Introduction
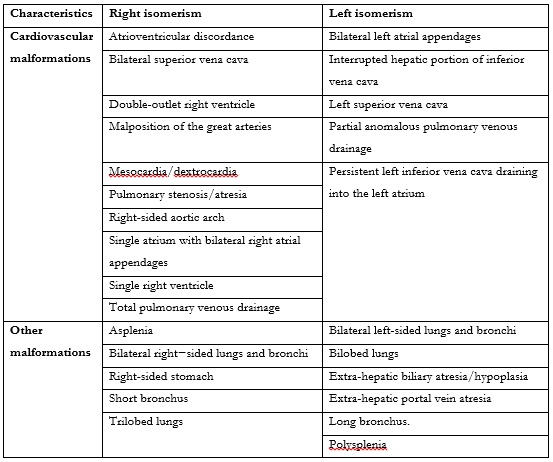
The heterotaxy syndrome is a rare congenital anomaly, with a high mortality rate due to the multiple cardiac abnormalities that may be classified in two major subcategories: heterotaxy syndrome with polysplenia (left isomerism) and heterotaxy syndrome with asplenia (right isomerism).1,2,3The polysplenia subcategory is associated with multiple spleens, in contrast to the asplenia subcategory.1,2However, both involve a large number of findings, which often overlap.1,2
Heterotaxy syndrome with asplenia is associated with congenital heart disease in 99-100% of the cases and is usually more severe compared to heterotaxy syndrome with polysplenia.1,2This explains the higher frequency of diagnoses of heterotaxy syndrome with polysplenia made incidentally in adulthood since the average lifespan of those with cardiac abnormalities is up to the first decade of life.1,2The 5-year survival of right isomerism is around 30% - 74%.4
Left isomerism has a less complex associated cardiac defect, which can be managed better, with the survival rate around 65% and 84%.4 Both right and left isomerism can present arrhythmias.5 The main characteristics of both isomerism are demonstrated in table 1.4,6 Both isomerisms can present agenesis of the corpus callosum, central nervous system abnormalities - spina bifida, clef plate, and intestinal malrotation.6
We demonstrate a case of heterotaxy syndrome with polysplenia without abnormality of the thoracic organs in an adult patient.
Case Report
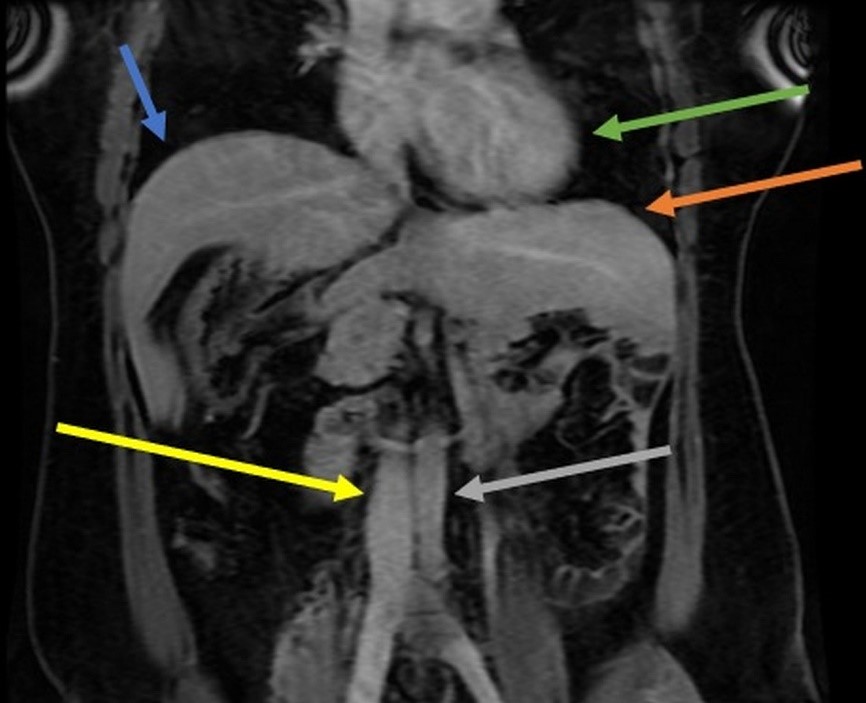
A 32-year-old female patient with longstanding abdominal pain. She mentions two previous cesarean sections. She presents a previous ultrasound examination describing a suspicion of a right adrenal gland nodule. The MRI shows ectopic spleen tissue simulating a right adrenal nodule; intestinal malrotation with gastric fundus on the right; dorsal pancreas agenesis. However, the heart is in its usual position in the left hemithorax(Figures 1, 2, and 3). The set of findings is compatible with heterotaxy syndrome with polysplenia without abnormalities in the thoracic organs. The patient is now under outpatient follow-up as the patient was asymptomatic and the MRI did not show volvulus or obstruction from a mesenteric band.
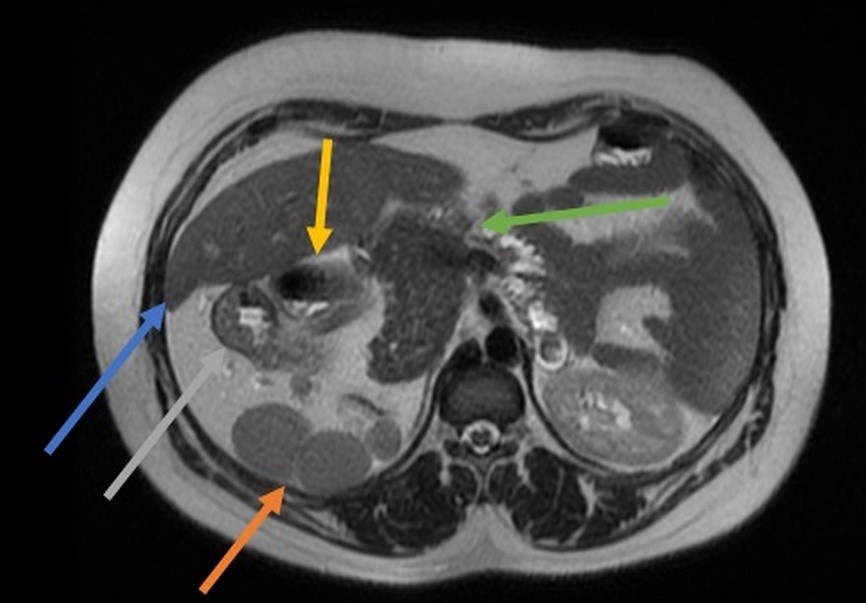
Figure 1: MRI in axial section in T2 sequence showing usual hepatic parenchyma in the right abdomen (blue arrow), ectopic splenic tissue with splenosis (orange arrow), gastric curvature in the right abdomen (gray arrow), duodenum (yellow arrow), and dorsal pancreas agenesis (green arrow).
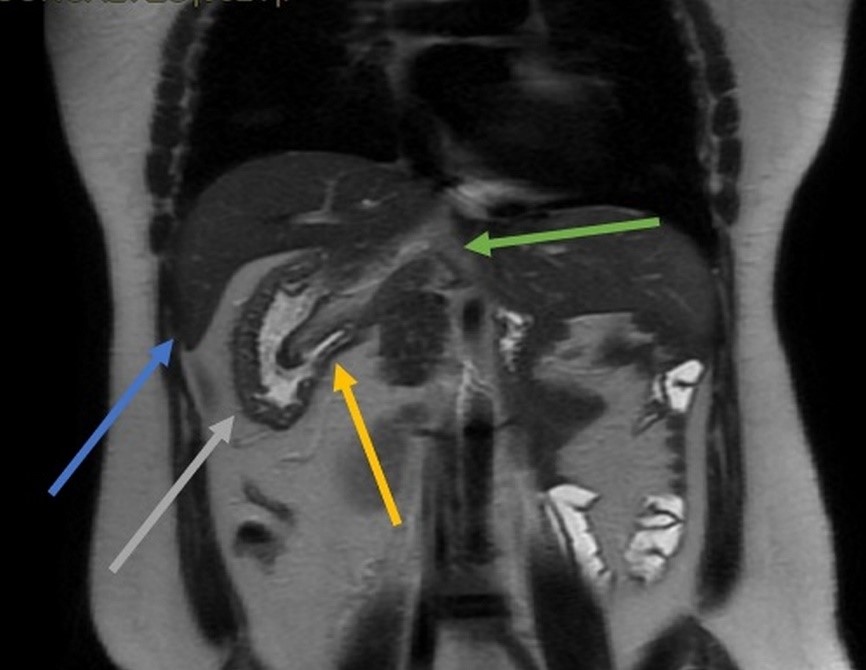
Figure 2: MRI in the coronal section of the T2 sequence showing usual hepatic parenchyma in the right abdomen (blue arrow), ectopic splenic tissue with splenosis (yellow arrow), gastric curvature in the right abdomen (gray arrow), and dorsal pancreas agenesis (green arrow).
Discussion
The orderly and habitual arrangement of organs in the human body begins with embryonic formation, based on genetic data and the loss of this organization can characterize situs inversus or a disordered and variable arrangement, as in the case of heterotaxy syndrome.7 The disease is more prevalent in men (2 male: 1 female).7
Although the heterotaxy syndrome with polysplenia and pancreatic disorder is a rare anomaly, it can be associated with the increased risk of pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus.8 Dorsal pancreatic agenesis is mostly encountered incidentally in an asymptomatic patient.8 This finding occurs when searching for other diseases.8 Nevertheless, patients can complain of abdominal pain and present hyperglycemia which is noticed in about 50% of the cases - it happens because of the loss of islet cells that are mostly located in the tail and body of the pancreas.8
Although heterotaxy syndrome with polysplenia is related to multiple spleens in most patients, some patients may present with only a lobulated spleen or even a normal spleen and may be associated with congenital heart disease, interruption of the inferior vena cava (IVC) with continuation to the azygous system, intestinal malrotation, pelvic and pancreatic abnormalities.1,2
In normal embryologic development, during the 6th week of fetal life, the midgut herniates into the umbilical stalk.9 It also undergoes a 90-degree counterclockwise rotation around the superior mesenteric artery.9 In the 10th week, the midgut returns to the abdomen and ends an additional 180-degree counterclockwise rotation.9 Malrotation directs to the failure of the midgut to complete the 270-degree counterclockwise rotation around the superior mesenteric artery - an action that can be stopped at any phase, with nonrotation being one of the possible consequences. In nonrotation, the first 90-degree counterclockwise rotation is concluded. But there is no further rotation once the midgut returns to the abdominal cavity, resulting in small bowel on the right and colon to the left of the midline.9 In general, patients are asymptomatic, and abdominal symptoms are most common in adults, and sometimes CT demonstrates intestinal malrotation.10
The syndrome is a rare congenital disorder, but the radiological recognition of the wide variety of presentations, as well as its adequate description, represents the best way to evaluate cases with a high risk of complications resulting from anatomical changes.11 The patients with complex cardiac lesions have a mortality of 85% per year if they present asplenia 50% in patients with polysplenia.2
The heterotaxy syndrome is a challenge and should be incorporated in a long-term treatment strategy.2 Albeit surgical death remains the leading cause of mortality, the sudden death is also common in patients with syndrome and atrial isomerism, which is characterized by symmetrical organs which are generally asymmetric,2 wherein, the survival of infants with isomerism is estimated at 64% at 5 years, 57% at 10 years and 53% at 15 years.12
The previously called "asplenia" usually presents duplication of the structures present in the right side, having trilobate lungs, left atrium with morphology equivalent to the right atrium, centrally positioned liver, aorta, and inferior vena cava located in the left, in addition to intestinal malrotation.7 In the previously called "polysplenia" there is usually duplication of the structures of the left side, with bilobar lungs, right atrium anatomically identical to the left atrium, liver with a central position, absence of the hepatic segment of the inferior vena cava with a continuation by the azygos or hemiazygos vein, in addition to intestinal malrotation.3 Cardiac abnormalities are less frequent and milder, explaining a higher prevalence of these findings in older individuals.7
Early surgical intervention is critical for those within this population who have cardiac abnormalities and gastrointestinal abnormalities, as it improves survival.2 But, despite interventions, mortality remains high.2 A frequent follow-up with a multidisciplinary team is of capital importance.2 Thus, radiological evaluation is essential in identifying and planning the approach to patients with cardiac complications.7