Introduction
Endoscopic full-thickness resection (EFTR) is an emerging minimally invasive endoscopic technique to resect complex colorectal lesions. As opposed to endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) or endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) which are limited to the mucosal and submucosal layers, EFTR may offer an en bloc transmural resection, avoiding the need for invasive surgery [1, 2].
The main indications for EFTR are non-lifting lesions, lesions at difficult locations such as near the appendicular orifice or diverticula, and small subepithelial lesions. Non-lifting lesions may include early colorectal cancer and recurrent lesions [1, 3].
Currently, a wide variety of EFTR approaches are available, including free-hand, device-assisted, exposed, and nonexposed techniques. Additionally, hybrid techniques may combine EFTR with traction, EMR or ESD methods [4].
This study focuses on nonexposed device-assisted EFTR. The full-thickness resection device (FTRD) by Ovesco Endoscopy AG (Tübingen, Germany) provides a single-step and close-then-cut transmural resection, after deployment of an over-the-scope clip. Although the drawback of FTRD is a limited resection size (≤3 cm), an even more restrictive cutoff (≤2 cm) has been associated with higher R0/curative rates and less adverse events [5-8].
Overall, the EFTR technique seems efficient with a technical success rate of 89% and R0 resection rate of 79%, however, with a not negligible procedure-associated adverse events rate of 12% and a recurrence rate of 8-12%. Nevertheless, the main advantage of this technique is that it can be used to nonsurgically resect complex lesions, which are not approachable or very difficult to resect by other endoscopic techniques due to location, deep invasion, or fibrosis [8, 9].
This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and adverse events of colorectal EFTR practiced in nine Portuguese centers. Additionally, it intends to compare the Portuguese experience with previous published literature.
Materials and Methods
Study Design
This was a multicenter retrospective study. Consecutive patients undergoing colorectal EFTR in nine Portuguese centers from March 2017 to September 2023 were included. A total of 129 colorectal EFTR were registered. All patients were informed about the risks and benefits of EFTR and provided written informed consent. Patient clinical data, follow-up exams, and consultations were obtained from their electronic medical records. Outcomes included technical success, R0 and curative resection rates, early and late adverse events, disease recurrence, need for additional endoscopic management, surgery, or adjuvant chemoradiation therapy, and disease-related mortality.
Inclusion Criteria
Consecutive patients submitted to therapeutic or diagnostic colorectal EFTR in the participating centers, from March 2017 to September 2023, were included.
EFTR Procedure
EFTR procedures were performed by different experienced therapeutic endoscopists in a single session, after dedicated training in the technique. Patients were under deep sedation with propofol administered by an anesthesiologist and received a single dose of intravenous antibiotics peri-intervention, according to local guidance (e.g., ceftriaxone 2 g). Lesions were routinely analyzed by white light and virtual chromoendoscopy with narrow band imaging or blue laser imaging to detect endoscopic evidence of submucosal invasion. FTRD (Ovesco Endoscopy AG, Germany) and CO2 insufflation were used. Endoscopic reports included description of lesions and procedures. All patients stayed hospitalized for clinical surveillance according to each center protocol. Follow-up bloodwork or exams were requested if suspicion of complications.
Histopathology Assessment
Resected specimens were pinned down with needles, measured, fixed in 4% neutral buffered formalin, and sent to the pathology department of each center. Pathology reports included dimension, type of neoplasm, invasion depth, involvement of margins, budding and lymphovascular invasion (when applicable). High-grade dysplasia and intramucosal carcinoma were considered synonyms.
Definitions
Procedural issues were defined as unreachable lesion, inability to incorporate lesion in the cap, or colonic perforation because of introduction of the FTRD. Technical issues were defined as snare or clip dysfunction. Hybrid procedures were defined as EFTR completed by another technique such as EMR or ESD. Technical success was considered when EFTR was macroscopically complete without fragmentation of the target lesion. En bloc resection implied removal of the entire lesion in a single piece. R0 resection referred to tumor-free horizontal and vertical margins on histology. Adenoma or adenocarcinoma resections were classified as curative or noncurative with high/local-risk recurrence according to the updated ESGE criteria [10]. Subepithelial lesion resections were considered curative if R0 resection was achieved. Adverse events included early or delayed perforation, bleeding, and appendicitis. Intraprocedural perforation was defined as an injured muscle layer with peritoneal cavity or fat tissue visualization not closed by the clip from the device. Delayed perforation was defined as clinically manifested perforation with imaging studies documenting collections and/or free intraperitoneal air. Intraprocedural bleeding was considered if bleeding dictated need for procedural change (with endoscopic therapy) or >5 min for its control during the procedure.
Major bleeding implied clinical instability, need for transfusion, surgery, or radiological intervention. Delayed bleeding referred to blood loss and/or hemoglobin fall of >2 g/L in the first 30 days after procedure.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis for patient and lesions’ characteristics, outcomes and identification of risk factors related to them, was performed in Microsoft Excel (version 2023) and STATA (version 17). Continuous variables were characterized by median and interval; and categorical variables were reported as frequency and percentage. To evaluate associations between potential risk factors (location and size) and outcome variables (technical issues, curative rate, adverse events), univariate and multivariate logistic regressions were performed. p value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Patients’ Characteristics and EFTR Indications
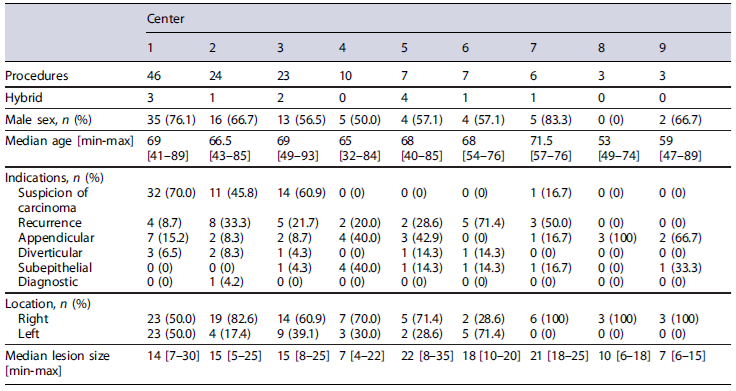
In total, 129 EFTR were registered in 9 Portuguese centers, between March 2017 and September 2023. Median patient age was 68 [32-93] years and 65.1% (n = 84) were male. Baseline characteristics of both patients and resections are presented and analyzed in Table 1. The main indications for EFTR were non-lifting sign and suspicion of early carcinoma (45.0%, n = 58), lesion recurrence not amenable for polypectomy/EMR (22.5%, n = 29), difficult anatomic locations such as the proximity to the appendicular orifice (18.6%, n = 24) or diverticula (6.2%, n = 8), subepithelial lesions (7.0%, n = 9), and diagnostic (0.8%, n = 1).
Lesions’ Characteristics
The majority of lesions were located in the right colon (64.1%, n = 82), mainly in the cecum (n =38),followedby the ascending colon (n = 25). The median resection size was 25 [10-45] mm, corresponding to a median lesion size of 15 [4-35] mm, with 17 (13.3%) lesions larger than 20 mm. Regarding their macroscopic morphology, 36.1% (n = 43/ 119) showed a depressed component and 61.1% (n = 58/95) had a non-granular appearance. On narrow-band imaging, 50.4% (n = 57/113) were classified as JNET2B or higher.
Main Outcomes
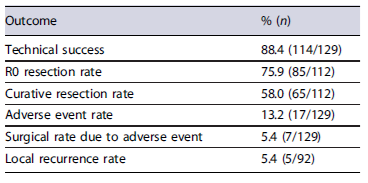
The main outcome results are listed in Table 2. The achieved technical success and R0 resection rates were 88.4% (114/129) and 75.9% (85/112), respectively, however, with an oncologic curative rate of only 58.0%(65/112). Adverse events occurred in 13.2% (17/129) of the resections, with 5.4% (7/129) needing surgery. Figure 1 describes the main study course, intercurrences impeding resection, curative intention and outcomes. Figure 2 depicts an example of a colorectal lesion excised through EFTR.

Fig. 2 Example of a colorectal EFTR. a, b Lesion observed in white light and narrow-band imaging, respectively. c EFTR device with the grasping forceps pulling the lesion into the cap. d Resection site after EFTR with the OTSC in situ.
Technique Outcomes
Procedural and technical issues were reported in 5.4%(n = 7) and 12.4% (n = 16) of cases, respectively. Procedural difficulties were mainly due to lesion not being incorporated (n =5)orachievable(n = 1) by the device. One procedure was immediately suspended due to colonic perforation before resection. EFTR was feasible in 94.6%(n = 122) of cases and hybrid in combination with EMR in 9.8% (n = 12). Technical difficulties occurred in 16 resections, 13 due to snare dysfunction and 3 due to clip dysfunction. Most were still endoscopically completed; however, 2 (1.6%) patients needed emergent surgery due to intraprocedural perforation. After excluding procedures which were aborted and those requiring emergency surgery due to intraprocedural perforations, 120 EFTRs were carried out. Overall, on an intention to treat analysis, the technical success achieved was 88.4% (114/129).
Diagnostic Procedure
The diagnostic EFTR corresponded to 1 patient with chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction syndrome, and enteric myopathy was the histological diagnosis. This procedure was excluded from the (non-)curative rates analysis.
Therapeutic Procedures and Resection Outcomes Regarding the 119 therapeutic EFTRs performed, 112 (94.1%) corresponded to lesions with malignant potential: 33 (29.5%) adenomas with low grade dysplasia, 30 (26.8%) adenomas with high grade dysplasia, 31 (27.7%) adenocarcinomas, 5 (4.5%) sessile serrated lesions without dysplasia, 3 (2.7%) sessile serrated lesions with low grade dysplasia, 6 (5.4%) neuroendocrine tumors, 1 GIST, 1 granular cell tumor, 1 hamartoma and 1 non entirely evaluated due to extensive fulguration. The remaining 7 (5.9%) suspected lesions demonstrated benign histology: 2 fibrotic tissues, 1 duplication cyst, 1 inflammatory tissue, 1 leiomyoma, 1 pseudopolyp, and 1 lymphoid tissue.
Considering resections with curative potential (n = 112), R0 was achieved in 75.9% (n = 85);, however, the achieved curative rate was 58.0% (65/112). According to ESGE criteria, resections were classified as 65 curative and 47 noncurative (10 local-risk and 37 high risk). Overall, local-risk noncurative resections were due to positive or nonevaluable horizontal margins mainly by piece fragmentation or hybrid procedures, without any other poor prognosis feature. High-risk stigmata for noncurative procedures included: invasion deeper than sm1 (n = 21), positive vertical margins (n = 16), lymphovascular (n = 14) or perineural (n = 1) invasion, and undifferentiated tumor (n = 3).
Subsequent Treatments and Follow-Up
From the 37 high-risk noncurative resections, 20 (54.1%) patients were referred to surgery (1 with additional chemoradiation) with favorable outcomes. Of these, only 6 (30.0%) demonstrated neoplastic tissue in the surgical piece and 3 already had lymph node metastasis. One patient showed systemic recurrence during follow-up and underwent chemotherapy. Five high-risk patients were not submitted to surgery due to high surgical risk comorbidities.
The remaining (n = 92) were kept under close surveillance according to protocol. During a median follow-up of 19.5 [0-61] months, 5 (5.4%) patients had local disease recurrence. Of these 60% (3/5) were previous R0, 2 were endoscopically treated and 3 were submitted to surgery, with favorable outcomes. Six patients died of non-related causes.
Adverse Events
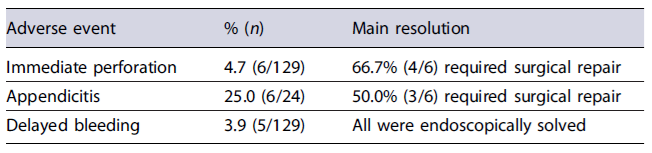
The overall rate of adverse events observed was 13.2%(17/129), being summarized in Table 3. No patient had more than 1 adverse event. There was no procedure-related mortality.
Immediate perforations occurred in 6/129 (4.7%) procedures. Of these, 5 were caused by technical or procedural issues: 1 during colonoscope introduction, 1 snare and 3 clip dysfunctions. Perforations were endoscopically closed in 50.0% of cases (3/6), mostly with an over-the-scope clip. In 1 immediate perforation, endoscopic closure was unsuccessful, the patient deteriorated and was posteriorly submitted to urgent surgery. Despite endoscopic closure in 3 patients, surgical repair was required in 66.7% (4/6) of cases. No delayed perforation (0%) was detected.
There were 24 lesions involving the appendiceal orifice. The overall rate of appendicitis was 25.0% (6/24) and 50% (n = 3) had to be managed with surgery. Conservative treatment was successful in the other half. From the available medical information, only 1 patient had previous appendicectomy and the majority was offered antibiotic prophylaxis during the procedure.
Bleeding occurred in 5/129 (3.9%), in all cases after the performed EFTR (delayed) and were managed endoscopically. Of these, only 1 patient was under anticoagulants. No luminal stenosis or post-polypectomy syndrome was detected.
Risk Factors for Poorer Outcomes
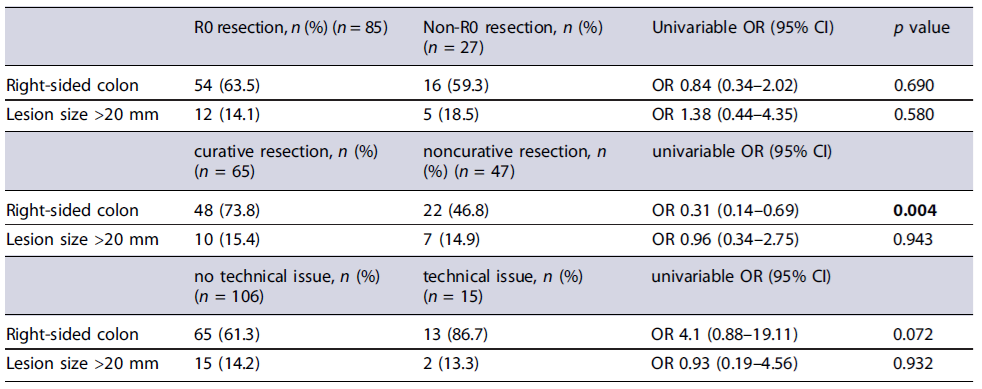
As seen in Table 4, on univariate analysis, lesion location in the right-sided colon was associated with a lower rate of noncurative resection (OR 0.31; 95% CI: 0.14-0.69; p = 0.004). Location in the right-sided colon was not significantly associated with non-R0 resection (p = 0.690), technical issues (p = 0.072), intraprocedural perforation (p = 0.348), or delayed bleeding (p = 0.069). Moreover, lesion size (>20 mm) was not associated with non-R0 (p = 0.580), noncurative resection (p = 0.943), technical issues (p = 0.932), intraprocedural perforation (NS), delayed bleeding (NS), or appendicitis (p = 0.447) (online supplementary material; for all online suppl. material, see https://doi.org/10.1159/000541642).
Discussion
Nonexposed colorectal EFTR is an established endoscopic resection technique for complex lesions not amenable to standard techniques. Previous experience demonstrates EFTR to be effective with high technical success and curative rates, and relatively low adverse events and recurrence rates. Additionally, EFTR requires less endoscopic experience, shorter procedure times, and may provide better histological and staging specimens when compared to other endoscopic resection techniques [1, 6, 8, 11, 12].
In our cohort, the overall technical success was 88.4%(114/129), which is similar to published literature. Indeed, EFTR is associated with difficulties in advancing the loaded device and incorporating the target lesion inside it. Additionally, the device may impair lesion visibility and flexibility of the endoscope tip. In our study, six procedures were impractical due to similar inconveniences. Interestingly, of these, no lesion was larger than 20 mm and only 50% (n = 3) were located in the right hemicolon [8, 9, 11].
Regarding resections with curative potential, our R0 resection rate was 75.9% (85/112), which is similar to published literature. However, our overall curative rate was only 58.0% (65/112), mainly due to the presence of one or more high-risk stigmata such as invasive adenocarcinomas staged deeper than T1 (n = 4) or with submucosal invasion deeper than sm1 (n = 10), lymphovascular (n =7)or perineural (n = 1) invasion, budding higher than grade 1 (n = 3) and histological undifferentiation (n = 1). Considering that not all features have the same significance and that isolated submucosal invasion >1,000 µm and peri-neural invasion have not yet been proven to be consistent independent risk factors, one might consider resections with only one of these high-risk stigmata (n =7)tobe curative. Indeed, 3 patients underwent surgery and did not have evidence of malignancy in the surgical specimen, and none were diagnosed with local or systemic disease recurrence during follow-up. This would have increased our curative resection rate to 64.3% (72/112) [8-11].
On statistical analysis, lesion size >20 mm did not influence technical success, R0 nor curative rate, which is discordant with published evidence which suggests R0 resection rates in these cases of 58.1%. Additionally, lesion location in the left-sided colon and rectum seemed to predict a higher noncurative resection rate, not influencing other outcomes. In fact, the result from our study is concordant with previous literature since the thicker and more rigid rectal wall seems to hamper resection [11-15].
With regard to adverse events, our cohort showed an overall adverse event rate of 13.2% (17/129) with a 3.1% (4/ 129) rate of emergency surgery for perforations, which is in line with previously published studies. The highest number of adverse events was from immediate perforations (4.7%), the majority requiring emergent surgical management. Bleeding occurred in 3.9% (5/129) of patients, all of which as delayed, which were all managed endoscopically, and were not associated with antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapy [1, 8, 9, 11].
Acute appendicitis is a known complication for the excision of appendicular lesions, and are conservatively dealt with in most cases. In our cohort, the overall appendicitis rate was higher than the previously reported rates (25.0% vs. 9.9-17.0%); however, half of them were still conservatively treated with success rates similar to those in previously published studies. Although no risk factors have been identified for the development of appendicitis, most patients received intravenous antibiotics peri-procedure and had no previous history of appendectomy as in literature. It has been suggested that EMR or hybrid techniques can overcome this inconvenience [1, 16-19].
On our analysis, no risk factor was associated with the development of adverse events. In fact, previous studies are concordant regarding lesion size not affecting them. Nevertheless, perforation has been slightly more associ-ated with left-sided resections and some centers even suggest the use of prophylactic laxative therapy to avoid it [1].
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first multi-centric study describing the Portuguese experience on colorectal EFTR. Its strengths lie on the multicentric nature of the work. However, some limitations include its retrospective nature and modest sample size, the heterogeneity in volume, indications for EFTR, gastroenterologists and pathologists’ performances among centers, the absence of a centralized assessment of outcomes, and the nonavailability of complete registry data in all patients. Future studies, namely prospective or randomized controlled trials, could enhance this area of study and compare different therapeutic endoscopic techniques in these complex contexts. In conclusion, this real-life multicenter study highlights the utility of colo-rectal EFTR for the management of complex and carefully chosen lesions, with an acceptable adverse events rate and need for surgery.