Apresentação de Tese “Vir sapiens dominabitur astris”. Astrological knowledge and practices in the Portuguese medieval court (King João I to King Afonso V).
Dissertação de Mestrado apresentada à Faculdade de Ciências Sociais e Humanas da Universidade da Universidade Nova de Lisboa em 2011. Orientação da Professora Doutora Maria de Lurdes Rosa e do Professor Doutor Kocku von Stuckrad.
This study addresses the practice of astrology and its cultural repercussions in the 14th and 15th century Portuguese court.
It is based in the comparative study of three sets of sources: 1) the astrology books from the royal libraries, which reveal the dominant concepts of astrology; 2) the writings of kings João I and Duarte, and prince Pedro, as examples of the practical application of these concepts; 3) the royal chronicles of Fernão Lopes; Gomes Eanes de Zurara and Rui de Pina. The comparative study of the astrological references in these three sets of sources allows a better understanding of the role of astrology and its cultural repercussions in the Portuguese medieval court.
The topic of astrology is addressed as a cultural practice within the Portuguese medieval court in the 14th and 15th centuries. The acknowledgment of this practice as a structural factor in medieval culture, as well as the correct understanding of the astrological system per se, allows a deeper knowledge of the medieval culture and mentalities.
Structure
Part I presents a survey on the existing studies on medieval astrology. This study revealed that the Portuguese historians seldom approach medieval astrology from the perspective of the History of Culture. When they do, most of them present it in a dismissive and unfavourable fashion, as an example of “medieval superstitious belief”, which was swiftly replaced by rational thought. Quite often, the references to astrology serve only to enhance the “improvements” and the “rationality” of the Renaissance thought. Nevertheless, there are a few relevant studies on the practice of astrology from the cultural perspective.
Part II offers a brief explanation on the foundations of medieval astrology. Astrology reveals itself as a complex body of knowledge, with specific rules and methods. Its principles were based on the natural movement of the celestial bodies: the rising and setting of the Sun, the sequence of the seasons, the phases of the Moon. These natural movements (which were apprehended by direct observation), were then correlated through the principle of analogy to events on Earth - whether these events are natural, social or personal. Astrology required good intellectual skills and a high level of education; it was practiced by court physicians and other learned man, as it is exemplified by the Negro Family. It was thus a sophisticated field of knowledge, far removed from superstition, divination and witchcraft.
Part III explores the astrological books from the royal libraries and on the writings of the royal House of Avis. Through the analyses of these works, we came to the conclusion that they reveal a surprising degree of astrological knowledge within the royal family and, by extension, in the royal court. Astrology is often referred to in their works, whether in “scientific” and philosophical discussions, or in more colloquial contexts. The relevance of astrology in medieval thought can be attested by the significant number of books and writings on the topic, the variety of arguments and perspectives surrounding it, and above all by the heated debates originated by these differences.
The authors chosen for the main research known to be available in 15th century Portugal: Claudius Ptolemy (Tetrabiblos1), Ali ben Ragel (El Libro ccumplido de los iudicios de las estrellas2), Abraham Zacuto (Almanach Perpetuum and Tratado Breve de las Ynfluencias del Cielo3). Also studied, though in lesser extent, are John of Hollywood (De Sphera4), Pseudo-Aristotle (Segredo dos Segredos5), Abraham ben Ezra (Beginning of Wisdom and Libro de los Juicios de las Estrellas6) and Egidio de Collona (Regimine Principum7).
As to the writings of the princes of Avis, we focused on the astrological references contained within the books written by King João I (Livro da Montaria8) and king Duarte (Leal Conselheiro and Livro dos conselhos de D. Duarte - Livro da Cartuxa9).
Example: A poem with astrological references (Duarte, Livro dos Conselhos, p. 157)
Talking about O que tomamos da Terra (What we seize from the Earth) king Duarte mentions several factors, which can contribute to personal traits:
Da terra compreison
Do leyte e viandas criaçom
Dos parentes Naçom
Das doenças e acontecimentos occasiom
Dos planetas constellaçom
Do senhor e amigos conuersação
De noso senhor deus per especial Jnspiração nos he outorgada condiçom e discreçom
Daquesto se deue tomar non falando da especial graça de noso senhor que per sy so faz mudar todas condições e discreções que cada hua per sy non he tam poderosa que das outras partes non receba torva ou ajuda.
(From the Earth [we seize] complexion / From milk and meat, sustenance / From relatives, nation / From illness and happenings, occasion / From the planets, constellation / From the sovereign and [from] friends, conversation / From our lord God, by special inspiration, it is conceded upon to us [social] condition and discretion. Of these things one must seize, not to mention the special grace for our lord who, by himself, causes all conditions and discretions to change, as each by itself is not as powerful that, from the others, it would not receive hindrance or assistance.)
Part IV presents a study of the the astrological references in the chronicles of Fernão Lopes, Gomes Eanes de Zurara and Rui de Pina. These chronicles offer several examples of the practical applications of astrology, and again confirm its pervasiveness in the Portuguese medieval culture.
Three main topics emerge from the astrological references in the chronicles: the validation of power, the explanation of manners and temperament of kings and noblemen, and the on-going (and heated) debate on determinism versus free will.
It also becomes apparent that the astrological arguments were used to support military decisions (as the conquest of Ceuta) and to provide guidance in crucial moments (as in the coronation of a king). In a more personal perspective, these arguments could also explain (and sometimes excuse) the manners, habits and decisions of noblemen, kings and princes.
Example: Astrological reasons presented as an excuse to personal flaws (Zurara, Gomes Eanes de, Crónica de Dom Duarte de Meneses, ed. Larry King, Lisboa, Universidade nova de Lisboa, 1978, pp. 64-67).
In the biography of Count Pedro de Meneses (1370-1432), governor of Ceuta, Zurara mentions one of his flaws - inconstancy - and relates it to astrological factors.
After many years governing Ceuta, Count Pedro travelled back to the kingdom of Portugal and transferred the government of the city to his son, Duarte (1414-1464). Before his departure, he promised Duarte that he would grant him the government of Vila Real (a city in Algarve). But this promise was soon to be broken. In Portugal, his older daughter, Beatriz, persuaded him to give Vila Real to her husband. Count Pedro promptly indulged his daughter’s plea, forgetting the promise he had made to Duarte.
The chronicler explains this lack of coherence by several factors: the influence of master Josepe (Beatriz’s Jewish physician), the advanced age of count Pedro (which made him easier to persuade), and his astrological inclination. Of the latter, he states “a natureza daquelle conde que era de mudauees propositos ca nacera em signo de dous corpos na triplicidade do fogo” (the nature of that count was of changeable purposes, for he was born in a sign of two bodies in the triplicity of fire). According to Ptolemy, the signs of two bodies are “Gemini, Virgo, Sagittarius, and Pisces”. As to the triplicity of fire, Ali ben Ragel states that it assembles “Aries, Leo and Sagittarius”. This is also confirmed by Abraham Zacuto: “Los communes y de dous querpos son geminis. virgo. sagitarius picis” (the common [signs] and of two bodies are Gemini, Virgo, Sagittatius and Pisces) and “aries. y leo. y sagitario son del fuego” (Aries, and Leo and Sagittarius are of the fire [element]). By crossing these references, it becomes clear that only one sign - Sagittarius - assembles both qualities: two bodies and fire.
As to the correlation between the astrological attributes and character traits, it can also be found in these authors. Ptolemy claims that “the bicorporeal signs make souls complex, changeable (…) unstable, fickle (…) prone to change their minds”, and Ali ben Ragel echoes his words: “los signos comunales fazen los espiritos convertibles que’s camian por que quiere e non se afirman en ninguna cousa, de diuersos asmamientos e non lo puede onme saber siesto de sos mannas (…)” (the common [or bicorporeal] signs make the spirits voluble and [causes them to] vary according to their whim and they are not steady in any matter, [they are] of diverse states of mind, and no one can know for certain their ways).
The term was born in a sign may refer not to a given period of the year (namely when the Sun is in Sagittarius - between the end of November and December), but to a specific hour of the day, when the sign of Sagittarius was rising (that is, when Sagittarius was the ascendant sign). If so, this means the chronicler knew the birth date and time - and therefore the astrological chart - of count Pedro de Meneses.
So, Zurara says that Sagittarius inclined count Pedro to be changeable; his inconstancy, therefore, was not entirely his fault, but an expression of his natural inclination.
From the comparative study of the astrological references in these three sets of sources - books, personal writings and royal chronicles - arises a better understanding of the role of astrology and its cultural repercussions in the Portuguese medieval court. Its relevance in medieval thought can also be attested by the significant number of books and writings on the topic, the variety of arguments and perspectives surrounding it - and the heated debates originated by these differences. Its presence in medieval thought is also attested by the frequent inclusion of astrological references into all sorts of conversations.
This study offers a rich contribution to the history of medieval society, culture and mentalities. It contributes to a better understanding of the medieval concept of the world, and its impact on religion, philosophical thought and practical life. Astrology is also a good example of the transmission of knowledge from the Classical sources to the Christian world, intermediated by the Islamic and Jewish cultures.
It also offers important information to the study of Social History, as the astrological medieval texts reflect the main concerns of society: the questions posed to the astrologers, and the respective answers offer a rich field of study. In a different perspective, the study of astrological calculation and instruments can also complement the History of Science and Technology.
Conclusions
Astrology was a cultured and courtly practice, and the astrological concepts and practices had wide participation in court life. It was considered a natural part of life. The astrological system offered a complete and functional description of the medieval cosmos. The astrological practice provided the natural integration between medicine, philosophy, culture and religion.
In sum, astrology was not a separate subject, it was deeply embedded in the fabric of medieval thought; to extract the astrological thread is to mutilate this fabric. The importance of astrological factors both in political decisions and in private life must therefore be underscored.
The most relevant finding of this research was the vibrant exchanges - in the cultural, scientific and religious fields - surrounding the debate of fate-versus-free will. Among cultured practitioners, this on-going discussion divided opinions and aroused heated arguments. But contrary to what could be expected, the fracture does not occur between those who passively submit to fate (that is, the determinists), and those who proclaim the supremacy of free will (the “free spirits”). The real division takes place between those capable of balancing these two instances (determinism and free will) in a practical concept of life, and those who consider them as mutually exclusive and therefore impossible to reconcile; the latter find it difficult to conciliate the practice of astrology with the Christian faith.
Throughout all these debates, it must be noted that the validity of astrology in itself is never in question. It is fully accepted by all authors (Duarte included) that astrology is functional (although not all of them agree on the causes and extent of this functionality). What is in debate are its limits (the extent of determinism and the extent of free will allowed to each individual) and, above all, its validity in face of the Church. The unsettling question arising from this debate is, as king Duarte puts it, “if all is constrained [by the stars], by our achievements we would have neither reward nor punishment”. The answer, quite ironically, had already been given two centuries before by Jewish mysticism - there is no conflict, as the “fear of the Lord” (that is, piety) is in the very core of wisdom.
The topics presented in this work are just a few of many possible lines of study. It is one of its goals to call the historians’ attention to this interesting topic in Portuguese historiography and to point out the many possibilities of research, which may be developed in future studies.
As possible lines of research:
- Astrology as a common ground for discussion between the three main religious groups in the Iberian Peninsula: Christians, Muslims and Jews. Much still remains to be explored regarding the role of the Jewish scholars as pivotal elements in the transmission of astrological knowledge, particularly in Portugal. From this investigation may also arise a comparative study of the astrological practice in different cultural contexts.
- Astrology as a vehicle of different philosophical lines of thought (Aristotelian, Stoic, Neoplatonic, etc.). The attitude of the astrologer towards determinism and prediction is shaped by his philosophical affiliation. A thorough study on this matter should offer many interesting perspectives.
- Astrology as a reflection of society. The study of the contents of certain books on astrology - namely the extensive work of Ali ben Ragel on interrogations - offers a vast field of research into the habits, concerns and practices of medieval society. This study could bring important contributions to the History of Culture and Mentalities.
- Astrology and social groups. A comprehensive study of the astrological practices among the different social strata still awaits future investigation; from the cultured courtesans, depicted in this work, to the common people, there are a number of nuances to the astrological practice, yet to explore.
Appendix
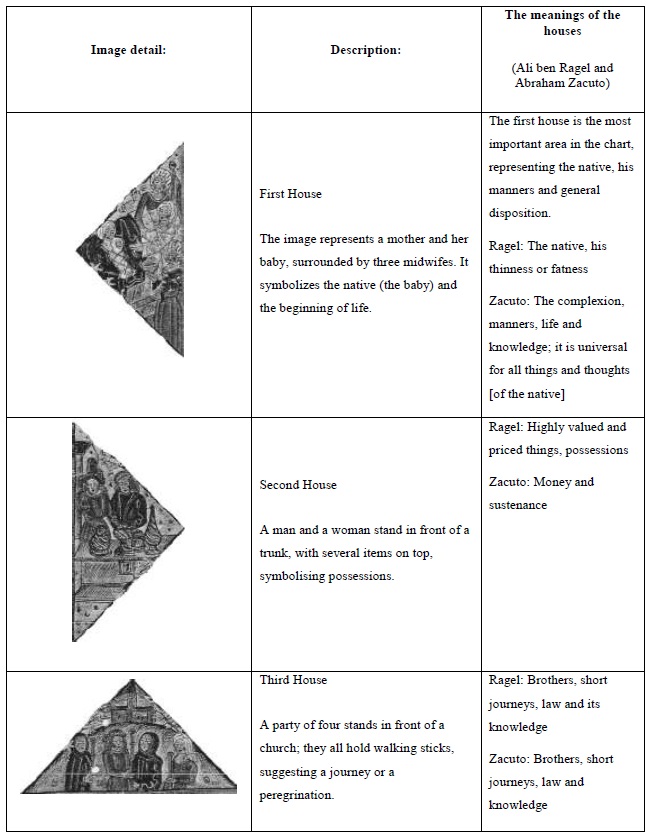
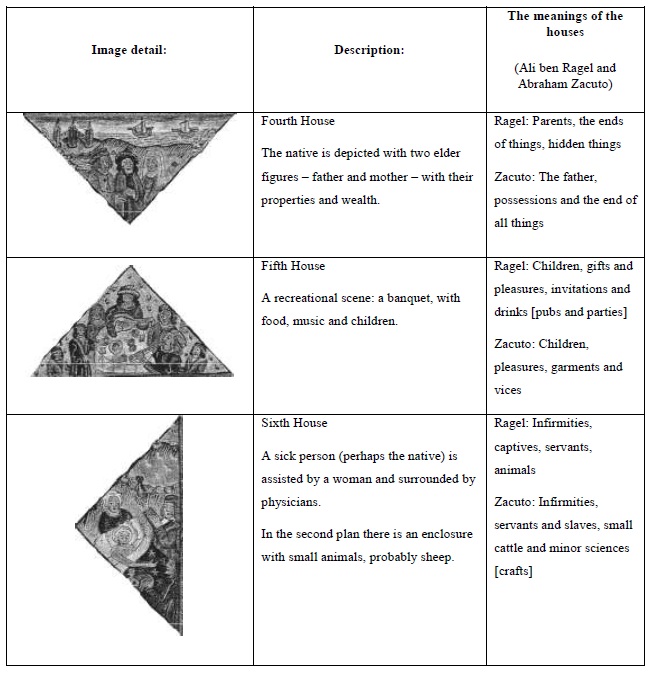
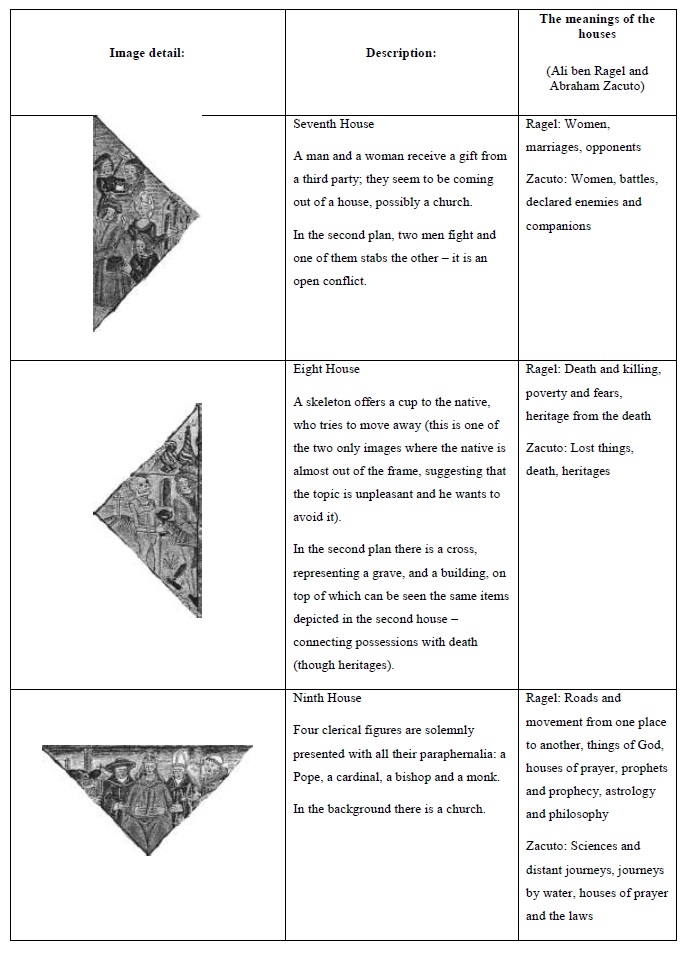
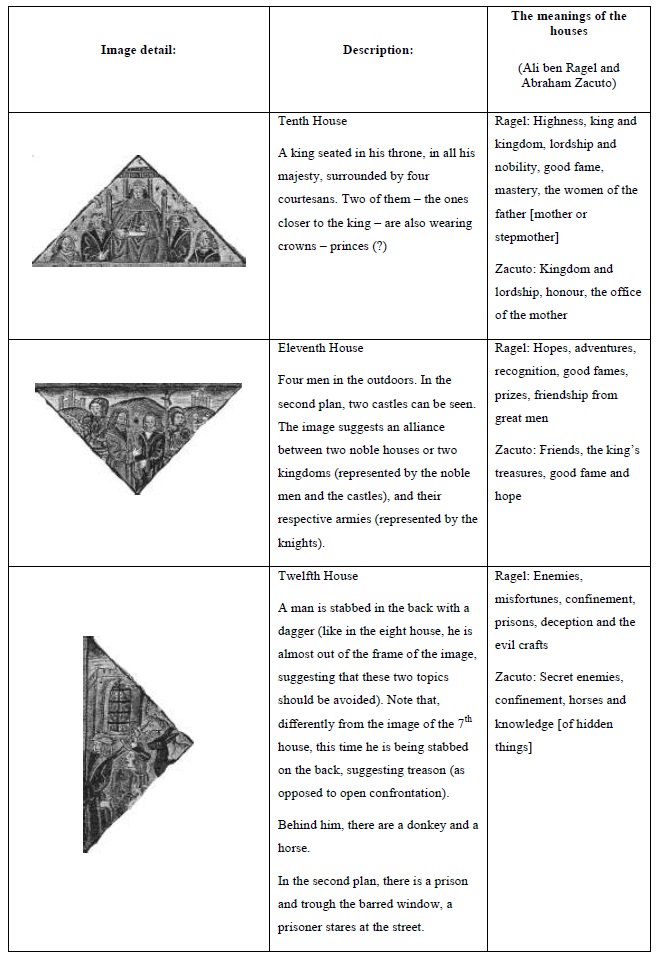
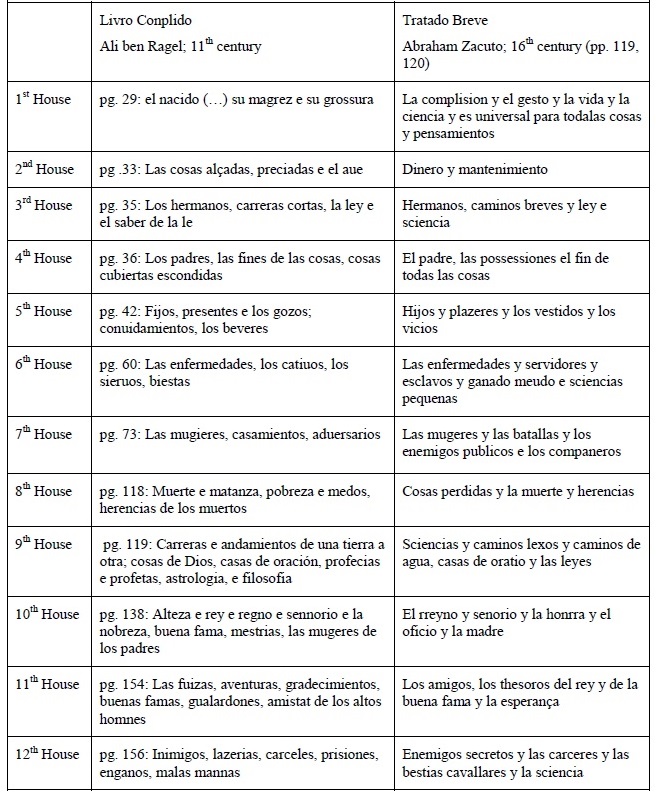
The astrological houses as a reflection of medieval society
The houses are divisions of the astrological chart, representing all aspects of life in medieval society. The meaning of each house was established in Antiquity and adapted to the medieval society; this meaning was flexible enough to adapt to any medieval society, whether it be Christian, Islamic or Jewish.
This image from the 15th century seems to be similar to the one presented in Appendix 1; but contrarily to that image, it does not display any planetary positions. It is an illustration for the meanings of the twelve astrological houses, not an individual horoscope.
In the centre of the image there is a world map, with top pointing the West. On the left there is Africa and on the right, Europe; the bottom section of the map is occupied by India and the Far East.
The houses are the triangular areas disposed around the central square. Their position reflects the relative importance of the issues they represent. The four main houses - the 1st, 4th, 7th and 10th - are designated angular houses, as they correspond to the angles of the chart. They represent the main aspects of life: personality (1st), paternal lineage (4th), partnerships (7th), honors (10th). The following houses - called succedent, as they succeed to the angles - are the 2nd, 5th, 8th and 11th. They signify the supporting aspects of life: possessions (2nd), children and enjoyments (5th), death and the correspondent inheritances (8th), allies and hopes (11th). The remaining four houses - the 3rd, 6th, 9th and 12th - are called cadent, because they fall from the angles. Two of them symbolize positive matters: brothers and short journeys (3rd) and journeys, religions and knowledge (9th); while the other two have negative meanings: sickness (6th), prisons and treason (12th).
The main meanings of the houses are also organized by axis: the native and the others (1st, 7th), gains and losses (2nd, 8th), short and long journeys (3rd, 9th), origins/the father and achievements/the mother (4th, 10th), pleasures/children and hopes/allies (5th, 11th) and finally sickness and imprisonment (6th, 12th).

Paris, B.N., Lat. 6276, f.1, from Kathleen L. Scott, Later Gothic Manuscripts, 1390-1490: a survey of manuscripts illuminated in the British Isles, Vol. I, London, Harvey Miller Publishers, 1996. (The image has copyright; for that reason, it is presented in black and white.)
Figure 1 The astrological houses and their attributions
The astrological houses, examined one by one:
When placed within its proper astrological context, this image becomes a valuable document for the study of medieval astrological symbolism. The thorough study of the astrological houses offers interesting clues to the understanding of medieval mentalities and society.
The translation and references for the table of the Houses: