Imagens de Interesse
Peritoneal Scintigraphy for Assessment of Pleuroperitoneal Communication
Cintigrafia Peritoneal na Avaliação de Comunicação Pleuroperitoneal
11Serviço de Medicina Nuclear, Centro Hospitalar e Universitário do Porto, Porto, Portugal
22Serviço de Nefrologia, Hospital Espírito Santo de Évora, Évora, Portugal
33Serviço de Nefrologia, Centro Hospitalar do Funchal, Funchal, Portugal
Abstract
A 19-year-old woman with chronic kidney disease (stage 5D), under peritoneal dialysis, was suspected of pleuroperitoneal communication. Peritoneal scintigraphy confirmed the diagnosis and the patient was transferred to hemodialysis.
Keywords: C3 glomerulopathy; Pleuroperitoneal communication; Peritoneal scintigraphy.
Resumo
Mulher de 19 anos com doença renal crónica estadio 5D, sob diálise peritoneal, apresenta suspeita de comunicação pleuroperitoneal. Solicitada cintigrafia peritoneal para confirmação do diagnóstico, tendo sido a doente transferida para hemodiálise.
Palavras-chave: Glomerulopatia C3; Comunicação pleuroperitoneal; Cintigrafia peritoneal.
A 19-year-old woman with chronic kidney disease (stage 5D, secondary to C3 glomerulopathy), under peritoneal dialysis since May 2019, presented with retrosternal pain and dyspnea during a Nephrology appointment. Chest radiography revealed right pleural effusion of moderate/ large volume.
The patient had been recently submitted to thoracocentesis.
The pleural fluid was a transudate with a glucose concentration of 200 mg/dL, which raised the suspicion of pleuroperitoneal communication. To confirm the diagnosis a peritoneal scintigraphy was requested.
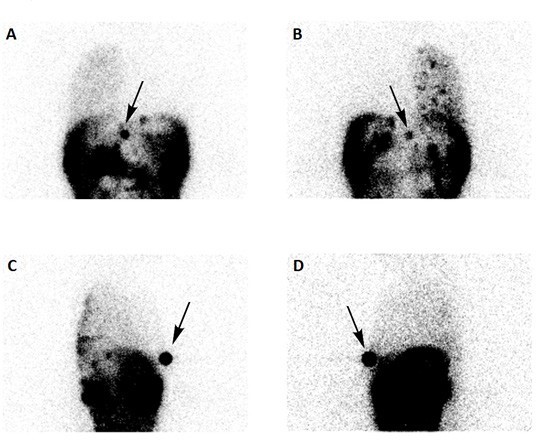
An intraperitoneal injection of 185 MBq of (99mTc) Tc-macroaggregated albumin was performed via the Tenckhoff catheter, along with the instillation of dialytic solution (2.3% glucose). Thoracic and abdominal static images were acquired 5 hours after the administration of the radiopharmaceutical in anterior (A), posterior (B) and lateral right (C) and left (D) views. In our department there are no SPECT-CT facilities, so a (99mTc) Tc-pertechnetate mark was placed at xiphoid process to help anatomy location (black arrow)(Fig. 1).
Peritoneal scintigraphy demonstrated leakage of peritoneal fluid into the right pleural cavity, with no abnormal tracer accumulation detected in the left hemithorax, thereby confirming a right pleuroperitoneal communication. The patient was transferred to hemodialysis. 1,2,3,4
References
1. Choudhary G, Manapragada P, Wallace E, Bhambhvani P. Utility of scintigraphy in assessment of noninfectious complications of peritoneal dialysis. J Nucl Med Technol. 2019;47:163-168.
[ Links ]
2. Kennedy C, McCarthy C, Alken S, McWilliams J, Morgan RK, Denton M, Conlon PJ, Magee C. Pleuroperitoneal leak complicating peritoneal dialysis: a case series. Int J Nephrol. 2011;2011:526753.
[ Links ]
3. Tokmak H, Mudun A, Türkmen C, Sanli Y, Cantez S, Bozfakioğlu S. The role of peritoneal scintigraphy in the detection of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis complications. Ren Fail. 2006;28:709-13.
[ Links ]
4. Ziessman HA, O’Malley JP. Gastrointestinal system. Nuclear medicine: the requisites. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2013;320.
[ Links ]