Services on Demand
Journal
Article
Indicators
-
 Cited by SciELO
Cited by SciELO -
 Access statistics
Access statistics
Related links
-
 Similars in
SciELO
Similars in
SciELO
Share
GE-Portuguese Journal of Gastroenterology
Print version ISSN 2341-4545
GE Port J Gastroenterol vol.22 no.3 Lisboa June 2015
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpge.2015.02.002
ENDOSCOPIC SNAPSHOT
Burkitts Lymphoma Diagnosed by Colonoscopy in Immunocompetent Patient
Linfoma de Burkitt Diagnosticado por Colonoscopia em Doente Imunocompetente
Rosa Coelhoa,∗, Regina Gonçalvesa, Jennifer Costab, Guilherme Macedoa
a Gastroenterology Department, Centro Hospitalar de São João, Porto, Portugal
b Pathology Department, Centro Hospitalar de São João, Portugal
* Corresponding author.
1. Case report
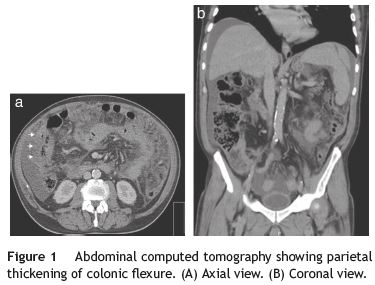
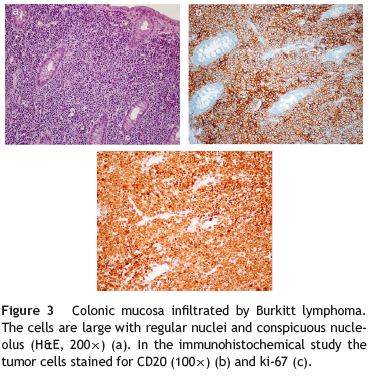
A 67-year-old caucasian man without significant past medical history presented with colicky abdominal pain, in the right lower quadrant, for the last 3 weeks. He also referred a total weight loss of 10% during the last month. Complete blood count revealed hemoglobin of 9.0 g/dL with normal platelet and leukocyte count. Biochemical tests showed elevated C-reactive protein 148 (N: <3 mg/L) and erythrocyte sedimentation 78 (N <20mm 1st hour). Serum lactate dehydrogenase levels were 1340 (N: 135-225 U/L). Abdominopelvic computed tomography (CT) showed hepatomegaly and splenomegaly and a small amount of ascitis consistent with peritoneal carcinomatosis (Fig. 1). CT also revealed parietal thickening of the intestinal wall in the hepatic flexure. Colonoscopy showed in the hepatic flexure one round shape lesion, with 20mm of maximum diameter, predominately with normal mucosa and central ulceration (Fig. 2). Biopsies were performed and histologic examination revealed fragments of colorectal mucosa type, some with chorion occupied by some malignant cells of diffuse pattern consisting of intermediate to large cells. Immunohistochemical studies revealed positive lymphoid cells staining for CD20 in the absence of expression of CD5 and cyclin D1. Malignant cells had expression of CD10 and Mib 1/Ki-67, with proliferative index of about 100% (Fig. 3). Epstein-Barr antibodies were IgG (VCA and EBNA) positive and IgM and IgG (early) negative.

Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy were performed and flow cytometry revealed expression of surface immunoglobulin M, CD10, CD22, CD23, CD38 and CD79b. Fluorescence in situ hybridization was negative for (8:14) (q24; q32). However, the translocation MYC (8q24) was present in 53% of the malignant cells. The diagnosis of Burkitt lymphoma (BL) was performed and R-hiper-CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin and dexamethasone) chemotherapy regimen was started.
The authors describe a case of BL diagnosed by colonoscopy through a unique lesion in the hepatic flexure.1 The colonic involvement by a sporadic form of BL is not a rare phenomenon. However, it is usually present in the terminal ileum or with massive abdominal involvement.2,3
In this case, the colonic involvement allowed a prompt diagnosis and the initiation of an appropriate therapy of this aggressive lymphoma. Taking into consideration the rapid growth of a BL, the diagnosis should be performed as soon as possible and made by the least invasive procedure.
References
1. Leoncini L, Raphael M, Stein H, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Kluin PM. Burkitt lymphoma. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al., editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press; 2008. p. 262-4. [ Links ]
2. Blum KA, Lozanski G, Byrd JC. Adult Burkitt leukemia and lymphoma. Blood. 2004;104:3009. [ Links ]
3. Ferry JA. Burkitts lymphoma: clinicopathologic features and differential diagnosis. Oncologist. 2006;11:375-83. [ Links ]
* Corresponding author.
E-mail address: rosacoelhoabrantes@hotmail.com (R. Coelho).
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Received 4 January 2015; accepted 1 February 2015














