A 64-year-old male presented to our emergency department with a 6-day history of generalized malaise, worsened by left lower back pain and anorexia for the last 2 days. Other symptoms were denied, and analytical evaluation only showed leucocytosis and elevated C-reactive protein. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CE-CT) was performed (Fig. 1), in which a thickened segment of sigmoid colon with diverticula, peri-colonic fat stranding and a small amount of extra-luminal gas were seen, in keeping with perforated diverticulitis. It also revealed air thrombi along the sigmoid veins and the inferior mesenteric vein, as well as a wedge-shaped hypoenhancing area in the spleen, interpreted as splenic infarction secondary to pylephlebitis.

Figure 1: Perforated diverticulitis complicated by pylephlebitis and splenic infarction. Admission contrast-enhanced CT reveals focal fat stranding and a small amount of extra-luminal gas (arrow, a) adjacent to a thickened segment of sigmoid colon with diverticula, suggesting perforated diverticulitis. Several filling defects, compatible with air thrombi, are seen along the densified sigmoid veins (arrowheads, a) and inferior mesenteric vein (arrowheads, b). The spleen has a wedge-shaped hypoenhancing area (asterisk, c), in relation to infarction caused by the air thrombi already described. There are neither local/distant abscesses nor signs of generalized peritonitis.
Despite initially showing complete clinical response under broad-spectrum antibiotics, the patient relapsed with fever and left lower back pain. CE-CT was again performed (Fig. 2), showing evolution of the previously documented splenic infarct into spontaneous splenic rupture. He was submitted to emergent splenectomy and peritoneal lavage, with posterior clinical recovery and discharge.
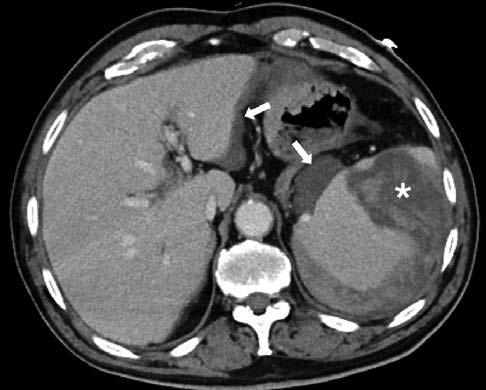
Figure 2: Spontaneous splenic rupture. In the contrast-enhanced CT performed twelve days later, the spleen is enlarged and an extensive intraparenchymal and subcapsular hematoma has developed in the infarcted area (asterisk). A small hemoperitoneum with no detectable foci of contrast extravasation (arrows) is also seen.
Acute diverticulitis is a well-documented cause of acute abdominal pain, often complicated by intra-abdominal abscess, fistulisation and perforation.1 Very rarely, due to high endoluminal pressure and bacterial transmigration, septic or gas emboli are released from the affected area and cause ascending venous thrombosis (pylephle-bitis).2 Mesenteric pylephlebitis may cause segmental bowel ischemia or, through embolization along the splenic and portal veins, distant abscess formation and infarction.1,2 Exceedingly rarely, pylephlebitis of the inferior vena cava occurs, resulting in septic pulmonary embolism.1,3
Because clinical presentation is often unspecific,2 CE-CT is the modality of choice. It allows not only visualization of thrombi and estimation of disease extent, but also identification of its underlying cause.1,2 Although the prognosis of gas in the venous system and spontaneous splenic rupture is generally very poor, it tends to be more favourable in cases of benign etiology as diverticulitis.1,2,4















