Serviços Personalizados
Journal
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Acessos
Acessos
Links relacionados
-
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO
Compartilhar
GE-Portuguese Journal of Gastroenterology
versão impressa ISSN 2341-4545
GE Port J Gastroenterol vol.27 no.1 Lisboa fev. 2020
https://doi.org/10.1159/000499679
ENDOSCOPIC SNAPSHOT
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia Combined with Submucosal Marsupialization of an Epiphrenic Diverticulum
Miotomia endoscópica peroral para tratamento de acalásia em combinação com marsupialização submucosa de divertículo epifrénico
Ricardo Rio-Tintoa, Miguel Bispoa, Paulo Fidalgoa, Jacques Devièrea,b
aDigestive Oncology Unit, Champalimaud Foundation, Lisbon, Portugal; bDepartment of Gastroenterology, Hepatopancreatology, and Digestive Oncology, Erasmus University Hospital – Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium
* Corresponding author.
Keywords: Achalasia, Advanced endoscopy, Esophageal diverticulum, Peroral endoscopic myotomy
Palavras-chave: Acalásia, Divertículo esofágico, Endoscopia avançada, Miotomia endoscópica peroral
Although developed as a technique for the treatment of achalasia, peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) has recently emerged as a therapeutic tool for other diseases such as diffuse spasm, nutcracker esophagus, and gastroparesis (G-POEM), and there is increasing evidence on its safety and efficacy. The potential applications of endoscopic tunneling and cutting seem to have no limits.
A 59-year-old woman with a 10-year history of dysphagia and a transhiatal resection surgery on an epiphrenic diverticulum 5 years previously was referred to our center due to progressive worsening of the dysphagia following surgery. Recurrence of the epiphrenic diverticulum was documented and type 3 achalasia was diagnosed, with an Eckardt score of 8 [1]. POEM, eventually combined with submucosal marsupialization of the epiphrenic diverticulum, was then proposed.
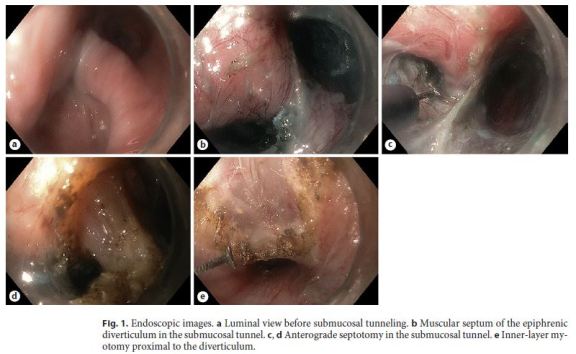
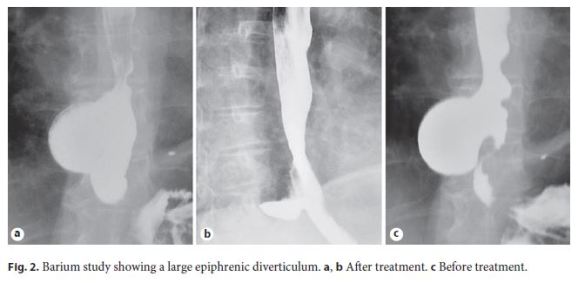
With the patient under general anesthesia, an upper endoscopy was performed (Fig. 1a). A mucosal incision was made 27 cm from the incisors, and anterograde submucosal tunneling was conducted laterally to the diverticulum pouch. The submucosal tunnel allowed reaching the lateral segment of the proximal end of the septum, where the submucosal space is divided by the septal muscle fibers (Fig. 1b). The submucosal tunnel was extended downstream up to 2 cm below the cardia, and the circular layer of the muscular wall was sectioned up to 3 cm above the gastroesophageal junction. Next, an anterograde septotomy was performed, creating a submucosal marsupialization of the diverticulum (Fig. 1b, c). The inner circular muscle layer was sectioned over an additional 3 cm over the septum (Fig. 1e), and the tunnel entry was closed with 5 clips. There were no adverse events. An immediate improvement in symptoms was noticed, and the patient remained asymptomatic (with an Eckardt score of 0) 12 months after the procedure. Follow- up esophagography illustrated marsupialization of the diverticulum and easy passage of contrast through the cardia (Fig. 2a, b), compared with the evident diverticular septum before the myotomy (Fig. 2c).
POEM is a promising minimally invasive endoscopic procedure for the treatment of achalasia, with favorable long-term outcomes [2, 3]. When achalasia is associated with a large epiphrenic diverticulum, treatment typically involves surgical myomectomy or diverticulectomy, which is associated with high morbidity [4]. However, a purely endoscopic technique, with a two-step approach, has recently been described: POEM, followed by the creation of a fistula from the esophageal diverticulum to the gastric fundus using a lumen-apposing metallic stent [5]. This case report demonstrates a single-session, modified POEM technique for the management of an epiphrenic diverticulum in the context of achalasia which was clinically effective in the long term.
References
1 Eckardt AJ, Eckardt VF. Treatment and surveillance strategies in achalasia: an update. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011 Jun;8(6):311–9. [ Links ]
2 Inoue H, Sato H, Ikeda H, Onimaru M, Sato C, Minami H, et al. Per-oral endoscopic myotomy: a series of 500 patients. J Am Coll Surg. 2015 Aug;221(2):256–64. [ Links ]
3 Li QL, Wu QN, Zhang XC, Xu MD, Zhang W, Chen SY, et al. Outcomes of per-oral endoscopic myotomy for treatment of esophageal achalasia with a median follow-up of 49 months. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018 Jun;87(6):1405–1412.e3. [ Links ]
4 Zaninotto G, Portale G, Costantini M, Zanatta L, Salvador R, Ruol A. Therapeutic strategies for epiphrenic diverticula: systematic review. World J Surg. 2011 Jul;35(7):1447–53. [ Links ]
5 Tieu AH, Kumbhari V, Ngamruengphong S, Haito-Chavez Y, Chen YI, Bukhari M, et al. Two-stage endoscopic approach for the management of a large symptomatic epiphrenic diverticulum in the setting of achalasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016 Nov;84(5): 848–9. [ Links ]
Disclosure Statement
The authors have no financial disclosures to report.
* Corresponding author.
Ricardo Rio-Tinto, MD
Digestive Oncology Unit, Champalimaud Foundation
Avenida Brasília
PT–1400-048 Lisbon (Portugal)
E-Mail ricardo_rio_tinto@yahoo.com
Received: December 19, 2018; Accepted after revision: March 5, 2019














