Introduction
Cutaneous angiosarcomas are rare and quite aggressive tumors that originate from the cells of the blood or lymphatic vascular endothelium. The incidence is higher in elderly men and Caucasians1. Risk factors include radiation, chemical exposure to arsenic, and previous history of chronic lymphedema2.
Epidemiologically, they represent less than 1% of all malignant neoplasms in the head and neck. In addition, angiosarcomas are described in the literature in other anatomical regions, such as the liver, spleen, bones, and heart1.
Regarding morphology, they can present as a papule, macula, plaque, or nodule of imprecise limits and variable extension, and hemorrhagic or necrotizing surface. The possibility of resection, presence of metastases, degree of differentiation, and lesion extension are very important prognostic factors3.
We report a case of angiosarcoma of the scalp, emphasizing the importance of considering it as one of the differential diagnoses in elderly patients since early diagnosis allows an extremely favorable outcome.
Therefore, the objective of this case report is to describe the appearance of angiosarcoma on the scalp of a patient who was being followed up after the excision of nasal basal cell carcinoma. It also aims to perform a literature review on angiosarcoma, approaching its pathophysiology, epidemiological aspects, clinical manifestations, both typical and atypical, and treatment.
Clinical case
A 90-year-old Caucasian male patient, with a history of controlled asthma, presented to a medical consult in October 2020 for the investigation of a rapidly growing lesion on the left nasal wing, measuring 2 cm. Biopsy confirmed basal cell carcinoma. The tumor was surgically removed, and the area was reconstructed. At the time, his medications included turmeric, paracetamol, vitamin B complex (B1, B6, B12), vitamin D, amlodipine, and inhaling fluticasone.
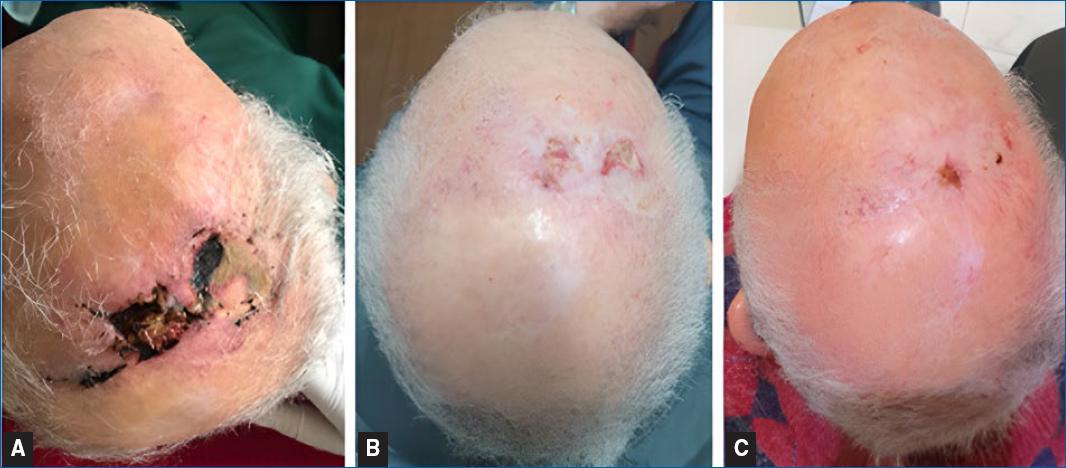
In July 2021, he returned for a follow-up and an investigation of new skin lesions on the scalp. There were changes to his pharmacological therapy, with the removal of the vitamin B complex and turmeric, and the addition of apixaban. Physical examination revealed the presence of two erythematous and infiltrative tumors, named “larger” and “smaller” lesions (Figure 1).
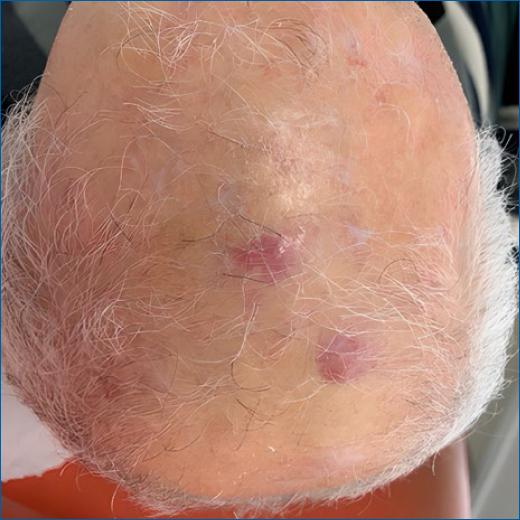
Figure 1 Erythematous lesions on the scalp measuring the largest 3.1 × 2.0 cm and the smallest 2.0 × 1.7 cm.
Incisional biopsies of the lesions suggested a poorly differentiated neoplasm infiltrating the dermis. The patient was then submitted to surgical resection of the lesions, and reconstruction was performed with a left iliac fossa skin graft and rotation flap, and 2nd intention healing area.
Gross anatomopathological evaluation of the surgical specimen showed two contiguous, whitish, elevated, and ill-defined lesions, with 3.1 × 2.0 cm with a maximum thickness of 0.6 cm, and 2.0 × 1.7 cm with a maximum thickness of 0.4 cm. Both were 0.5 cm distant from the radial margin. Microscopic examination revealed a poorly differentiated invasive neoplasm involving the dermis and muscle fascia. The architectural pattern was solid, and there were numerous mitotic figures (Figure 2) and moderate peritumoral lymphocytic infiltrate. Deep and radial surgical margins were clear. The immunohistochemical study, including antibodies for the differential diagnosis between carcinoma, melanoma, and angiosarcoma, confirmed the vascular lineage markers cluster of differentiation 31 (CD31), CD34, D2-40, and friend leukemia integration 1 transcription factor (FLI-1) (Figure 3). Other markers for epithelial and melanocytic lineages were negative. The final diagnosis was high-grade angiosarcoma.

Figures 2 Histopathological characteristics of the neoplasm. A: small magnification, showing the neoplasm occupying dermis (40×, H&E). B: atypical cells with permeating lymphocytes (100×, H&E). C: detail showing nuclear pleomorphism and mitotic figures (400×, H&E).
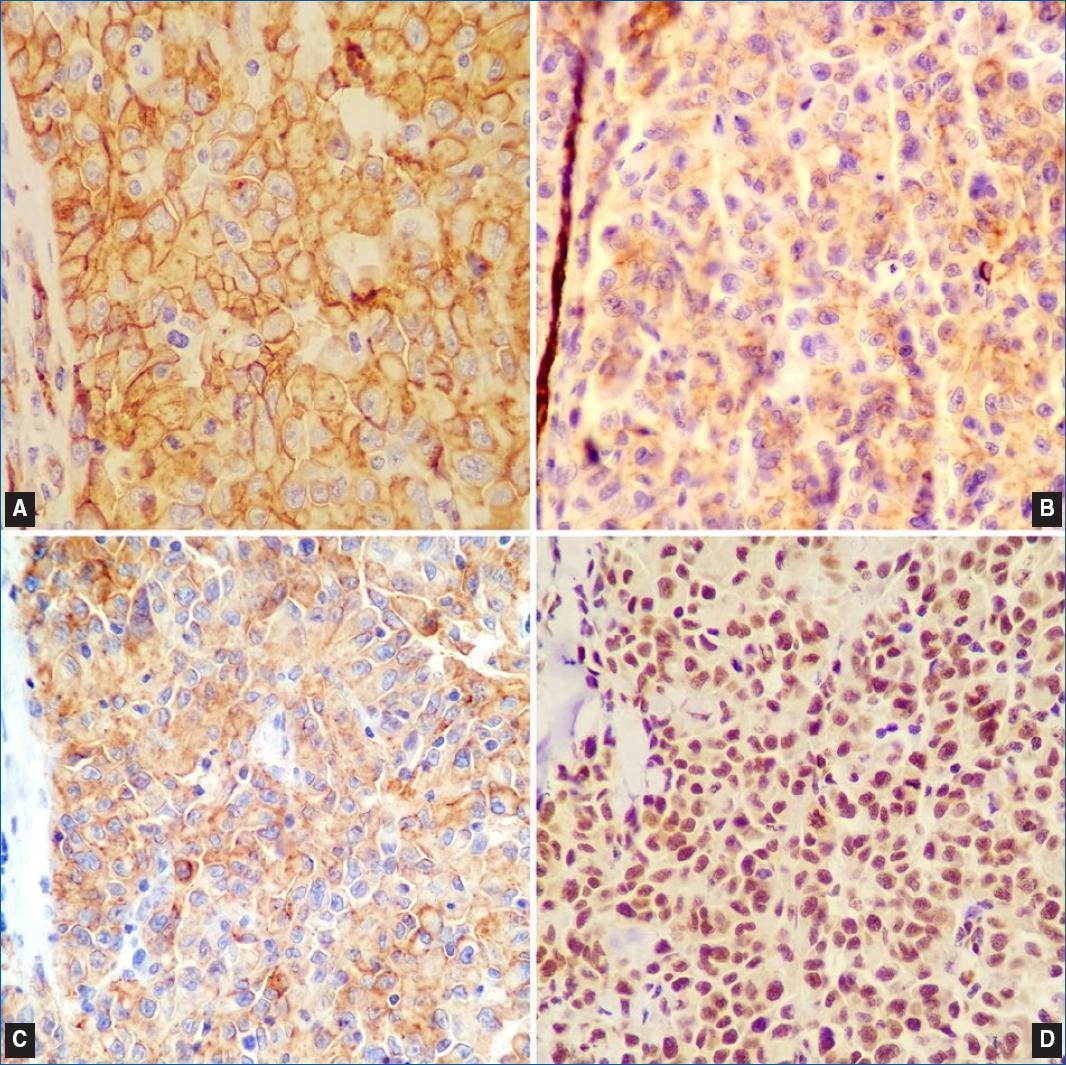
Figures 3 Immunohistochemical characteristics of the neoplasm (100×, IHC). Positivity in neoplastic cells for the markers. A: CD34. B: CD31. C: D2-40. D: FLI-1.
In the immediate postoperative period, the patient presented partial necrosis of the graft. However, approximately one month after the removal of the lesions, the patient was reassessed and the surgical wound was in the process of healing, with no signs of necrosis or infection. The patient underwent ten sessions of adjuvant radiotherapy and was discharged (Figure 4). By the end of the treatment, the patient developed metastatic lesions in the trunk and died soon after.
Discussion
Primary cutaneous angiosarcoma is the main form of angiosarcoma, which evolves rapidly, and the main affected sites are the scalp and face, the latter being considered the most aggressive topography4.
Epidemiologically, in angiosarcomas overall, there is no significant prevalence difference between men and women4, however, when located on the scalp, the prevalence is higher in elderly Caucasian men, as seen in the reported case5.
Although still much debated, the main hypothesis for the origin of this neoplasm is the endothelium of smaller blood or lymphatic vessels or their progenitor cells6. Rarely do these tumors arise from large vessels5. Radiotherapy and chronic lymphedema are known risk factors6.
Macroscopically, the lesion is poorly delimited, and can present in different morphologies-areas of sub- cutaneous hematoma, bluish macules, peripheral erythematous ring and satellite nodules, as reddish, raised papules7 or as flat, infiltrative plaques5. In more advanced stages, lesions can be elevated, nodular, and ulcerated5. It has irregular growth and may acquire a multicentric appearance, containing bluish plaques, and nodules within4. It tends to bleed spontaneously or due to minimal trauma4,5.
Microscopically, they are poorly differentiated and can compromise the dermis and soft tissues5. From the morphological point of view, they can be classified as low or high-grade lesions. Low-grade angiosarcomas are described as neoplasms of atypical endothelial cells arranged in single or multiple layers, while high-grade angiosarcomas are described as neoplasms of undifferentiated and pleomorphic cells, with disorganized architecture, high mitotic index, and foci of hemorrhage and necrosis4,5. The final diagnosis requires immunohistochemistry studies, especially in high- grade neoplasia, with positivity for endothelial markers such as D2-40, CD31, CD34, and FLI-18, as in the reported case4,9.
The prognosis of the neoplasm is poor3,5,6. The survival rate is directly associated with patient age, lesion site, and disease stage7. Factors favoring a better prognosis would be lesions in smaller quantity and size, younger patients, and clear surgical margins5.
The most effective form of treatment is surgical resection, despite the high recurrence rate and difficulty in achieving free surgical margins4,5. Multimodal therapy requires an assessment of the age and the general clinical condition of the patient. Chemotherapy is used in patients with incomplete surgical resection or with distant metastasis, such as lungs, liver, spleen, and cervical lymph nodes4,6,10.
Radiotherapy is also a viable treatment option, and patients who received it as a form of therapy had a median survival rate four times higher when compared to those who did not use this approach5.
The combination of surgery and radiotherapy can be associated with a better prognosis when combined with the previously mentioned factors, but only if applied to lesions smaller than 5 cm in diameter5.
Scalp cutaneous angiosarcoma is the most aggressive form of this neoplasm, affecting mostly elderly Caucasian men. Its main treatment is surgery, which can be complemented with adjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy, or both. Despite its rarity, angiosarcoma cannot be ignored as a potential diagnosis since the microscopy is very variable and may mimic other neoplasms such as other sarcomas, melanoma, and carcinomas, which highlights the importance of considering a broad spectrum in the differential diagnosis.