Serviços Personalizados
Journal
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Acessos
Acessos
Links relacionados
-
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO
Compartilhar
Revista de Gestão Costeira Integrada
versão On-line ISSN 1646-8872
RGCI vol.16 no.1 Lisboa mar. 2016
https://doi.org/10.5894/rgci629
ARTICLE / ARTIGO
Mapping of coral reefs in the continental shelf of Brazilian Northeast through remote sensing*
Mapeamento de recifes de corais na plataforma continental rasa do nordeste brasileiro por sensoriamento remoto
Paulo Victor do Nascimento Araújo@, 1, 2; Ricardo Farias do Amaral2
@Corresponding author to whom correspondence should be addressed.
1Instituto Federal de Educação, Ciência e Tecnologia do Rio Grande do Norte (IFRN), Campus Macau. Rua das Margaridas, 300, Conjunto COHAB, CEP 59500-000, Macau-RN, Brasil. e-mail: Araújo <paulo.araujo@ifrn.edu.br>
2Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte (UFRN), Departamento de Geologia, Centro de Ciências Exatas e da Terra. Laboratório de Estudos Geoambientais (LEGeo), Programa de Pós-graduação em Geodinâmica e Geofísica (PPGG), Caixa Postal 1524, Campus Universitário Lagoa Nova, CEP 59078-970, Natal-RN, Brasil. e-mail: Amaral <projeto_corais@yahoo.com.br>.
ABSTRACT
The Continental Shelf has great importance in the study of coastal evolution, provided this area was affected by fluctuations in sea level during the Quaternary period. In the shallow continental shelf of the Northeastern Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil, submerged important geomorphological features can be found in the distance of 6 km from the coastline. Among these features, highlights the reef complex called Parrachos of Rio do Fogo. This study aims to characterize and analyze geomorphological features and benthic surface features found in this reef complex, from the analysis and interpretation of remote sensing products and in situ data collection. In this work, a digital model of bathymetry was created based on unpublished bathymetric data and compositions from images bands of satellite sensors OLI/Landsat-8, MS/GeoEye and PAN/WordView-1, and then analyzed, interpreted and validated through field work. All obtained data and information were stored in a Geographic Information System (GIS). The following geoenvironmental units were mapped: intertidal reefs, submerged reefs, spurs and grooves, pools, sandy bank, sea grasses, bank of algaes, submerged roads, Barreta Channel and the Rio do Fogo Channel. The use of the proposed methodology provided a detailed analysis of submerged geomorphology in the study area. This study may be used as a guide for future decision-making for environmental management in the region.
Keywords: Continental Shelf; Bathymetry; Geomorphology; Remote Sensing; Geoenvironmental Mapping.
RESUMO
A Plataforma Continental possui grande importância no estudo da evolução costeira, pois representa uma área afetada pelas oscilações do nível do mar no período Quaternário. Na plataforma continental rasa do Nordeste do Rio Grande do Norte, Brasil, importantes feições geomorfológicas submersas podem ser encontradas a cerca de 6km da linha de costa, dentre estas feições, se destaca o complexo recifal denominado Parrachos de Rio do Fogo. O presente estudo objetiva caracterizar e analisar as feições geomorfológicas e da superfície bentônica, encontradas neste complexo recifal, a partir da análise e interpretação de produtos de sensores remotos e coleta de dados in situ. Neste trabalho foi criado um modelo digital de batimetria com base em dados batimétricos inéditos e composições de bandas de imagens dos sensores orbitais OLI/Landsat-8, MS/GeoEye e PAN/WordView-1, ambos analisados e interpretados de forma integrada e validados em trabalhos de campo. Todos os dados e informações obtidas foram armazenados em um Sistema de Informações Geográficas (SIG). Foram mapeadas as seguintes unidades geoambientais, os recifes intermareais, os recifes submersos, rastros e sulcos, piscinas, o banco arenoso interno, fanerógamas marinhas, o banco de algas, caminhos submersos, o Canal de Barreta e o Canal de Rio do Fogo. O emprego da metodologia proposta possibilitou uma análise detalhada sobre a geomorfologia submersa da área de estudo, podendo ser norteador, em futuras tomadas de decisão no manejo e gerenciamento ambiental da região.
Palavras-chave: Plataforma Continental; Batimetria; Geomorfologia; Sensoriamento Remoto; Mapeamento Geoambiental.
1. Introduction
Tropical coral reefs are the richest and most complex benthic communities in the oceans. These were formed over millions of years (about 500 million years ago) from the deposition of calcium carbonate from coral skeletons, and they are among the oldest known marine communities (Wilkinson, 2002). In Brazil, geological history of the current coral reefs indicates that they only began to grow 7,000 years ago, in the Quaternary period, when the sea level rose and completely flooded the current continental shelf (Prates, 2003).
Tropical coral reefs are considered the marine ecosystems that contain the highest levels of biodiversity, only exceeded by the tropical rainforests on land (Connell, 1978). Estimations point that at least 3,000 species of animals can be found in a single coral reef. Despite reefs occupy less than 1% of the total area of the oceans, 25% of all known species of fish are unique to these environments. According to Prates (2003), among the coral species in the world (350 species) at least 20 species (true and hydrocorals corals) were recorded in Brazil, and eight are endemic.
The high productivity associated with reef-building corals has a unique importance as a source of fisheries for coastal communities and corals are also important as (1) natural protective barriers to the coast of wave action, (2) sources of pharmacotherapy and (3) areas for tourism. Despite greater ecological and economic importance, coral reefs are subject to various factors that threaten their vitality and biodiversity (Hoegh-Guldberg, 1999; Moreira & Reuss-Strenzel, 2009). Recent studies, coordinated by the World Resources Institute (WRI) which monitors coral reefs, warned that coral reefs are currently suffering from high temperatures and ocean acidification more than in any other time, in the course of the last 400,000 years (Burke et al., 2011). If we continue down this path, all corals are likely to be threatened by 2050, as 75% are experiencing critical threat levels. The same report of WRI offers reason to hope: reefs around the world have demonstrated an ability to recover from damage, even in extreme cases, whereas it is the duty of environmental management to protect reefs and aid the recovery of some areas. These factors further confirm the importance of thorough studies concerning coral reefs, particularly when that environment is suffering risk of environmental degradation – from the both biotic and abiotic points of view. This is the case of the area under research in this project.
In 2001, the Conservation Unit called "Environmental Protection Area of Coral Reefs" (Área de Proteção Ambiental dos Recifes de Corais - APARC) was created in the state of Rio Grande do Norte, in the Northeast region of the Brazilian coast (Figure 1). This area corresponds to the marine region covering the coastal strip of Maxaranguape, Rio do Fogo and Touros municipalities. In this area, we highlight coral reef complexes, which are shallow bodies, with intertidal stretches, mainly formed by bioconstructions of algae and corals on a mud bottom and carbonate sand beyond rhodolith.
These bodies, locally called "Parrachos", are costal reefs and are aligned parallel to the coastline. They grow over a hard bottom, probably lines of sandstone, related to the ancient coast lines (Branner, 1904; Vianna et al., 1989; Amaral, 2002; Santos et al., 2007). This area is composed of clear water during the major part of the year. Among its most important features, the Parrachos of Maracajaú, Rio do Fogo and Cioba are considered the most sensitive areas of APARC, given their environmental characteristics. Laborel (1967, 1969) describes the reef complex in the region under study as a group of oval-shaped reefs, located a few miles off the coast, constituted of simple structures, formed generally by numerous pinnacles in a shallow sandy bottom and a reduced number of species. Leão et al. (2003) comments that coral reefs belonging to the study area usually are oriented NW-SE, with a length from 8 to 12 km, parallel to the coastline and they are presented as a set of knolls and patch reefs. These bodies are described and related to the area known as "sublittoral turbid zone", by Testa & Bosence (1999).
APARC is currently suffering from intense pressure from use and occupation, which has led to a growth in environmental degradation. Overfishing, coastal occupation and disorderly tourist operation in a clear process of expansion are among the main reasons for the degradation in APARC and associated platform (Amaral, 2005). However, fishing activities – traditional or touristic – are the major method of gathering resources for the local population. The situation is aggravated by the lack of information needed for effective management, although isolated studies already exist and discuss the sustainability of the region.
In Brazil, the mapping and studying of coral reef evolution, through the orbital sensing images employment, emerged at the same time the first environmental satellites were released in the 70s. In the 80s and 90s, some studies (Vianna & Solewicz 1988 ; Solewicz, 1989; Viana et al., 1989; Viana et al., 1991; Viana et al., 1993; Testa et al., 1997; Testa & Bosence, 1999) made the first utilization of satellite images for the understanding of regional structures, followed by field verification. Prates (2003) warns that there are few maps with location and complex coral coverage area due to the impossibility of using traditional techniques of drilling in the extensive shallow areas where the reefs occur. The exploration work carried out to date in the region of APARC and the determination of some physical parameters (Testa, 1997; Feitoza et al., 2001; Lima, 2002; Amaral, 2005; Santos et al., 2007; Henriques, 2008) underlie the need for more detailed mapping levels for the study area.
According to Hill & Wilkinson (2004), knowledge of the spatial characteristics of an area is a prerequisite for any study involving the environment and their rational and sustainable use.
In this sense, the availability of habitat maps is an excellent tool in land management, guiding strategies for sampling and identifying conservation areas (Hamel & Andréfouët, 2010). Habitat maps are great but geomorphic maps can be used as proxies and are easier to produce (e.g., Hamylton et al., 2012). The potential use of satellite sensor data for this type of research has been demonstrated in several studies worldwide (Luczkovich et al., 1993; Green et al., 1996; Mumby et al., 1997; Andréfouët et al., 2001; Andréfouët & Riegl, 2004; Scopélitis et al., 2010).
Thus, this research aims to map the Geo-environmental features and the benthic surface of the Parrachos of Rio do Fogo and its surroundings, aiming for the acquisition and development of appropriate methodologies for its mapping, with the integrated utilization of several types of remote sensing products in orbital and underwater platforms. This will facilitate the determination of geographical and geological and biophysical indicators of threats to ecosystems.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study area
The studied area has approximately 90 km2. It is located on the northeastern coast of Rio Grande do Norte State (Figure 1) and it is inserted in the Environmental Protection Area of Coral Reefs (APARC). APARC involves all marine regions with depths up to 25 meters, and their limit is the continental sector, the coastal areas of the Maxaranguape municipalities, Rio do Fogo and Touros.
The climate regime of the continental region adjacent to the study area is of ‘As’ type, "hot and humid" according to the Köppen classification (Köppen, 1918). The main feature of this regime is a rainy season that includes the months from February to July, and a dry season, with more rigorous drought between October and December (Carneiro, 2011). The local weather pattern is largely influenced by air masses from the Atlantic Ocean and the winds from the SE (Silva, 2002). Current velocity between the east and northern coasts of Rio Grande do Norte varies between 1.39 cm/s and 24.92 cm/s, averaging 6.32 cm/s (Hazin et al., 2008). The surface temperature of the sea water varies from 26.5°C during the winter at 28.5C in the summer period (Servain et al., 1990) and the salinity is between 36 and 37‰ (Testa, 1996). The predominant current direction during periods of peak intensity was to the NW. The wave climate for the sector covering the study area is defined by significant wave height of 1.0 m and 5 seconds to incident waves of ENE and 1.5 m and 6.5 seconds of SSE waves (Bittencourt et al., 2002). The region has a semidiurnal tidal regime, with an average approximate range of 1.5 m, reaching 2.2 m in spring tides, and according to Hayes (1979), can be classified as a strand of mesotide. Turbid water is generally high, especially in the rainy season, with high visibility during the spring and summer seasons (October to March). Turbidity is natural and consequent action of the winds and/or tidal currents that cause the particle suspension (Maida & Ferreira, 1997).
Fishing artisanal activities represent the main source of economic resources for the local population (Amaral, 2005). Bonilha (2003) reinforces that fishing communities in the region could be classified as small-scale merchants. And that the region also represents a great potential for the development of tourist, sport and recreational (such as scuba diving, boat rides and sport fishing) activities – provided they may be conducted inside a set of technical and social criteria (preferably the social inclusion of the local community) – what constitutes an opportunity for the eco-development of the region in a perspective of community wealth management of natural resources.
2.2. Coral mapping
The term geoenvironmental adopted by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), was created to adequately describe the work done by geoscience professionals on the environment. The aforementioned work contemplates the application of technical knowledge to the various instruments and mechanisms of environmental management. The geoenvironmental concept favors the integration of knowledge and experiences when determining homologous areas. This mapping was conceived in this integrating perspective. In this study, the geoenvironmental mapping is mainly based in geomorphological criteria furthermore adding information pertaining to the type of sea floor, coral density and correlation between coral and height of tide.
2.2.1. Bathymetric analysis
Bathymetric surveys were conducted in April 2013, using a vessel equipped with Global Positioning System (GPS) and echo sounder (single-beam transducer, 200KHz). Details of the procedures that led to the establishment of the Digital Bathymetric Model (DBM) are described in Supporting Information I.
In the analysis of bathymetric profiles, the aim was to identify the main geomorphological areas of this reef complex. The following has been identified:
- Back Reef. Reef region facing the coast, which usually suffers less impact of the waves due to the protective effect by Reef Crest and Reef Front.
- Reef Crest. The highest portion of the reef at any stage of their growth, and in shallow water, the part of the top of the reef that receives most of the wind and waves.
- Reef Front. This zone extends from the surf zone (end of Reef Crest) to an indefinite depth (beginning of Fore Reef), where the topographic slope begins softening or changing pattern. This zone also absorbs much of the energy from the waves.
- Fore Reef. Located in the outer portion of the reef, after the Reef Front, and stand as far as the environmental topography stabilizes.
2.2.2. Orbital remote sensing products
The optical sensors used in this study were: MS (Multispectral Sensor) of the GeoEye-1 Sattelite, PAN (Panchromatic) sensor of the WorldView-1 Sattelite and OLI (Operational Land Imager) sensor of the Landsat-8 Sattelite. Details of procedures are expressed in Supporting Information II.
2.2.3. Interpretation of remote sensing produc
Initially, images were submitted to atmospheric and geometric correction (Drury, 1993; Richards, 1995; Walsh et al., 1998). A cut was made around the study area in the collected images in order, so that the external features not to influence the variability of this information. After the corrections, a hybrid image was generated (RGBI-4328) with the OLI/Landsat-8, properly contrasted. Then, another hybrid image was generated (RGBI-RGBPAN) with high spatial resolution sensors, MS/GeoEye-1 and PAN/WorldView-1, properly contrasted. These two hybrid images were the basis for the visual interpretations of the objects. All image processing activities were carried out by the ERMAPPER v7.1 software (ERDAS, 2008).
Finally, there was the "ground truth". Three diving expeditions were conducted in the field, considering three occurrences of independent dives in each of the mapped homologous areas. At the dives the following parameters were observed and analyzed via georeferenced photography and filmography: types of sea floor; coral density and correlation between coral and height of tide. This allowed the interpretations validation of the data obtained with the processing of digital imagery. Data collection occurred in areas that were pre-selected during the processing of digital imagery according to procedures adopted by Amaral & Gonçalves (2004) and by Hill & Wilkinson (2004).The collected data were georeferenced through GPS receivers.
3. Results and discussion
Mapping of the study area allowed the assessment in greater detail, geomorphological features and the benthic surface, integrating the use of remote sensing and in situ data collection.
An elliptical shape is evident in the reef complex, with the semi-major axis oriented in the SE-NW direction. Has about 12 km long and 3 km wide, a ratio length x width of approximately 4:1.
3.1. Bathymetric analysis
Generation of Digital Bathymetric Models (DBM) from data interpolation is a highly widespread technique in coastal studies (e.g., Righton & Mills, 2006; Ryan et al., 2007). In the working area previous studies (Nogueira & Amaral, 2009 and Araújo Filho, 2011) used DBM to outline their concerns about large-scale area of morphology. Santos (2006) already alerted to the need to work bathymetry so that it is utilized more precisely, in order to model the Parrachos in the region in order to position them properly. In this study the use of EBK interpolation method helped with the production of models of the stubby coral banks (typical of the region) in good regional scale. The same model presented with a standard average error margin of 0.609 when subjected to the cross-validation process (Table 1).
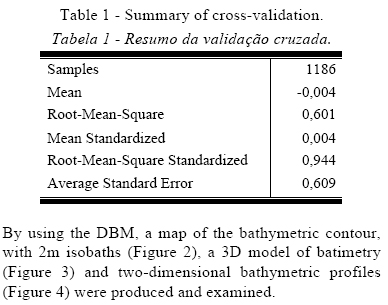
By using the DBM, a map of the bathymetric contour, with 2m isobaths (Figure 2), a 3D model of batimetry (Figure 3) and two-dimensional bathymetric profiles (Figure 4) were produced and examined.
The information drawn from these products complement each other and thus can have a more precise idea of the geomorphology of the study feature. The mapped area has a depth range of approximately 14m. The complex of the Rio do Fogo Reef is defined between the isobaths of 4 and 6 m, under which we see a rapid increase in the slope to a depth of approximately 10 meters. The DBM allowed the observation of a bank to SW from the Parrachos, an elevation between the reef complex and the mainland, limited by isobath 6m, with approximately 2 km wide. This bank has approximately the NS direction and is joined to the mainland near the Rio do Fogo community. His presence is not clear in the studied satellite images, so being called internal sand bank. It is also observed the presence of at least three transverse morphological discontinuity to the reef body (Figures 2 and 5):
(I) The first, further north, clearly visible, is the morphological expression called Barreta Channel, separated into two bodies: Recife das Garças (further northwest) and Rio do Fogo reef. This channel will be described later.
(II) Approximately in the center of the body other transversal discontinuity with direction SW-NE is clearly observed in both the bathymetric model as the satellite image. His evidence extends toward the platform until the isobath 10 meters in front reef.
(III) Finally, a third discontinuity is observed just south, thus, more subtly evident, although clear, both in the DBM as in the images.
In the external sector of the reef body, positioned parallel to this, at a distance of 1000 meters, the isobath 12 meters shows an elongated depression with about 9km long. This channel limits the Front Reef and its presence is also seen in the satellite image. Its depth reaches 14 meters and the call of Rio do Fogo Channel.
By analyzing bathymetric profiles (Figure 4), it was noticed that the back reef has a greater length in the CC' profile 3.5km, while the other sections, the back reef was approximately 1km. This is due to the presence of the internal sandbar previously mentioned. The area of the Reef Crest has a small variation in width throughout the complex, ranging from 0.5 to 1.2 km, being wider at the CC' profile, the central region of the study area. The width in the Reef Front region varied between 1.5 and 2 km in length, showing the greatest variation in the BB' profile. Finally the Fore Reef did not change, and in 4 sections, about 1km long. In profiles BB', CC' and DD', the outer limit of the Reef Front may be marked by the keel of the "Rio do Fogo Channel."
The outer edge of the reef front has sharp inclination, in general, owing to the fact that Rio do Fogo Channel, as described above, is more than 12 meters deep, while the Back Reef maximum depth may be less than 6m, mainly due to internal sand bank. Leão et al. (2003) had already drawn attention to this morphology, pointing in the outside of Parrachos an almost vertical wall, with approximately 6m tall and indoors a height of about 4 m. This morphological difference is most likely associated with sediment thickness between Parrachos and the mainland, which can be reduced by the constant turbidity of water in this region due to the positioning of Parrachos that confines sediments moving towards the ocean. Ferreira (2013) detected the presence of a high concentration of suspended particulate matter in this region.
These reef bodies are associated with fluctuations in sea level during the Holocene by authors such as Vianna et al. (1989), Testa (1997) and Testa & Bosence (1999). According to Amaral (2005), Parrachos in the region can be interpreted as evidence of ancient shorelines. The substrate necessary for fixation should possibly have been ferruginous sandstone beach or sandstone formation barriers, rocks abundantly present along the entire eastern coast of Rio Grande do Norte. About this bedrock would have settled the main reef colonies. As the sea level rose, under specific environmental conditions, these bodies have established their geometry (Amaral, 2005).
The history of sea level at the end of the Holocene shows that the Brazilian coast experienced considerable fluctuations in relative sea level (Martin et al., 1979; 1985; 1996). These fluctuations have had profound effects on the morphological evolution of coral reefs, as the relative sea change exerts control on the geometry and architecture of these bodies (Wright & Burchette, 1996).
3.2. Interpretation of Remote Sensing Products
The mapping technique selected in this work was the classification of visual analysis, thus minimizing potential problems of "confusion" on automatic recommendation rating of authors such as Morelli (2000) and Spalding et al. (2001).
The classification adopted takes into account primarily geomorphological aspects of submerged bodies and is based on that adopted by researchers in the field, as for Prates (2003), based on the discussion between various technical seminars in Brazil (Maida et al., 1997; MMA, 1998 ).
Although the shallow and the channel has already been observed and mapped in hydrographic charts from 1886 and discussed by Branner (1903), description based on bathymetric specific measures and observation by satellite sensors is now preformed in accordance with their geometry in plan. This procedure adds a host of new information. Associated with fieldwork, facilitate the analysis of the overall behavior of the focus area, allowing, for example, the determination of "pilot areas" for a more detailed study.
Viana et al. (1988), Costa Neto (1997) Testa & Bonsence (1999), Amaral (2002), Leão et al. (2003), Santos et al. (2007), present studies of the analysed area. Amaral (2002) classifies the shallows of Maracajau, Rio do Fogo and Cioba in immersed and submerged reef bodies, marine phanerogam bottoms, clear bottoms and bottoms with clear rhodolith concentrations. Prates (2003), also uses similar classification setting the behavior of reef bodies with respect to the tides as one of the parameters and defining the intertidal and submerged reefs, in addition to describing the pools, island, sand on the reef and the slab/block. Here, as in previous classifications, the body's relation criterion with the tide level to sort the intertidal reefs and submerged reefs was kept. The type of background was also incorporated as a parameter. Accordingly, the following features were classified: pools, sandy bank, sea grasses and bank of algaes. Finally, three other features were determined based on detailed morphological characteristics of the reef body: spurs and grooves and submerged roads, the latter already being the result of human action on reef bodies and Barreta Channel.
The shallows can be interpreted as evidence of ancient shorelines. The substrate necessary for its determination shall have been ferruginous sandstone beach or sandstone formation barriers, rocks abundantly present along the entire eastern coast of Rio Grande do Norte. The first reef colonies would have established over this bedrock and, as the sea level rose, under specific environmental conditions, these bodies have established their geometry.
The hypothesis above is based on samples collected in other nearby areas (e.g., Vianna et al., 1988). Reports from anglers and from personal diving observations in deeper areas close to the reef body where development of corals covers the bedrock, was less efficient. Works that aim to clarify the evolutionary development of these bodies should try to collect sandstones with better spatial accuracy and its absolute dating methods. From this perspective the following descriptions of the features assigned to this work.
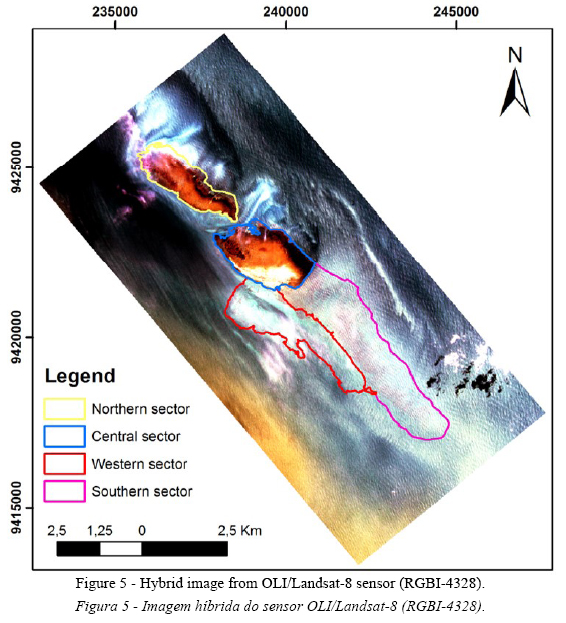
Supported by literature, fieldwork and bathymetric studies, a visual interpretation of satellite sensing images was performed, based on the hybrid composition of the OLI/Landsat-8 (RGBI-4328). In this interpretation was possible to distinguish, based on parameters such as texture, color and hue, 4 main sectors in Parrachos: (1) North, (2) Central, (3) South, (4) West (Figure 5).
The North Sector stands isolated from the others, separated by a transverse channel in the reef body, the Channel Barreta, as described above. Along with the central, comprises the area most clearly distinguished the compound, this composition arises in warm colors, as a result, possibly the highest reflectance of seaweed and coral cover the wavelength band 4 in the red channel. The West and South sectors are dominated by deeper areas, but clearly different. In the field, we associate the West sector benthic cover with the presence of Marine Phanerogams as noted by Williams (2002) in Parrachos of Maracajau, south of the study area. Finally, the Southern sector is the one with less information, although the dives showed the presence of algae.
According to Santos (2006), Siderastrea stellata (Verrill, 1868) is the main coral reef formation in this region, with 80% prevalence, occurring on the plateau of these reefs. Maida & Ferreira (2004) further reported the presence of Favia gravida (Verril, 1886) on the plateau of the reefs and Monstastrea cavernosa in greater depths. Arantes (2004) highlights that it was observed the occurrence of calcareous algae (Lithothammniom sp. and Foslielia sp.) covering areas between colonial species on the reef and sandy substrate by concretions. These algae were observed in this study, in the southern sector.
In addition to the demarcated areas in the outer region east of the reef complex, a tonal variation on the ocean surface is observed. Faced with the bathymetric study, this behavior is associated with Rio do Fogo Channel.
With the hybrid image MSPAN (RGBI-RGBPAN), high spatial resolution sensors, we could identify six well-defined units from the elements adopted in the visual interpretation, combined with validation of interpretations (Table 2). The following were used as attributes: ratio of bioconstructed bodies with the tide level (intertidal and submerged reefs); type of fund and the presence or absence of vegetation (pools, sandy bank, bank of algaes, sea grasses) and more detailed morphological attributes such as bumps, holes and scars (spurs and grooves and submerged roads). Rio do Fogo and Barreta channels are major features.
These mapped Geoenvironmental units are described below:
- Intertidal reefs. Bioconstructed solid and porous bodies composed of calcareous algae, shells and other cnidarians invertebrates "welded" or next to each other and emerged in the lowest tide. They are locally known as Cabeços (bollards). They form an area of approximately 0.21 km2 are observed in northern and central sector of the Parrachos.
- Submerged reefs. Emerged bodies are differentiated because they feel more apart from each other by the same remain submerged lower tides and by having the lower height. They occupy an area of approximately 3.75 km2. They are positioned in lateral continuity to intertidal reefs.
- Pools. Pools are depressions in the flat reef (Pereira et al., 2010) and are connected with the outside of the reef, focusing on the western central sector. In the study area, pools are approximately 0.73 km2. The bottom is filled out with sandy sediments and in the larger pools are an isolated mushroom form of coral called “chapeirões.”
- Sandy bank. This feature is concentrated in the western sector and has an area of 2.56 km2.
- Sea grasses. Bank of phanerogam plants, tracheophytes, stem type rhizomes buried in the substrate. Concentrated on the western sector, having an area of approximately 1.90 km2. According to Bonilha (2003) the internal portion of the APARC which is constituted by the region between the stubby coral banks and the coast line, includes a prairie community of shoalweed (of a yet unknown width) probably constituted by Halodule wrightii. It can be highlighted that this type of prairie community of shoalweed is commonly associated with coral reefs, developing thanks to the hydrodynamic protection offered by the barrier, usually growing in the internal, protected section of the reef. They are also scientifically known as marine nurseries aiding in the development of many fish and crustacean species of commercial importance: these species tend to spend their youth benefitting from the physical protection of the vegetation (Silva, 1995).
- Bank of algae. Banks of calcareous algae. Encompasses the entire southern sector and spreads it on an area of 7.60 km2.
- Spur and groove. Recesses and small and repetitive bumps on the outer edge of the reef body. Common area of Fore Reef, due to continued erosion effects caused by waves and currents. The morphology of these structures consists of small linear ridges separated by grooves (depressions) of sediments and debris (Figure 6b). The physical strength of wave energy acts as a controller in the morphology of these formations. They act as effective breakwaters and dissipate wave energy and intensity currents (Roberts et al., 1992). These features are concentrated in the northern and central sectors of the complex, having a total area of 1.72 km2.
- Barreta Channel. Araújo Filho (2011), based on water depth profiling studies, described that the width of this channel measures 100m at the central part and depth between 3 and 7 meters. In image analysis and bathymetric study of the geometry of this channel could be deepened so that it was found he has actually hourglass shape, approximately 120 feet wide in its most central section and edges measuring 1000 meters (Figure 6c).
- Rio do Fogo Channel. This feature is not included in Table 1, since it corresponds only to an elongated depression close to the oriental rim of the stubby coral reef that is typical in the area. The spatial distribution of Geoenvironmental units can be seen in Figure 7, already integrated all sector counterparts and the Rio do Fogo channel, whose limits given based on the 12 m isobath. The space between the main reef complex body and this channel corresponds to the fore reef slope.
- Submerged roads. This feature was observed in the field. It wasn’t mapped, however, for we found that further studies are still required in order to more clearly determine its characteristics. In the northern and central sectors, some linear features are observed. These features are locally called estradas (roads) (Figure 6b). Based on fishing reports and field observations, these paths were formed from accidental bumps boats on coral complex. Historically, coral reefs located in the region were stages of several shipwrecks. According to Medeiros (2014), through reports in the eight former newspaper sinkings occurred between 1840 and 1898. These were the vessels of different nationalities, carrying diverse merchandise.
It was estimated that the reef complex has approximately 46.75% (5.68 km2) environments dominated by bioclastic constructions (intertidal reefs, submerged reefs, spur and grooves), by calculating the total of each mapped area.
The full detail in the determination of homologous areas is suitable to be checked by comparing this mapping with previous mappings. This is due to a more detailed bathymetry and the use of higher spatial resolution remote sensing images and radiometric (this in the case of Landsat-8), and the use of more than one interpretation tool concatenated form.
4. Conclusions
The Parrachos of Rio do Fogo are characterized as a complex environment composed of corals and algae. Among the features that arise in this environment, we highlight the Barreta Channel, intertidal reefs, submerged reefs, spurs and grooves, pools, sandy bank, sea grasses, bank of algaes, submerged roads beyond Rio do Fogo Channel and its internal sandy bank.
Some features, as seen, are clearly visible in all these approaches. Some are observed, for example, in water depth analysis; although they are not much clear in the analysis of satellite images. Even in the satellite image analysis, a mere difference of spatial resolution allows the mapping of sectors based on diverse criteria. All these approaches are complementary and might be enhanced based on knowledge of the area by the interpreter and though fieldwork for the elaboration of detailed maps of the bodies in shallow reef platforms.
The process of interpretation of satellite images, integrated to bathymetric analysis and field checks used as a method for mapping of Rio do Fogo reefs respond adequately to what was proposed. In light of the available data collected, the application of this methodology, allowed to obtain a product that brings both some quantitative information (areas, lengths, perimeters, depth of the analyzed features) as also qualitative (characteristics of Geoenvironmental units). The visual interpretations combined with the bathymetric data and validation in the field (dives), enabled the integration of knowledge of geomorphology in the region contributing to the definition of Geoenvironmental units of the coral reefs of Rio do Fogo. The results achieved are a real contribution to the technical and scientific knowledge highlighting the Geoenvironmental features of the shallow continental shelf, northeastern Brazil, mainly in relation to its morphological character.
The proposition of mapping through the integration of bathymetry and digital processing allows for the application of new subsidies to update the plan for how the Environmental Protection Area of Coral Reefs (Área de Proteção Ambiental dos Recifes de Corais APARC) should be handled, especially as it pertains to the environmental zoning. Thus aiding in the promotion of social and economic activities while protecting the environment and the coral reef ecosystems and also serving as a north when it comes to zoning important regions of the stubby coral reefs, such as: (i) Integral Protection Areas; (ii) Intensive Usage Areas (tourist acitivities); (iii) Extensive Usage Areas – Type I (fishing activities); and (iv) Extensive Usage Areas – Type II (autonomous diving activities).
Acknowledgments
We would like to express the deepest appreciation to the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) for the financial support of Rio do Fogo Project Mapping of Underwater Habitats and Associated Benthic in "Parrachos of Rio do Fogo/RN": A comparison Between Products of Remote Sensors and New Methods of Classification (Public notice MCT/CNPq n° 14/2011 – Universal: Process n° 479646/2011-2). In addition, we thank to Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), by granting research scholarship to the researchers involved in this work. We would also like to thank Mr. Flavio and Mr. "Dedinho" for their substantial help in field collection.
References
Amaral, R.F. (2002) - Mapeamento da Área de Proteção Ambiental dos Recifes de Corais – Fase Exploratória. 50p, UFRN, Departamento de Geologia/IDEMA, SUGERCO. Relatório Interno, Natal, RN, Brazil. Unpublished.
Amaral, R.F. (2005) - Diagnóstico Ambiental da “Área de Uso Turístico Intensivo” no Parracho de Maracajaú. 157p., UFRN, Departamento de Geologia/IDEMA, SUGERCO. Relatório Interno, Natal, RN, Brazil. Unpublished.
Amaral, R.F.; Gonçalves, L.M.G. (2004) - Using Small Format Aerial Photographies (SFAP) to Map Coral Reefs in Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil. Journal of Coastal Research (ISSN: 0749-0208), SI 39 (Proceedings of the 8th International Coastal Symposium), Itajaí, SC, Brazil. [ Links ]
Andréfouët, S.; Riegl, B. (2004) - Remote sensing: a key tool for interdisciplinary assessment of coral reef processes. Coral Reefs, 23(1):1-4. DOI: 10.1007/s00338-003-0360-z [ Links ]
Andréfouët, S.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Hochberg, E.J.; Hu, C.; Carder, K.L. (2001) - Change detection in shallow coral reef environments using Landsat 7 ETM+ data. Remote Sensing of Environment. 78(1-2):150-162. DOI: 10.1016/S0034-4257(01)00256-5 [ Links ]
Arantes, S.V. (2004) - Descrição do recobrimento e ocorrência de macroinvertebrados bentônicos nos Parrachos de Maracajaú, município de Maxaranguape – RN, 74p., Monografia de Bacharel em Ciências Biológicas, Programa de Graduação em Ciências Biológicas, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte (UFRN), Natal, RN, Brazil. Unpublished.
Araujo Filho, L.P. (2011) - Caracterização geomorfológica e modelagem de dados espaciais na plataforma. 114p., Dissertação de Mestrado em Geodinâmica e Geofísica, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte (UFRN), Natal, RN, Brazil. Available on-line at http://repositorio.ufrn.br:8080/jspui/handle/123456789/18818 [ Links ]
Bonilha, L.E.C. (2003) - Considerações quanto ao uso atual, conservação e situação socioambiental no ecossistema recifal/coralino dos “parrachos” do Rio Grande do Norte – (Município de Maxaranguape a Rio do Fogo). 19p., Relatório GEREX – IBAMA / RN, Natal, RN, Brazil. Unpublished.
Bittencourt, A.C.S.P.; Martin, L.; Dominguez, J.M.L.; Silva, I.R.; Sousa, D.L.A. (2002) – A significant longshore transport divergence zone at the Northeastern Brazilian coast: implications on coastal Quaternary evolution. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências. 74(3):505-518. DOI: 10.1590/S0001-37652002000300012
Branner, J.C. (1904) - The stone reefs of Brazil, their geological and geographical relations, with a chapter on the coral reefs. 500p., Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology, 44 (Geol. Ser. 7):207-275, Cambridge, MS, U.S.A. Available on-line at https://openlibrary.org/books/OL24171492M/The_stone_reefs_of_Brazil
Burke, L.; Reytar, K.; Spalding, M.; Perry, A. (2011) - Reefs at Risk Revisited. 10p., World Resources Institute. Washington, DC. U.S.A. ISBN: 978-1569737620. [ Links ]
Carneiro, M.C.S.M. (2011) - Monitoramento das dunas utilizando o sistema de mapeamento a laser (lidar) aerotransportável: um estudo do campo de dunas do município de Rio do Fogo, RN, Brasil. 132p., PhD thesis, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco (UFPE), Recife, PE, Brazil. Available on-line at http://repositorio.ufpe.br:8080/handle/123456789/6122 [ Links ]
Connell, J.H. (1978) - Diversity in Tropical Rain Forests and Coral Reefs. Science, 199(4335):1302-1310. DOI: 10.1126/science.199.4335.1302 [ Links ]
Costa Neto, L.X. (1997) - Evolução Geológica-Geomorfológica Recente da Plataforma Continental Interna ao Largo do Delta do Rio Açu, Macau-RN. 212p., Dissertação de Mestrado, Universidade Federal Fluminense, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil. Unpublished. [ Links ]
Drury, S.A. (1993) - Image interpretation in Geology. 2nd ed. 283p., Chapman & Hall, London, U.K. ISBN: 041248809. [ Links ]
English, S.; Wilkinson, C.; Baker, V. (1997) - Survey Manual for Tropical Marine Resources, 2nd ed., ASEAN - Australia Marine Science Project: Living Coastal Resources, Australian Institute of Marine Science, Townsville, Australia. [ Links ]
ERDAS. (2008) - ER Mapper - User's Guide. 266p., Norcross-GA, U.S.A. [ Links ]
Feitoza, B.M.; Sampaio, D.A.; Araújo, M.E. (2001) - Ictiofauna recifal dos Parrachos de Maracajaú (RN) na área dos flutuantes: inventário e estrutura da comunidade. Arquivos de Ciências do Mar (ISSN: 0374-5686), 35: 39–50, Fortaleza, CE, Brazil.
Ferreira, A.T.S. (2013) - Monitoramento Ambiental na Costa do Rio Grande do Norte com Base em Sensoriamento Remoto e Geodésia de Precisão. PhD thesis, Uiversidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte (UFRN), Programa de Pós-graduação em Geodinâmica e Geofísica, Natal, RN, Brazil. Available on-line at http://repositorio.ufrn.br/handle/123456789/18367.
Ferreia, B.P; Maida, M. (2006) - Monitoramento dos recifes de coral do Brasil. 250p., Ministério do Meio Ambiente, Brasília, DF, Brazil [ Links ]
Green, E.P.; Mumby, P.J.; Edwards, A.J.; Clark, C.D. (1996) - A Review of Remote Sensing for the Assessment and Managemente of Tropical Coastal Resources. Coastal Management, 24(1):1-40. DOI: 10.1080/08920759609362279 [ Links ]
Hamel, M.A.; Andréfouët, S. (2010) - Using very high resolution remote sensing for the management of coral reef fisheries: Review and perspectives. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 60(9):1397–1405. DOI: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.07.002
Hamylton, S.; Andréfouët, S.; Spencer, T. (2012) - Comparing the information content of coral reef geomorphological and biological habitat maps, Amirantes Archipelago (Seychelles), Western Indian Ocean. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 111:151-156. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecss.2012.06.001 [ Links ]
Hayes, M.O. (1979) - Barrier island morphology as a function of tidal and wave regime. In: S.P. Leatherman (ed.), Barrier islands from the Gulf of St. Lawrence to the Gulf of Mexico, pp.1-27. Academic Press, New York, U.S.A. ISBN: 978-0124402607. [ Links ]
Hazin, F.H.V.; Wor, C.; Oliveira, J.E.L.; Hamilton, S.; Travassos, P.; Geber, F. (2008) - Resultados obtidos por meio do fundeio de um correntógrafo na plataforma continental do Estado do Rio Grande do Norte, Brasil. Arquivos de Ciências do Mar (ISSN: 0374-5686), 41(1):30–35, Fortaleza, CE, Brazil.
Henriques, A.P.M. (2008) - Classificação de imagens de ambientes coralinos: uma abordagem empregando uma combinação de classificadores e máquina de vector de suporte. 149p., PhD thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte (UFRN), Natal, RN, Brazil. Unpublished. [ Links ]
Hill, J.; Wilkinson, C. (2004) - Methods for ecological monitoring of coral reefs, Version 1, A Resource for Managers. 117p, .Australian Institute of Marine Science, Townsville, Australia. Available on-line at http://www3.aims.gov.au/bitstream/handle/11068/7495/HillMethodsforecologicalmonitoring2004.pdf?sequence=1 [ Links ]
Hoegh-Guldberg, O. (1999) - Climate change, coral bleaching and the future of the world.s coral reefs. Marine and Fleshwater Research, 50(8):839-866. DOI: 10.1071/MF99078 [ Links ]
IDEMA (2002) - Atlas do Rio Grande do Norte. Instituto de Desenvolvimento Econômico e Meio Ambiente do Rio Grande do Norte (IDEMA), Natal, RN, Brazil. [ Links ]
Köppen, W. (1918) - Klassification der klimate nach temperatur, niederschlag und jahreslauf. Petermanns Geographische Mittei-lungen, 64:193-203, Gotha, Germany. Available on-line at http://koeppen-geiger.vu-wien.ac.at/pdf/Koppen_1918.pdf [ Links ]
Laborel, J.L. (1967) - A revised list of Brazilian scleractinians corals and descriptions of a new species. Postilla, 107:1-14, Yale University, New Haven, CT, U.S.A. Available on-line at http://biostor.org/reference/118495 [ Links ]
Laborel, J. (1969) - Les peuplements de madreporaires des côtes tropicales du Brésil. 260p., Annales de l'Université d'Abidjan, Abidjan, Côte d'Ivoire. [ Links ]
Leão, Z.M.A.N.; Kikuchi, R.K.P.; Testa, V. (2003) - Corals and corals reefs of Brazil. In: Jorge Cortés (ed.), Latin American Coral Reefs, pp.9-52, Elsevier Science B. V., Amsterdam, The Netherlands. ISBN: 0444513884. DOI: 10.1016/B978-044451388-5/50003-5. [ Links ]
Lima, W.S.G. (2002) - Geologia e Geomorfologia dos Recifes de Maracajaú – RN e Plataforma Rasa Adjacente. 91p., PhD thesis, Uiversidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte (UFRN), Programa de Pós-graduação em Geodinâmica e Geofísica, Natal, RN, Brazil. Available on-line at http://repositorio.ufrn.br/jspui/handle/123456789/18777.
Luczkovich, J.J.; Wagner, T.W.; Michalek, J.L.; Stofflee, R.W. (1993) - Discrimination of Coral Reefs, Seagrass Meadows, and Sand Bottom Types from Space: A Dominican Republic Case Study. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 59(3):385-389, American Society of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Bethesda, MD, U.S.A. [ Links ]
Maida, M.; Ferreira, B.P. (1997) - Coral Reefs of Brazil: an overview. Proceedings of the 8th International Coral Reef Symposium, 1:263-274. [ Links ]
Maida, M.; Ferreira, B.P. (2004) - Recifes de coral brasileiros. In: E. Eskinazi-Leça, S.L. Neumann & M.F. Costa (orgs). Oceanografia: um cenário tropical, pp.617- 640, Bargaço, Recife, PE, Brazil. ISBN: 8574095826 [ Links ]
Maida, M.; Pontes, A.C.P.; Ferreira, B.P.; Castro, C.B.; Pires, D.O.; Rodrigues, M.C.M. (1997) - Relatório do workshop sobre os recifes de coral brasileiros: pesquisa, manejo integrado e conservação. 30p., Tamandaré, PE, Brazil. [ Links ]
Martin, L.; Flexor, J.M; Vilas-Boas, G.S.; Bittencourt, A.C.S.P.; Guimarães, M.M.M. (1979) - Courbe de variations du niveau relatif de la mer au cours des 7000 dernières années sur un secteur homogène du littoral brésilien (nord de Salvador-Bahia). In: K. Suguio, T. R. Fairchild, Martin Louis & J. M. Flexor (eds.), Proceedings of the International Symposium on Coastal Evolution in the Quaternary, pp.264-274, São Paulo, SP, Brazil. Available on-line at http://www.documentation.ird.fr/hor/fdi:41921 [ Links ]
Martin, L.; Flexor, J.M.; Blitzkow, D.; Suguio, K. (1985) - Geoid change indications along the Brazilian coast during the last 7000 years. Proceedings of the Fifth International Coral Reef Congress, 3: 85-90, Tahiti, French Polynesia. Available on-line at http://horizon.documentation.ird.fr/exl-doc/pleins_textes/pleins_textes_6/b_fdi_35-36/41896.pdf [ Links ]
Martin, L.; Suguio, K.; Flexor, J.M.; Dominguez, J.M.L.; Bittencourt, A.C.S.P. (1996) - Quaternary sea-level history and variation in dynamics along the central Brazilian coast: consequences on coastal plain construction. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciencias (ISSN: 1678-2690), 68(3):303-354, Rio de Janeiro RJ, Brazil. [ Links ]
Medeiros, R. (2014) - Maracajaú e Rio do Fogo – Antigos Cemitérios de Barcos da Costa Potiguar. Blog Tok de História, http://tokdehistoria.wordpress.com/2014/01/07/maracajau-e-rio-do-fogo-antigos-cemiterios-de-barcos-da-costa-potiguar/
Moreira, P.P.; Reuss-Strenzel, G.M. (2009) - Mapeamento de habitats do recife de coral Pedra de Leste, Abrolhos, utilizando uma imagem multiespectral Landsat7 ETM+. Anais XIV Simpósio Brasileiro de Sensoriamento Remoto, pp.6595-6602, Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais (INPE), Natal, RN, Brazil. Available on-line at http://marte.sid.inpe.br/col/dpi.inpe.br/sbsr@80/2008/11.17.21.38/doc/6595-6602.pdf [ Links ]
Morelli, F.M. (2000) - Mapeamento dos recifes costeiros de Paripueira, Barra de Santo Antônio e Passo do Camaragibe (AL), através da classificação de imagens Landsat-TM e HRV-SPOT. Dissertação de Mestrado, Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais (INPE), São José dos Campos, SP, Brazil. Unpublished. [ Links ]
Mumby, P.J.; Green, E.P.; Edwards, A.J.; Clark, C.D. (1997) - Coral Reef Habitat-mapping: How Much Detail Can Remote Sensing Provide?. Marine Biology, 130(2):193-202. DOI: 10.1007/s002270050238 [ Links ]
Nimer, E. (1989) - Climatologia do Brasil. 2nd ed., 421p., Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil. ISBN: 978-8524002823. [ Links ]
Nogueira, J.D.L.; Amaral, R.F. (2009) - Comparação entre os métodos de interpolação (Krigagem e Topo to Raster) na elaboração da batimetria na área da folha Touros – RN. Anais XIV Simpósio Brasileiro de Sensoriamento Remoto, pp.4117-4123, Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais (INPE), Natal, RN, Brazil. Available on-line at http://marte.sid.inpe.br/col/dpi.inpe.br/sbsr@80/2008/11.18.00.22/doc/4117-4123.pdf
Pereira N.S.; Manso V.A.V.; Silva A.M.C.; Silva M.B. (2010) - Mapeamento Geomorfológico e Morfodinâmica do Atol das Rocas, Atlântico Sul. Journal of Integrated Coastal Zone Management / Revista da Gestão Costeira Integrada, 10(3):331-345. DOI: 10.5894/rgci209. [ Links ]
Prates, A.P.L. (2003) - Atlas dos recifes de coral nas unidades de conservação brasileiras. 180p., Ministério do Meio Ambiente. Secretaria de Biodiversidade e Florestas, Brasília, DF, Brazil. [ Links ]
Richards, J.A. (1995) - Remote sensing digital image analysis: an introduction. 340p., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-30062-2. ISBN: 978-3-642-30061-5. [ Links ]
Righton, D.; Mills, C. (2006) - Application of GIS to investigate the use of space in coral reef fish: a comparison of territorial behaviour in two Red Sea butterflyfishes. International Journal of Geographical Information Science. 20(2):215-235. DOI: 10.1080/13658810500399159 [ Links ]
Roberts, H.H.; Wilson, P.A.; Lugo-Fernandez, A. (1992) - Biologic and geologic responses to physical processes: examples from modern reef systems of the Caribbean-Atlantic. Continental Shelf Research, 12(7-8):809-834. DOI: 10.1016/0278-4343(92)90046-M [ Links ]
Ryan, D.A; Brooke, B.P.; Collins, L.B.; Kendrick, G.A.; Baxter, K.J.; Bickers, A.N.; Siwabessy, P.J.W.; Pattiaratchi, C.B. (2007) - The influence of geomorphology and sedimentary processes on shallowwater benthic habitat distribution: Esperance Bay, Western Australia. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science. 72(1):379-386. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecss.2006.10.008 [ Links ]
Santos, C.L.A. (2006) - Mapeamento de recifes no Rio Grande do Norte: Touros a Macau/RN. 88p., Dissertação de Mestrado, Uiversidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte (UFRN), Natal, RN, Brazil. Available on-line at http://repositorio.ufrn.br/jspui/handle/123456789/18736
Santos, C.L.A.; Vital, H.; Amaro, V.E.; Kikuchy, R.K.P. (2007) - Mapeamento de recifes submersos na costa do Rio Grande do Norte, NE Brasil: Macau a Maracajau. Revista Brasileira de Geofísica, 25(1):27-36. DOI: 10.1590/S0102-261X2007000500004. [ Links ]
Scopélitis, J.; Andréfouët, S.; Phinn, S.; Arroyo, L.; Dalleau, M.; Cros, A.; Chabanet, P. (2010) - The next step in shallow coral reef monitoring: Combining remote sensing and in situ approaches. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 60(11):1956–1968. DOI: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.07.033.
Servain, J.; Sévea, M.; Rual, P. (1990) - Climatology comparison and long-term variations of sea surface temperature over the tropical Atlantic Ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 95(C6):9421-9431. DÓI: 10.1029/JC095iC06p09421 [ Links ]
Silva, E.A.J. (2002) - As dunas eólicas de Natal/RN: datação e evolução. 127p., Dissertação de Mestrado, Uiversidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte (UFRN), Natal, RN, Brazil. Available on-line at http://repositorio.ufrn.br:8080/jspui/handle/123456789/18750
Silva, E.T (1995) - Modelo Ecológico de Fundos Vegetados Dominados por Ruppia maritima L. (Potamogetonaceae) do Estuário da Lagoa dos Patos-RS. Tese de Mestrado, Uiversidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte (UFRN), Natal, RN, Brazil. Unpublished.
Solewicz, R. (1989) - Feições fisiográficas submarinas da Plataforma Continental do Rio Grande do Norte visíveis por imagens de satélite. 163p., Dissertação de Mestrado, Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais (INPE), São José dos Campos, SP, Brazil. Unpublished. [ Links ]
Spalding, M. D.; Ravilious, C.; Green, E.P. (2001) - World atlas of coral reefs. 424p., University of California Press / World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC), Berkeley LosAngeles London. ISBN: 0520232550. Available on-line at http://fnad.org/Documentos/worldatlasofcora01spal.pdf [ Links ]
Testa, V. (1996) - Quaternary Sediments of the Shallow Shelf, Rio Grande do Norte, NE Brazil. 411p., PhD thesis, University of London, London, U.K. [ Links ]
Testa, V. (1997) - Calcareous algae and corals in the inner shelf of Rio Grande do Norte, NE Brazil. Proceedings of the 8th International Coral Reef Symposium, 1:737-742, Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute, Panama. [ Links ]
Testa, V.; Bosence, D.W.J. (1999) Physical and Biological controls on the formation of carbonate and siliclastic bedforms on the northeast Brazilian shelf. Sedimentology, 46(2):279302. DOI: 10.1046/j.13653091.1999.00213.x [ Links ]
Testa, V.; Bosence, D.W.J.; Viana, M.L. (1997) - Submerged lithologies as indicators of relative sea-level oscillations in Rio Grande do Norte, NE Brazil. Anais VI Congresso Brasileiro de Estudos do Quaternário, pp.155-160. [ Links ]
Vianna, M.L.; Solewicz, R.; Cabral, A.P.; Testa, V. (1991) - Sands-tream on the northeast Brazilian shelf. Continental Shelf Research, 11(6):509–524. DOI: 10.1016/0278-4343(91)90008-T
Vianna, M.L.; Solewicz, R. (1988) - Feições fisiográficas submarinas da plataforma continental do Rio Grande do Norte visíveis por imagens de satélite. Simpósio de Sensoriamento Remoto (SBSR), pp.581-5871988, Natal, RN, Brazil. Available on-line at http://marte.sid.inpe.br/col/dpi.inpe.br/marte@80/2008/07.25.13.26/doc/581-588
Vianna, M.L., Solewicz, R., Cabral, A.P. (1989) - Early Holocene stillstands in the brazilian northeast mapped by satellite. International Symposium on Global Changes in South America During the Quarternary: Past-Present-Future, pp.250-254, São Paulo, SP, Brazil. [ Links ]
Vianna, M.L.; Cabral, A.P.; Gherardi, D.F.M. (1993) - TM-Landsat imagery to the study of the impact of global climate change on a tropical coastal environment during the last deglaciation. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 14(16):2971-2983. DOI: 10.1080/01431169308904413 [ Links ]
Walsh, S.J.; Butler, R.; Malanson, G.P. (1998) - An overview of scale, pattern, process relationships in geomorphology: A remote sensing and GIS perspective. Geomorphology, 21(3-4):183-205. DOI: 10.1016/S0169-555X(97)00057-3 [ Links ]
Wilkinson, C.R. (2002) - Status of coral reefs of the world. 363p., Australian Institute of Marine Science, Townsville, QLD, Australia. Available on-line at http://www.icriforum.org/icri-documents/associated-publications/status-coral-reefs-world-2002 [ Links ]
Wright, V.P.; Burchette, T.P. (1996) - Shallow-Water Carbonate Environments. In: Harold G. Reading (ed.), Sedimentary Environments: Processes, Facies and Stratigraphy, 3rd ed., pp.368-377, John Wiley & Sons. London, U.K. ISBN: 978-0632036271. [ Links ]
*Submission: 5 AUG 2015; Peer review: 12 SEP 2015; Revised: 14 JAN 2016; Accepted: 4 FEB 2016; Available on-line: 5 FEB 2016
Appendix
This article contains supporting information online at http://www.aprh.pt/rgci/pdf/rgci-629_Araujo_Supporting-Information.pdf














