Introduction
Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis is a rare entity that clinically and radiologically mimics breast cancer. Rarely associated with pregnancy, this clinical case shows the importance of thinking about this condition in order to avoid unnecessary conduct associated with the most frequent cancer in women.
Case report
A 23-year-old female, without relevant personal and family history, G3, P1,A1 (normal delivery 2 years ago, breastfeed for 6 months).
She goes to the emergency room, 38 weeks pregnant, for diffuse pain in the right breast with 1 month of evolution associated with an increasing lump. On examination, the superior-external quadrant of the right breast showed a painful swelling associated with edema, heat and redness, for which she was medicated empirically with amoxicillin + clavulanic acid for seven days, without clinical improvement. On the next day, after medical appointment, she started a new scheme with clindamycin.
One week after starting treatment with clindamycin, the breast lesion worsens, this time showing a fluctuation zone. We decided to perform a surgical drainage, after two weeks of starting antibiotic therapy, in the operating room of the emergency unit. When draining the abscess, purulent content with a foul odor emerges in abundance.
The pregnant woman remained always apyretic, with negative inflammatory parameters (leucocytes and C-reactive protein). The culture of the exudate drained was negative for aerobic, anaerobic microorganisms, as well fungal culture.
At the breast specialist appointment, she presented a persistent thickening of the right breast’s upper outer quadrant associated with inflammatory skin lesions (Figure 1). Pouch and Trucut biopsies were performed. Meanwhile, corticosteroid therapy was started with prednisolone 40 mg per day due to a presumptive diagnosis of an Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis.

Figure 1 Right breast with persistent thickening of the upper outer quadrant associated with inflammatory skin lesions
The breast echography showed a subcutaneous collection with a small depth trajectory.
The histological results confirmed the diagnosis of Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis (Figure 2), and the following therapeutic regimen of corticosteroid therapy was proposed to the patient: 60 mg/day 2 months, 50 mg/day 1 month, 40 mg/day 1 month, 30 mg/ day 1 month, 20 mg/day 1 month, 10 mg/day 2 months; due to persistence of the slurry of the breast, azathioprine 50 mg 12/12h was associated after two weeks.
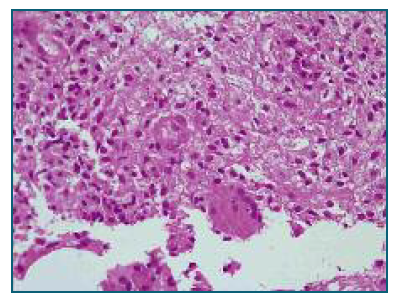
Figure 2 Breast fragments consisting of adipose tissue. There is an inflammatory process with epithelioid granulomas. The inflammatory infiltrate consists of lymphocytes, plasma cells, some polymorphonuclear cells and histiocytes. PASD and Ziehl Neelsen stains and AE1/AE3 immunohistochemistry were negative.
After improvement of the skin lesions and the swelling of the right breast, one month of the beginning of corticoid therapy, the patient decided to stop the corticoid and immunosuppressive sparing therapy, with the swelling worsening within 1 week.
The corticosteroid therapy was restarted with complete resolution of symptoms after 6 months. Currently, about 2 years later, she had another pregnancy and remains asymptomatic.
Discussion
Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis is a rare entity that mimics breast cancer, whose etiology, incidence and treatment are yet to be defined.
First described by Kessler and Wolloch in 1972, one of the possible etiologies of this disease is an inflammatory response to milk proteins and lipids, having a strong correlation with pregnancy and lactation. In opposite of this case, this condition rarely happens in pregnancy, being more usual 6 months to 2 years after breastfeeding1.
Other causes have been proposed for this entity: autoimmune disease, oral contraceptives, trauma, infection, diabetes, smoking, hyperprolactinemia, and alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency1.
Although its incidence is unknown, it affects mostly women of childbearing age, which contrasts with breast cancer, whose peak age is later2.
As in the present case, it manifests as a swelling, which may be accompanied by pain and other inflammatory signs, skin changes and adenopathies, making the differential diagnosis with breast cancer mandatory, namely inflammatory breast carcinoma3.
The echographic findings were benign in this clinical case, however it is usual to manifest as a mass with irregular shape and contour, also making the differential diagnosis with breast cancer difficult. (2
The gold standard method for diagnosis is the histology diagnosis4.
Diagnosis is made by the histological pattern of breast lobes surrounded by granulomatous inflammation without caseous necrosis, excluding: Brucellosis, Bartonella, tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, Wegener’s granulomatosis, fungal infections1),(5,6.
The treatment, also non-consensual, can be medical and/or surgical. Surgical treatment consists of abscess drainage and even excision of the affected area. Medical treatment involves the use of antibiotics and immunosuppressive therapy, corticosteroids and antimetabolites such as azathioprine and methotrexate. Corticosteroids in high doses (60 mg with progressive decrease) for periods of 3 to 6 months are recommended6 - the present case reflects the need to maintain immunosuppressive therapy in order to avoid relapses.
The simultaneous existence of breast carcinoma and granulomatous mastitis is rare, with only about 5 published cases in the literature where these two entities coexist4.
Finally, knowledge of this disease is essential: its timely diagnosis avoids unnecessary costs and improves the patient’s approach.
Patient has given informed consent for publication of this clinical information and related pictures.















