Introduction
Gastric adenocarcinoma is the fifth most common and fourth most mortal cancer worldwide [1]. Its high mortality can be explained by the absence of screening and early-diagnosis strategies, resulting in the diagnosis of gastric cancer (GC) at an advanced stage.
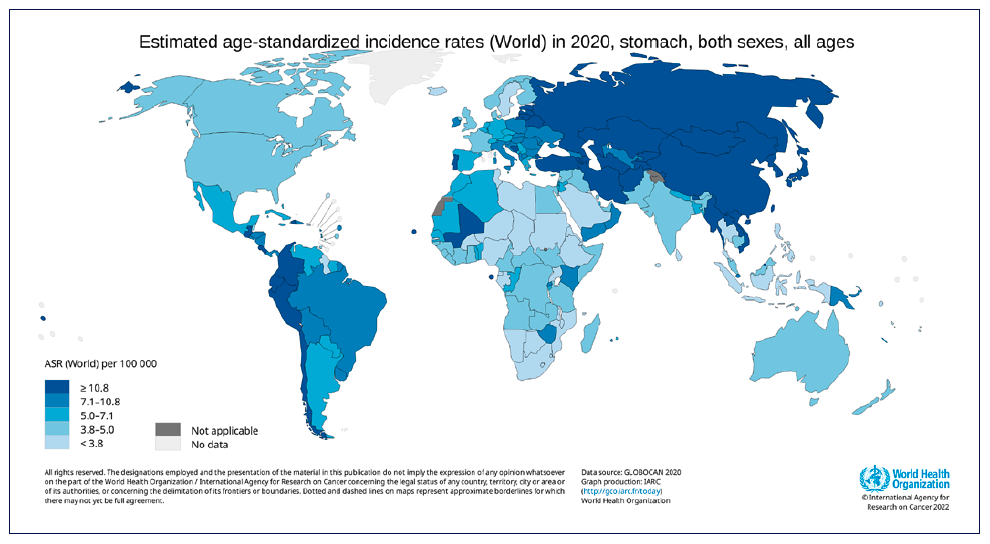
Currently, screening for gastric adenocarcinoma in the opposite, in low to intermediate-risk countries (i.e., Western countries), is only recommended for high-risk groups (e.g., extensive preneoplastic conditions, history of GC in a first-degree relative, genetic syndromes associated with GC risk) [2]. Classically, it is usual to aggregate Western countries in GC risk, but it is important to clarify that it differs between the countries, and so it is essential to adjust screening and/or clinical investigation accordingly to the specific country’s risk (shown in Fig. 1).
Most cases of gastric adenocarcinoma are sporadic, with a minority of cases (10%) occurring in a context of familial aggregation or heritable syndromes [3]. GC can be classified into several subtypes depending on the classification, being the mostly used Lauren or WHO classifications. Lauren’s classification was established in 1965 and specifically subdivided the gastric adenocarcinoma into intestinal (53%), diffuse (33%), or indeterminate histologic type (14%) [4]. The indeterminate type may correspond to other subtypes according to WHO classification. Despite its simplicity, Lauren’s classification is useful to guide the investigation of affected or familial individuals with gastric adenocarcinoma.
Sporadic adenocarcinoma is generally of the intestinal type, associated with Helicobacter pylori infection, and corresponds to the last stage of the Correa cascade, which represents the progression of precancerous conditions, although family aggregation exists also in this GC sub-type. On the other hand, diffuse adenocarcinoma is less frequent and, as it may be associated with a genetic disorder (hereditary diffuse gastric cancer; HDGC), this condition should be carefully evaluated.
High-risk population includes individuals with heritable syndromes associated with GC and individuals with risk factors for sporadic GC (mainly extensive precancerous conditions associated with H. pylori). The lack of gastric adenocarcinoma screening in the general population in low to intermediate-risk countries is associated with the lack of firm evidence of cost-effectiveness, although it is important to identify individuals with a higher risk of GC that may benefit from screening/surveillance.
The scarcity of literature on this topic led to this review. We intend to summarize (i) diagnostic criteria of heritable syndromes associated to GC, (ii) risk factors for sporadic GC, (iii) timing to start screening, and (iv) sur-veillance of high-risk population. Methods of detection, surveillance, and prophylactic or therapeutic interven-tions will not be discussed in this review.
Methods
A narrative non-systematic review was performed based on an electronic search through the medical literature using PubMed. The keywords “Heritable Gastric Cancer,” “Familial gastric cancer,” “Sporadic cancer,” “Lynch syndrome,” “Li-Fraumeni syndrome,” “Gastrointestinal polyposis syndromes,” “Gastric Adeno-carcinoma and Proximal Polyposis of the Stomach,” “Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer,” and “Familial intestinal gastric cancer” were used. No publication date restrictions were imposed, but guidelines and systematic reviews in the past 10 years from gastroenterology, endoscopy, oncology, genetics, and histopathology were preferred. When more than one guideline concerning the same subject was available, the most updated one was selected. Only articles published in English were considered. The majority of articles refer to European or North American studies. However, Asian articles were punctually included if relevant to the manuscript.
Hereditary Cancer
Familial aggregation of gastric adenocarcinoma can occur in up to 10% of the patients, but a deleterious genetic variant is only identifiable in about 1-3% of cases [3]. Familial/hereditary GC may be part of a genetic syndrome involving multiple organs or be exclusive to the stomach.
Familial aggregation is defined through a high prevalence of GC among first-degree relatives (siblings, parents, and children). Indeed, the existence of a first-degree relative with GC confers an increased risk (OR 2-10) of the disease [5].
However, it is important to clarify that familial GC aggregation may be linked to shared environmental and lifestyle factors, thereafter increasing the incidence of cancer in a genetically susceptible family [6]. In fact, first-degree relatives have a higher prevalence of H. pylori infection, atrophy, and intestinal metaplasia [7]. This finding validates the recommendation to perform esophago-gastroduodenoscopy (EGD) every 3 years in individuals with precancerous conditions (non-extensive) and a family history (1st degree relatives) of GC, and every 1-2 years in patients with a family history of GC and extensive precancerous conditions according to MAPS II [8]. On the other hand, the risk of GC in second-degree relatives is lower [6] and, therefore, there is no indication for screening these individuals [8].
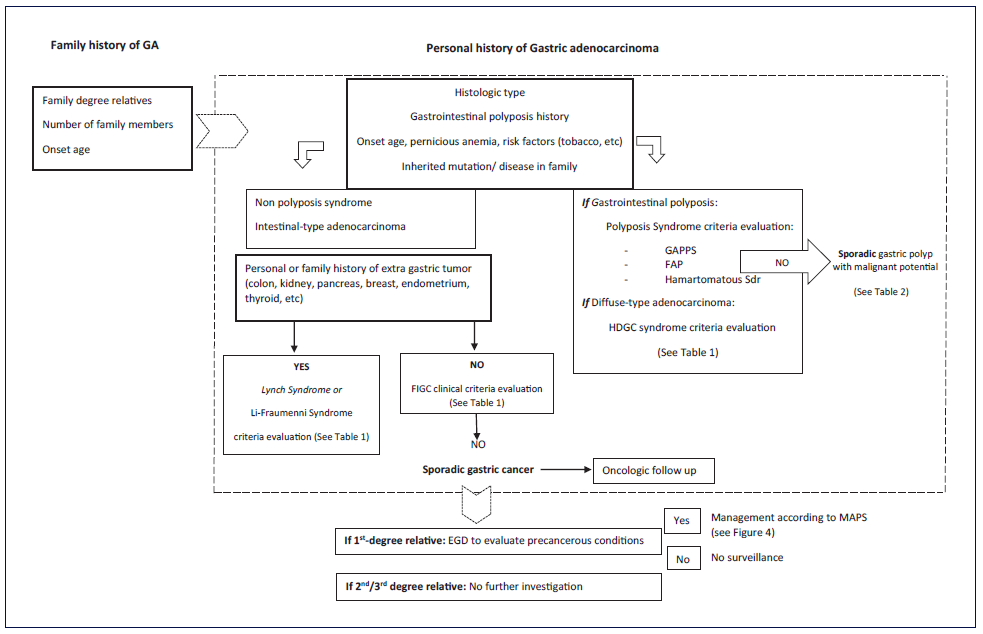
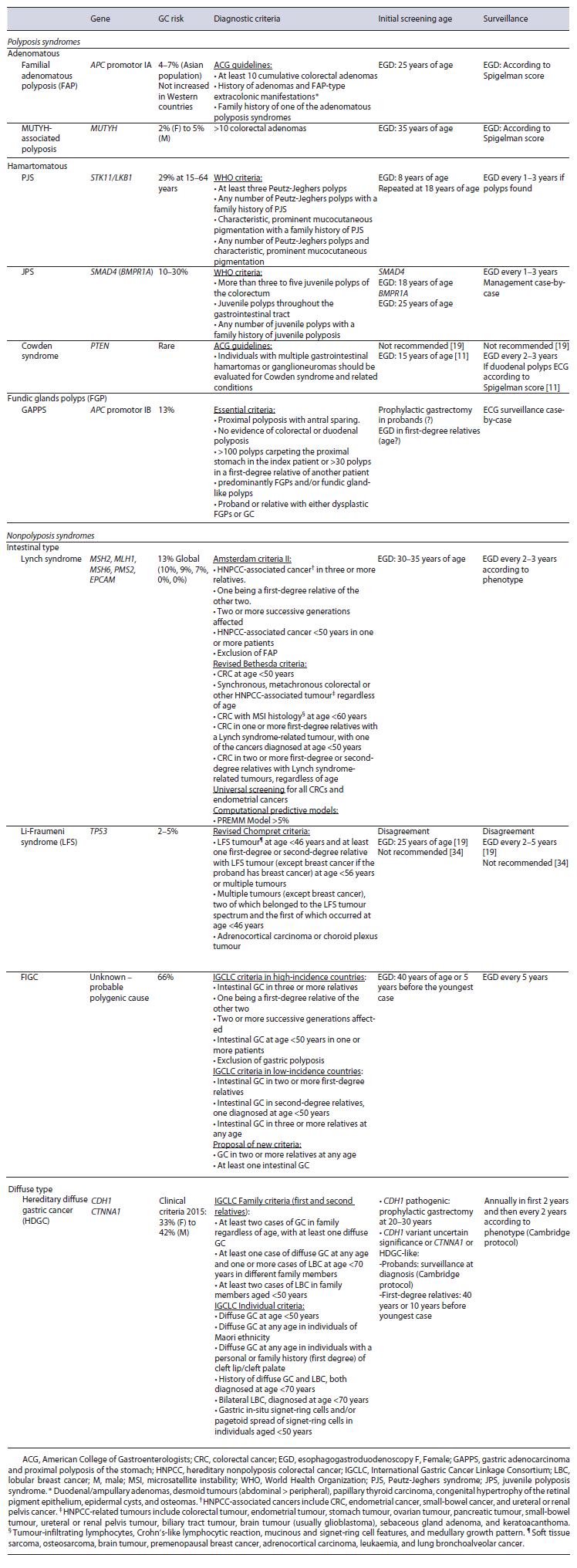
In the initial approach of a familial aggregation of gastric adenocarcinoma, certain topics must be assessed to recognize patients at high risk of hereditary gastric adenocarcinoma: histological type, presence of gastrointestinal polyposis and extra-gastric neoplasms, a detailed family tree of affected family members, and any known inherited mutation/disease in the family (shown in Fig. 2). These elements are essential in the evaluation of the criteria defined to motivate further risk assessment of heritable GC (shown in Fig. 3) [9]. Briefly, these include two or more relatives with the same cancer; cancer in at least two generations; cancer diagnosed at a young age; multiple neoplasia in the same individual; a family with an unusual cancer pattern; and cancer associated with a known heritable syndrome.
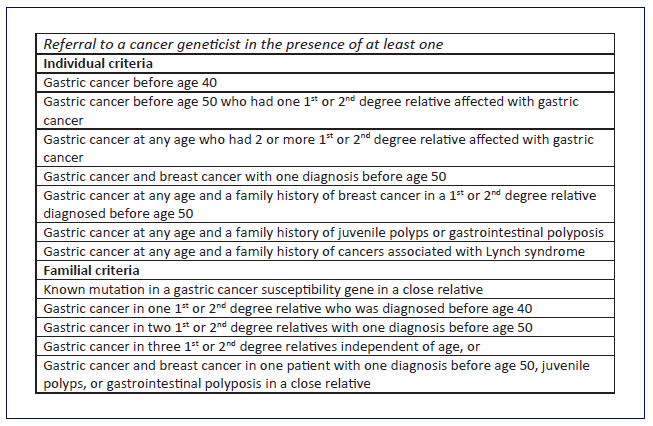
Fig. 3 Criteria for further risk evaluation for high-risk syndromes associated to GC (adapted from [9]).
Hereditary causes are rare but multiple and, although the diagnoses are mostly clinical, some can be confirmed through genetic tests. Hereditary GC can be included in polyposis and nonpolyposis syndromes. The polyposis syndrome with the highest risk is gastric adenocarcinoma and proximal polyposis of the stomach (GAPPS), and those without polyposis are HDGC and familial intestinal gastric cancer (FIGC).
In this section, the main different causes will be discussed with a resume of diagnostic criteria, screening initiation, and surveillance (shown in Table 1, adapted from [10-12]). Prophylactic or therapeutic endoscopic or surgical interventions will not be thoroughly discussed. Additionally, other rarer hereditary syndromes associated with GC (ataxia-telangiectasia, Bloom syndrome, hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome, and xeroderma pigmentosum) will not be described due to the lack of information that supports recommendations on screening and surveillance [9].
Polyposis Syndromes
Hamartomatous Syndromes
The presence of hamartoma polyps in the digestive tract should raise the clinical suspicion of a genetic syndrome and, therefore, there is an indication for genetic study. Hamartomatous syndromes include Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, juvenile polyposis syndrome (JPS), and Cowden syndrome.
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is characterized by perioral hyperpigmentation and hamartomatous polyps [13] and is mostly associated with STK11/LKB1 tumour suppressor gene variants [14]. Although most polyps are located in the small bowel (60-90%), 15-30% are located in the stomach [14]. The risk of gastric adenocarcinoma is 29% at 15-64 years of age, with an average diagnosis between 30 and 40 years of age [15]. Screening should start at 8 years of age and, in the absence of lesions, repeated at 18 years of age. Surveillance depends on phenotype and should be performed every 1-3 years [10].
JPS is diagnosed in the presence of at least one hamartomatous polyp in the stomach [11], and in 40-60% of the cases there is a deleterious variant in the SMAD4 or BMPR1A genes [16]. The gastric phenotype is normally associated with variants in the SMAD4 gene [16], and the risk of extracolonic cancer is difficult to assess, ranging from 20% to 60%, including GC [17]. The current recommendation is to start screening in SMAD4 variant carriers at 18 years of age and in BMPR1A variant carriers at 25 years of age. Surveillance should be performed every 1-3 years according to phenotype [10].
Cowden’s syndrome is characterized by the existence of several neoplasms dispersed through multiple organs and, concerning the stomach, gastric hamartomas associated with variants in the PTEN gene. The risk of gastric adenocarcinoma is higher, but its incidence is unknown [18]. GC screening and surveillance in these individuals is not consensual. Older guidelines recommended screening at 15 years of age and surveillance every 2-3 years [11]; however, more recent NCCN updates no longer recommend EGD due to lack of evidence [19].
Adenomatous Syndromes
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is mostly a colorectal disease, associated with an autosomal dominant mode of transmission and variants in the APC gene, which can be classified as classic or attenuated, according to the number of colorectal adenomas. However, gastric polyps may occur in more than 60% of the patients [20], with different malignant risk.
Most gastric polyps associated with FAP are fundic gland polyps that may present with low-grade dysplasia in up to 40% of the cases [21], with high-grade dysplasia (HGD) and malignant transformation being rare [22, 23]. However, it should be recognized that sporadic fundic gland polyps associated with proton-pump inhibitor can also occur in FAP, and these hardly harbour dysplasia [18].
Up to 20% of polyps correspond to adenomas, encompassing foveolar-type adenomas (85%), pyloric gland adenoma (15%), and intestinal-type adenoma (1-2%), with a corresponding increased risk of malignancy [21, 22]. Foveolar-type adenomas are rare in an absolute matter being the majority associated with APC variants and appearing as an isolated sporadic lesion within normal mucosa and, thus, a low progression risk. Pyloric gland adenomas, which are also rare and associated with normal mucosa, present HGD and adenocarcinoma foci at a higher frequency (10-15%). In contrast, intestinal-type adenomas are highly associated with advanced lesions (HGD or adenocarcinoma), intestinal metaplasia, gastritis, and also synchronous adenocarcinoma. This may be explained by other risk factors than APC variants, such as H. pylori infection. These facts elucidate its lower frequency but high malignancy risk.
The risk of GC in FAP in Western countries is low and was previously described as comparable to the risk of sporadic fundic gland polyps [23]. However, recent case series discovered advanced gastric lesions (including adenocarcinoma) in extensive areas of sporadic fundic gland polyps [24, 25]. This fact may lead to the creation of specific protocols for screening and surveillance of GC in this population, which currently are lacking.
On the other hand, the risk of duodenal adenocarcinoma is known to be highly associated to duodenal polyposis and, therefore, is recommended starting screening at 25 years of age and surveillance according to Spigel-man’s classification. Consequently, this is an opportunity to surveille gastric mucosa in an attempt to early detection of GC and precursors lesions, as recommended in the ESGE guideline [10].
MUTYH-associated polyposis is an autosomal recessive syndrome associated with biallelic variants in the MUTYH gene. This syndrome also has an increased risk of duodenal (4%) [21] and GC (2-5%) [12], thus an EGD should be performed at 35 years of age and then maintained similarly to FAP [10].
Gastric Adenocarcinoma and Proximal Polyposis of the Stomach
GAPPS is a recently described gastric polyposis syndrome characterized by an excess of fundic gland polyps that affects the fundus and gastric body, sparing the antrum and small curvature, and no colorectal phenotype. Its diagnosis is clinical and must meet specific criteria (shown in Table 1) [26]. It is an autosomal dominant hereditary disease with incomplete penetrance secondary to variants in the promoter IB of the APC gene [27]. This syndrome has a high risk (13%) [26] of intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma and HGD, unlike other GC associated polyposis, like FAP and fundic gland polyps [28].
The natural history of GAPPS is variable, and additional mutations can arise that lead to malignant transformation and earlier progression. Thus, affected patients should initiate screening (as their first-degree family members) and endoscopic surveillance. However, there are still no clear recommendations in this issue [26]. There are case-reports where dysplastic, or even neoplastic, lesions are undistinguished within polypoid carpet in patients who present with metastatic disease. This fact may support the recommendation for prophylactic total gastrectomy [28].
Nonpolyposis Syndromes
Lynch Syndrome
Lynch syndrome is the most common cause of heritable gastrointestinal cancer and is an autosomal dominant syndrome linked to germline variants in one of the DNA mismatch repair (MMR) genes (MSH2, MSH6, MLH1, PMS2) or exonic deletions in the EPCAM gene [29]. Diagnosis of Lynch syndrome can be difficult, so there are different methods to support the diagnostic approach. These include the Amsterdam II criteria (family related clinical criteria; sensitivity 22%, specificity 98%), the Bethesda criteria (individual clinicopathologic criteria; sensitivity 82%, specificity 77%) and, finally, computational predictive models (MMRpredict, MMRpro, and PREMM) (shown in Table 1). The latter can be used when Lynch syndrome is suspected and is impossible to confirm the criteria (dead or distant relatives, etc.). The PREMM model is more practical and applicable to the general population, with higher sensitivity but lower specificity (90% and 67%, respectively). A probability greater than 5% means that the patient is admissible for genetic testing [29].
The lifetime risk of GC in Lynch Syndrome patients remains not deeply studied. An old Finnish study referred to a 13% lifetime risk [30], but a more recent Dutch study reported a lower relative risk (3.4 incidence ratio) [31]. Also, it demonstrated a higher risk in males (8%) compared to females (5.3%) [31]. Since the intestinal type is the most frequent, there is a possibility of surveillance; however, there is a lack of data for robust recommendations [29]. A recent retrospective study has found that patients with MMR deleterious variants have a high prevalence of precursor conditions (HP infection in 58.3%, intestinal metaplasia in 38.2%, and multifocal atrophy in 33.6%). (Raquel Ortigão et al., Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, in press).
Thus, it is currently recommended to screen patients with Lynch syndrome or MMR deleterious variants with EGD at 30-35 years of age with biopsies for screening for H. Pylori and eradication, if present. Surveillance should be performed every 2-3 years according to individual risk, i.e., family history of gastric adenocarcinoma and/or presence of precancerous conditions [29].
Li-Fraumeni Syndrome
Li-Fraumeni syndrome is an autosomal dominant disease characterized by multiorgan neoplasms associated with deleterious germline variants in TP53 [32]. The risk of GC in these patients does not seem to be completely determined, with older studies showing a high prevalence (26%) [33], while more recent ones showed a non-superior risk in this population compared to the general population [34].
Thus, the recommendations are discordant regarding screening and surveillance of gastric cancer. NCCN 2022 update recommends surveillance at 25 years of age or 5 years before the earliest GC in the family and to be repeated every 2-5 years [19]; on the other hand, the UK 2021 consensus recommends H. pylori testing and eradication, if required, but does not recommend EGD for surveillance, due to lack of evidence [35].
Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer
HDGC is a rare autosomal dominant syndrome defined by the presence of, at least, one diffuse GC plus lobular breast cancer associated with CDH1 or CTNNA1 germinative variants [36]. Additionally, some families have an isolated phenotype of lobular breast cancer, designated as hereditary lobular breast cancer, while others fulfil clinical criteria but do not carry a genetic variant, known as HDGC-like.
In 2020, the International Gastric Cancer Linkage Consortium (IGCLC) updated the practice guidelines on clinical criteria for genetic testing (shown in Table 1) [18]. Each subgroup is assigned a different risk of GC, and therefore a different therapeutic approach and surveillance.
Patients and families with HDGC-CDH1 should undergo prophylactic total gastrectomy after excluding more advanced lesions on endoscopy at the time of diagnosis. In those who have decided to undergo endoscopic surveillance and in hereditary lobular breast cancer, EGD must be performed annually according to the Cambridge protocol.
In patients with CTNNA1 variants, CDH1 variants of uncertain significance, or HDGC-like, EGD should be performed annually in the first 2 years and then the interval may increase according to the features. In first-degree relatives, surveillance should be started at 40 years of age or 10 years before the youngest case.
Familial Intestinal Gastric Cancer
FIGC is an autosomal dominant syndrome [37], which remains genetically unexplained but is postulated to be a polygenic syndrome [38]. Diagnosis is clinical and based on GC incidence [38]. In high-incidence countries, the diagnosis respects the Amsterdam criteria, similar to Lynch syndrome, and in low to intermediate-incidence countries the criteria are intestinal GC in two or more first-degree relatives; intestinal GC in second-degree relatives, one diagnosed at age <50 years; and intestinal GC in three or more relatives at any age (shown in Table 1). There are only a few general recommendations such as starting surveillance at 40 years of age or 5 years before the youngest case, H. pylori test-and-treat [39] and every 5 years thereafter [40].
Family History without Heritable Cancer Criteria
So far, recommendations for screening and surveillance of patients with clinical and/or genetic criteria for hereditary syndromes associated with GC have been described. However, with the increase in the incidence of GC, there are more and more individuals with a family history of GC without hereditary criteria, that is, patients with only one relative with GC.
Concerning this issue, there are no clear recommendations regarding GC screening in family relatives. What is known, as discussed below, is that the existence of a first-degree relative with GC confers an increased risk of GC [5] and a higher prevalence of H. pylori infection, atrophy, and intestinal metaplasia [7]. On the contrary, the risk of GC in second-degree relatives is lower [6].
Despite low evidence, the British Society of Gastroenterology Guidelines suggests that endoscopic screening should be considered in individuals older than 50 years of age with a family history [41]. Additionally, in MAPS II, the existence of familial GC modifies the follow-up of precursor lesions [8].
Thus, there may be a proposal for EGD at age 50 years of age (or before if early-onset in a family relative) in individuals with GC in first-degree relatives (but not in second-degree) to evaluate precursor conditions and/or H. pylori infection. If present, management according to MAPS II is recommended; if absent, no further screening is recommended [41].
Sporadic Cancer
As discussed above, the existence of hereditary syndromes and familial risk is responsible for an elevated cancer risk compared to the general population and, therefore, an earlier screening and laborious surveillance is recommended. However, most cancers are sporadic, which increased difficulties in identifying high-risk patients who may benefit from a screening.
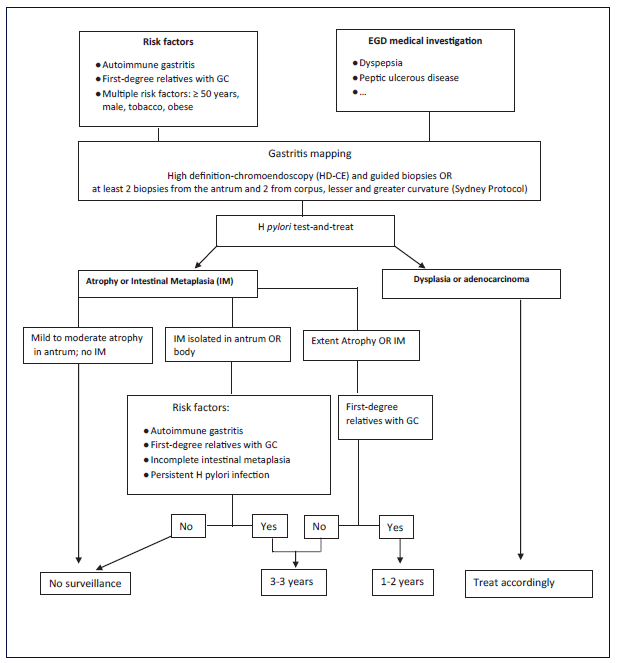
The major risk factor associated with sporadic GC is the existence of precancerous conditions (gastric atrophy and intestinal metaplasia), which are mainly caused by chronic H. pylori infection. The onset and management of precancerous conditions and their risk factors are elucidated in MAPS II recommendations [8] and summarized in Figure 4.
Other risk factors are autoimmune gastritis; a minority of sporadic gastric polyps; and sociodemographic risk factors. Autoimmune gastritis is a chronic disease with malignant potential for adenocarcinoma or neuroendocrine tumours (OR 2.18 and 11.4, respectively) [42]. A meta-analysis calculated a relative risk of GC of 6.8 and an annual incidence/person of 0.27% [43]. It is recommended to perform an EGD at diagnosis and then every 5 years for GC risk [8].
A minority of sporadic gastric polyps have a malignant potential (even being low) to cause gastric adenocarcinoma. This includes fundic gland polyps, hyperplastic and adenomas; setting aside inflammatory fibroid polyps, which have no malignant potential [44], and sporadic hamartomas that are extremely rare to support data. The main cause and features of the different sporadic gastric polyps associated with gastric adenocarcinoma and their management are summarized in Table 2 [44-46]. In general practice, biopsies should be performed according to the Sydney protocol to determinate surveillance (independently of polyp histology) and in the surrounding area to detect precancerous conditions or adenocarcinoma [45].
Table 2 Sporadic gastric polyps’ characteristics associated to gastric adenocarcinoma and their management

Other risk factors associated with GC risk are age, gender, ethnicity, smoking, and history of gastric surgery for benign disease. The risk of GC appears to be increased after 45 years of age [47, 48], in non-Caucasian individuals [49-51] and in individuals with previous gastric surgery (more than 30 years ago) [52]. However, all of them can be related to H. pylori infection chronicity. Additionally, men and current smokers are also at higher risk (1.3-3 times and OR 1.45, respectively) [49, 53, 54]. Despite low evidence, endoscopic screening should be considered in individuals older than 50 years with multiple risk fac-tors for gastric adenocarcinoma, especially in those with family history [41].
Conclusion
GC remains one of the most prevalent and deadly cancers worldwide, but its screening in the general population is only effective in countries with high incidence. In countries with low to intermediate risk of gastric adenocarcinoma, screening is only cost-effective in high-risk populations. High-risk population includes sporadic pre-cancerous conditions (intestinal metaplasia or atrophy) and several genetic syndromes with different risk to gastric adenocarcinoma, being the highest risk attributable to GAAPS, HDGC, and FIGC.
The management of these patients is hampered by the overlap of genetic and environmental risk factors, which by working synergistically may increase the risk of gastric adenocarcinoma. To conclude, clinicians should recog-nize high-risk patients, and although hereditary adenocarcinoma is rare, that possibility must be considered and the diagnostic criteria applied. However, the lifetime risk of gastric adenocarcinoma differs, and so screening and surveillance protocols may be adapted to local conditions.
Key Points
Importance of a complete personal and family history of gastric (and extra-gastric) cancer.
Awareness of heritable syndromes with GC risk.
All individuals with precancerous conditions and/or heritable syndromes should be tested-and-treated to H.pylori, especially in high prevalence countries.
Interaction between environmental factors and heri-table syndromes, especially H. pylori infection.
Importance of family history (and others risk factors) in management of precancerous conditions.