Introduction
In recent years, the number of patients on antiretroviral therapy (ART) for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection has increased significantly [1]. Although antiretroviral drug-induced liver injury is the first hypothesis when elevation of liver enzymes occurs after starting these therapies, immune reconstitution-related autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) must be considered. In HIV-infected patients, HIV-associated cholangiopathy, co-infection with hepatitis B or C virus, opportunistic infections, alcohol abuse, and nonalcoholic fatty liver must also be excluded, among others.
About three dozen cases of AIH have been described in HIV-positive patients with no prior history of abnormal liver enzymes, who developed transaminase abnormalities months to years after starting ART [2-5]. These cases are mainly of AIH, with only two overlap syndromes with primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) and AIH being reported in the literature [6, 7]. The mechanism for this increasingly described entity of immune reconstitution syndrome is not fully understood, but probably involves the rapid increase in CD4+ lymphocyte number after starting ART. In AIH, cellular infiltrates in the liver are rich in CD4+. In particular, the pro-inflammatory Th17 subtype that releases IL-17 has been found to be elevated in AIH. Furthermore, these patients have decreased numbers of Treg cells, which suppress effector T cells and maintain tolerance to self-antigens. The rapid increase in CD4+ cells following ART may produce a larger proportion of Th17 cells without appropriate Treg cell numeri cal and functional reconstitution, thereby creating a “perfect storm” for AIH onset [2]. Additionally, other autoimmune disorders, such as vasculitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, and Graves’ disease, have been described in HIV patients treated with ART [3].
It is challenging to start immunosuppressive therapy in patients with HIV infection, given the risk of worsening HIV status and increasing the risk of opportunistic infections or malignancies [5]. However, cases of AIH in HIV-infected patients have been described and successfully managed with either prednisolone alone or in combination with azathioprine, while on ART [3-5]. From the published data, only 4 cases of life-threatening infections occurred in HIV patients with AIH treated with immunosuppressors [8], although some reports have insufficient follow-ups. Current AIH guidelines recommend individualized immunosuppressive therapy in this population [9]. Particular attention is also needed for possible drug-drug interaction between immunosuppressive medications like azathioprine and antiretroviral medications, as they share common elimination and metabolism pathways such as cytochrome P450 enzyme system or P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated protein pathways [5].
Case Report
Case 1
This case concerns a 59-year-old Caucasian man with HIV (CDC Atlanta stage A1 [10]) infection controlled with abacavir, dolutegravir, and lamivudine (ABC/DTG/3TC) and hypercholesterolemia treated with simvastatin. He was otherwise healthy and fit, his body mass index (BMI) being 22.6 kg/m2. Previously to ART, he already had pruritus and a slight elevation of liver enzymes, with an alkaline phosphatase (ALP) of 154 U/L, gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) of 201 U/L, and alanine transaminase (ALT) of 68 U/L. A significant increase in hepatic enzymes occurred 3 years after starting antiretrovirals: ALP 541 U/L (4 times the upper limit of normal [ULN]), GGT 1,025 U/L (17 times the ULN), and ALT 262 U/L (6 times the ULN), with normal bilirubin. The patient denied excessive alcohol consumption and intake of new drugs or herbal and dietary supplements (HDS). Viral and metabolic liver diseases were excluded. Positive antinuclear anti-bodies (ANA) (1:640), positive anti-mitochondrial antibodies (AMA) (1:160), elevated immunoglobulin G (1,824 mg/dL), and immunoglobulin M (478 mg/dL) were found. Abdominal ultra-sound and computed tomography revealed a normal sized liver without bile duct alterations. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography was not performed due to orthopedic metallic material. Liver biopsy revealed a mixed inflammatory infiltrate with lymphocytes, plasmocytes, neutrophils, and some eosinophils, with features of cholangitis, such as exuberant ductular proliferation and intraepithelial lymphocytes in bile ducts, without cholestasis or steatosis, with moderate interface hepatitis with bridg ing necrosis and a chronicity index of 2/6 according to Ishak criteria (shown in Fig. 1).
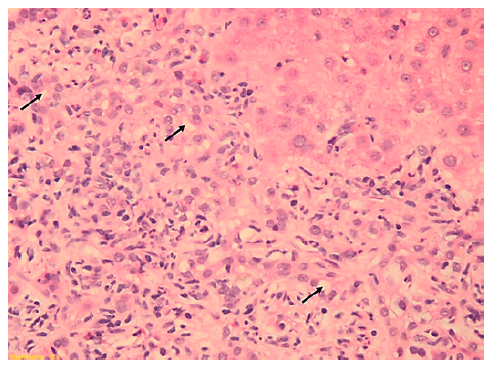
Fig. 1. Liver biopsy (9 portal spaces) revealed an intense inflammatory infiltrate with features of cholangitis (exuberant ductular proliferation (arrows exampling some) and intraepithelial lymphocytes in bile ducts) without cholestasis, with moderate interface hepatitis and bridging necrosis. Hematoxylin and eosin, ×20.
A diagnosis of PBC with features of AIH, meeting Paris criteria for AIH-PBC overlap syndrome (ALP >2 times the ULN and GGT > 5 times the ULN, positive AMA >1:40 and florid bile duct lesion on histology for PBC; ALT more than 5 times the ULN and histology with moderate interface hepatitis for AIH), was established, and ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) was started at 1,000 mg/day. According to Paris II criteria (ALP more than 1.5 times the ULN or aspartate transaminase [AST] more than 1.5 times the ULN or bilirubin more than 1 mg/dL), the patient had an incomplete response to UDCA at 12 months (ALP 541-261 U/L), despite ALT and AST improvement (from 150 U/L and 103 U/L to 51 U/L and 46 U/L, respectively). Although most recent guidelines suggest the association with obeticholic acid in these cases [11], data concerning its use with concomitant ART were lacking. Because the association of UDCA with bezafibrate has been shown to be promising as an alternative [12], bezafibrate 400 mg/day was added after confirming its safety in combination with ART. At this point, ALT and AST were at the ULN. A substantial improvement 6 months after starting bezafibrate was noted, with ALP normalization (91 U/L) and a significant reduction in GGT (318-140 U/L). One year after concomitant therapy with UDCA and bezafibrate, ALT, AST, and ALP are within the normal range, with a slight GGT elevation (110 U/L). Transient elastography improved from 13.3 kPa to 9.1 kPa. Although this patient met Paris criteria for “PBC with secondary AIH,” a normalization of ALT and immunoglobulin G was achieved with the treatment for PBC. Therefore, no immunosuppressive treatment was initiated.
Case 2
This case concerns a 49-year-old Caucasian man with HIV in-fection diagnosed in the context of disseminated cytomegalovirus disease (esophagitis and proctitis) (CDC Atlanta stage C3 [10]), with complete remission and with recovery of immunological state (CD4 count> 500 cels/μL) and suppression of viral load with ABC/3TC/DTG since then. He was otherwise fit and had a BMI of 24.3 kg/m2. An oscillating elevation of hepatic enzymes was noticed 2 years later, with maximum values of ALP 289 U/L, GGT 554 U/L, ALT 613 U/L, and AST 371 U/L, with normal bilirubin. He denied excessive alcohol intake, recently introduced drugs, or HDS. An extensive liver panel excluded viral and metabolic liver diseases. The patient had positive ANA (1:640), positive AMA (1:80), and elevated immunoglobulin G (2,536 mg/dL). Abdominal computed tomography revealed a cirrhotic liver. Liver biopsy, performed 6 months after starting UDCA 13 mg/kg/day (which had been initiated in the Infectious Diseases Clinic, previously to hepatology referral), confirmed fibrosis 5/6 according to Ishak criteria and features compatible with AIH (lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, moderate to severe interface hepatitis, and emperipolesis) and biliary inflammation without duct destruction (shown in Fig. 2). Upper endoscopy excluded esophageal varices.
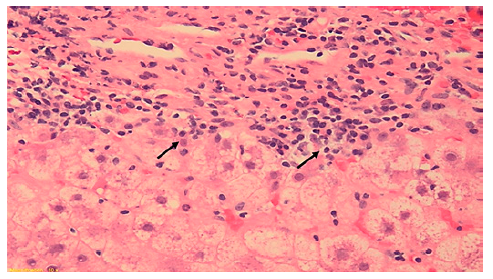
Fig. 2. Liver biopsy (6 portal spaces) revealing features of autoim-mune hepatitis (moderate to severe lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, interface hepatitis, and emperipolesis) with ductular proliferation without ductopenia. Arrows showing inflammatory cells permeat-ing through hepatocytes. Hematoxylin and eosin, ×20.
A diagnosis of AIH with features of PBC (meeting Paris criteria for overlap syndrome: ALP >2 times the ULN, GGT >5 times the ULN, and positive AMA >1:40 for PBC; histology with moderate to severe interface hepatitis and ALT >5 times the ULN for AIH) was established. Considering the severity of his initial HIV presentation and concerns regarding immunosuppression in this scenario, a decision was made to start prednisolone monotherapy, at an initial dose of 60 mg/day, without azathioprine. A significant analytical improvement was noted 1 month later (AST 244-42 U/L, ALT 326-69 U/L, ALP 170-104 U/L, GGT 276-45 U/L). Since interferon gamma release assay was positive, the patient was treated with isoniazide for latent tuberculosis for 9 months, while tapering prednisolone. However, the dose required to maintain a complete biochemical response was 15-17.5 mg. Recently, almost 2 years after diagnosis and after completing SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, azathioprine was added at 50 mg/day (0.5 mg/kg) which allowed for prednisolone tapering to 10 mg, with sustained complete bio-chemical response.
Case 3
This case concerns a 53-year-old black overweight woman (BMI 28.4 kg/m2) with long-term HIV infection (CDC Atlanta A2 stage [10]) treated with darunavir, emtricitabine, tenofovir, and ritonavir, with a good immunological state. She presented with acute abdominal pain, nausea, and new-onset jaundice, without fever or encephalopathy. Liver enzymes were increased (ALT 158 U/L, AST 395 U/L, ALP 171 U/L, GGT 328 U/L, and total bilirubin 9.76 mg/dL), and prothrombin time prolonged (20.9 s, with INR 1.8), hence meeting criteria of acute liver injury. She denied alcohol consumption, recently introduced drugs, or HDS. Abdominal Doppler ultrasound was normal. Viral hepatitis was excluded. Due to positive ANA (1:640) and significantly increased immunoglobulin G (5,100 mg/dL), liver biopsy was performed. Histology revealed features typical of AIH (lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, inter-face hepatitis, emperipolesis, and hepatocellular rosette formation) with severe inflammatory activity, massive bridging necrosis, and parenchymal collapse, with an activity index of 13/18 and a chronicity index of 3/6 according to Ishak criteria (shown in Fig. 3).
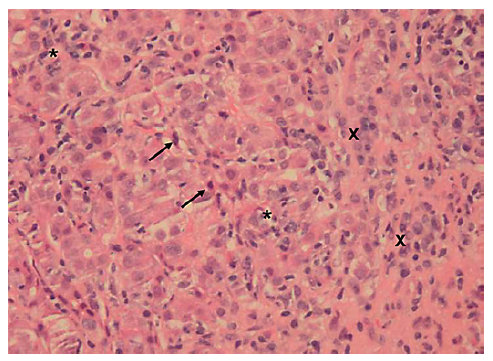
Fig. 3. Liver biopsy (10 portal spaces) revealing features of autoimmune hepatitis (lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, with severe intra-lobular inflammatory activity (stars evidencing inflammatory infiltrate and crosses evidencing plasma cells aggregates) and necrosis (arrows showing apoptotic bodies). Hematoxylin and eosin, ×20.
Prednisolone was started (initial dose 50 mg/day), and the patient was safely discharged after 2 weeks. Azathioprine was added 1 week after discharge, when MELD-Na improved from 23 to 15 and with a total bilirubin of 4.75 mg/dL at this time, while tapering corticosteroids. The patient reached complete biochemical response almost 1 year after the initial presentation, while on 10 mg/day prednisolone and 50 mg azathioprine. Although liver biopsy during acute presentation showed a chronicity index of 3/6, more recent transient elastography values range from 20.2 to 15.1 kPa (1 month and 1 year after biochemical remission, respectively) and she presents fluctuating mild thrombocytopenia (with no varices on upper endoscopy), suggesting the development of compensated advanced chronic liver disease [13]. At the time of publication (2 years after the initial presentation), the patient remains in bio-chemical remission with 7.5 mg/day of prednisolone and 50 mg/day of azathioprine.
Conclusion
Our three reports (Table 1) are different manifestations from a same spectrum of autoimmune liver diseases, all arising in patients with HIV infection. The first case has the particularity of bezafibrate success after UDCA incomplete response in a patient with PBC with features of AIH, with the concern of unknown drug interactions between ART and the currently recommended second-line drug, obeticholic acid. The second case has additional immunosuppression concerns, since HIV diagnosis was made during a disseminated cytomegalovirus work-up and due to the advanced liver disease. Moreover, the use of isoniazid for latent tuberculosis adds further complexity to AIH management, since multiple potential causes for elevated liver enzymes can be present (AIH, azathioprine, or isoniazidinduced hepatotoxicity). The third case, which had a severe acute presentation with acute liver injury, occurred after our experience with the first 2 cases. This not only led to a more straightforward diagnosis, but also allowed for greater confidence when starting immunosuppression. The authors point out that the second patient maintained CD4+ lymphocyte counts > 200 cells/μL and the first and third patient >400 cells/μL, with negative HIV viral load during immunosuppressive treatment, and no prophylactic treatment for opportunist infections was needed. No adverse events related to either UDCA, bezafibrate, prednisolone, or azathioprine were reported during follow-up, including infectious complications - Table 1.
With this case series, we also emphasize the importance of liver biopsy, given the extensive differential diagnosis in patients with liver function test abnormalities and an HIV infection, as previously mentioned. To con clude, in an era of generalization of ART therapy, it is important to remain alert to these increasingly incident autoimmune entities and their diagnostic and therapeutic challenges.