of the participants did not answer the question. It is important to highlight that none of the participants used a collector, association of producers, medium and large retailers or even fairs.
2.4 Characterization of hazelnut distribution practices
All of the participants, 100.0%, sold hazelnuts in shell and one participant also sold hazelnuts in kernel and processed, but in a very low percentage. Most of the participants, 60.0%, sold mixtures, 20.0% only sold isolated varieties and 20.0% of them sold both isolated varieties and mixtures. According to Correia et al. (2017c), in general, hazelnut is commercialized in shell or as hazelnut kernels (peeled hazelnut).
From the participants who sold hazelnuts in shell, 80.0% of them used net bags, 20.0% used plastic bags and 20.0% of the producers used pallets. As for the participant that sold hazelnuts in kernel as well as processed, he used vacuum for packaging in both situations.
The hazelnut distribution was done at room temperature and without relative humidity control.
None of the participants bought hazelnuts from other countries.
When the producers were asked about the main problems in the sector of nuts’ distribution, they referred difficulties in competing with foreign market prices and also lack of demand in the Portuguese market.
2.5 Characterization of hazelnut industry practices
According to the results obtained, it was verified that the varieties most used by the industry were Grada de Viseu, Ennis and Tonda de Gifoni, being the last one the most productive with a medium caliber.
The fruits were kept in the warehouse in pallets, with a capacity for 250-300 kg, and also in raffia bags, with a capacity for 25 kg.
The hazelnuts in shell were kept at room temperature and without relative humidity control. As for the kernel, it was stored in a cooling chamber at a controlled temperature between 0 and 10 ⁰C and with a relative humidity below 70%.
When this industry was asked about the main problems during the fruits storage, it was answered that the main problem was the appearance of pests, followed by the development of moulds, loss of fruit weight, rancification and finally the alteration of texture. When asked about the variety that had more problems during storage, it was indicated that they did not work with a specific variety, but with mixtures of varieties. The mixtures were separated according to size, being classified as follows: 11-13 mm, 13-15 mm, 15-17 mm, 17-19 mm and ( 20 mm.
When hazelnut caliber was higher than 20 mm, then the fruit was sold in shell. Hazelnuts with sizes between 11 and 19 mm were crushed and fruits with calibres smaller than 11 mm were considered small.
In this industry, hazelnut was essentially sold without shell (85%), mainly for use in pastry and bakery.
The fruit, both in shell and kernel, was used for self-consumption and also commercialized in national/regional as well as international markets. A small number of fruits was also exported to Spain.
Hazelnuts in shell were sold in net bags and also in other packages, namely raffia bags and low density polyethylene (LDPE) plastic bags. As for the hazelnut kernels, they were sold in raffia bags with a capacity for 25 kg and also in LDPE plastic bags with a capacity for 10 kg. The kernels were also sold in vacuum packed plastic bags with a capacity for 5 kg. The processed fruits were sold in LDPE plastic bags.
Hazelnut distribution was done in a short time, at room temperature and without controlling the relative humidity. Taking into consideration that the time until distribution/commercialization of the fruit was very short, it was indicated that there were practically no problems during these actions. Despite this, the most frequent problem was the appearance of pests.
It was indicated that this industry only sold mixtures that bought from foreign countries, namely in Spain.
When this participant was asked about the main problems in the distribution of nuts sector, he referred competition, price fluctuations, and sometimes the producers’ failure to comply with good post-harvest practices.
Conclusions
This study allowed concluding interesting results, namely that the age group of the surveyed producers was high, with the majority of them having university degree, but without studies in agricultural areas.
The hazelnuts’ plantations were essentially in the form of orchard, with reduced areas (<10 ha), most of them being twenty years old or more. Most of the producers had two parcels.
The main varieties used by the producers were Grada de Viseu, followed by Segorbe, Fertile de Coutard, Butler and Negreta. Grada de Viseu was considered the most important, both in terms of production and productivity.
The harvest was done mainly manually, and all producers indicated that they did not deliver the fruits right after the harvest. The hazelnuts storage was made in warehouses or garages, at room temperature and without relative humidity control. Furthermore, the participants indicated that they preferred to keep the fruits in the warehouse until delivery, on the floor, covered and that the main problem during storage was the loss of fruit weight.
As for the hazelnuts’ transportation, in most cases it was made in net bags and in an open vehicle. Moreover, all of the participants sold hazelnuts in shell and 60% of them sold mixtures.
The main problems identified by the participants regarding the nuts sector were lack of incentivises, difficulties in competing with foreign market prices and lack of information.
Regarding the industry practices, the main varieties used were Grada de Viseu, Ennis and Tonda de Giffoni. The hazelnuts in shell were kept at room temperature and without relative humidity control, but the kernels were stored at a controlled atmosphere.
As for the hazelnuts transportation by the industry, for the fruits in shell it was made in net bags, raffia bags and low LDPE plastic bags. The kernels were transported in raffia bags, as well as LDPE plastic bags and also vacuum plastic bags. On the other hand, processed hazelnuts were distributed in LDPE plastic bags.
The main problems reported by the industry were competition, price fluctuations, and producers’ failure to comply with good post-harvest practices.
Overall, the results also revealed that the producers are facing difficulties whether in the production or even in the marketing of hazelnuts.
The findings of this study are very important because they highlighted the importance of create strategies that can improve the hazelnut production and transformation in Portugal.