Anastomotic leak is a major complication of colorectal surgery associated with high morbidity and mortality [1,2]. Endoluminal vacuum-assisted therapy (EVT) is a minimally invasive method for leakage treatment. It facilitates intestinal continuity and improves the function of the neorectum, especially if started within 6 weeks [1-3].
A 58-year-old male was submitted to anterior resection of the rectum due to a T2-rectal adenocarcinoma. One week later, the patient was admitted to the ER for fever and abdominal pain. Abdominopelvic CT revealed a hydro-aerial collection (68 × 87 mm) adjacent to the rectal suture. Conservative treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics and CT-guided percutaneous drainage was subsequently performed.
Rectosigmoidoscopy allowed the identification of the anastomotic leak reaching half of the rectal perimeter, at 2 cm from the anal verge, communicating with a 9-cm cavity containing purulent exudate and the previously placed pigtail drain (Fig. 1a). EVT with Endo-SPONGE® was attempted 4 weeks after surgery. The procedures were performed in an outpatient setting, with high-definition gastroscopes (Olympus®GIF-H180; Olympus®GIF-H185) every 48-72 h. The length and size of the abscess cavity were measured, and the Endo-SPONGE® was then cut accordingly. After the introduction of the scope into the cavity, an overtube was advanced into the deepest position. The scope was withdrawn, and the Endo-SPONGE® was inserted into the cavity using a pushing probe and subsequently connected to a vacuum suction system.
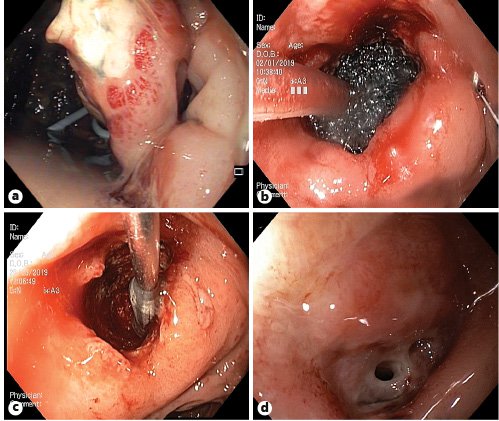
Fig. 1. a Anastomotic leakage of half of the rectal perimeter communicating with a 9-cm cavity containing purulent exudate and pigtail drain at index evaluation.bCorrect positioning of the Endo-SPONGE® checked endoscopically.cFG placement with an external applicator under endoscopic visualization.dLeak with a residual cavity (0.5 mm) after EVT and FG.
The patient was submitted to 50 exchanges over 5 months. There were no EVT-related complications. After this period, a small cavity (1 cm) with granulation tissue remained. Therefore, 4 mL of fibrin glue (FG) was applied, under endoscopic visualization (Fig. 1c). Reevaluation 1 week later confirmed technical success. Reassessment 4 weeks later confirmed the closure of the leak (Fig. 2). The patient was subsequently submitted to ileostomy closure and intestinal transit reconstruction.
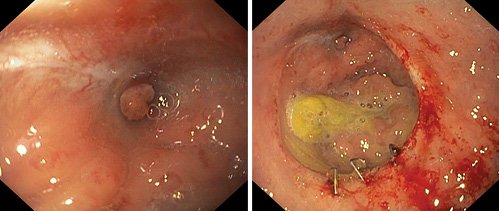
Fig. 2. Endoscopic evaluation 4 weeks after FG sealing, confirming closure of the anastomotic leakage.
Duration of EVT until complete healing is estimated to be 11-244 days [4]. In this case, the large dimension of the leakage made endoscopic resolution particularly challenging. After a multidisciplinary discussion, it was decided to preclude surgery and maintain EVT since there was a response to endoscopic treatment. Changing the sponge from its intracavitary position to an intraluminal position may have shortened therapy duration.
Additional interventions after EVT are needed in 9.1% [4]. Thus, when a residual cavity persists, complementary therapies should be considered to avoid surgery namely FG application, synthetic absorbable monofilament mesh placement, or over-the-scope clip closure [4,5]. In this case, given the size of the residual cavity, spontaneous closure might have been achieved. Nonetheless, FG sealing was attempted once it was safe and minimally invasive.
Better outcomes may be obtained when EVT is performed in patients with distal anastomotic leakage who already have a non-functioning stoma, without sepsis [4]. EVT complications occur in 13.8% and include pelvic abscess, stenosis, bleeding, complete dehiscence, ileal/urethral fistula, residual sinus, pouch dysfunction, and severe pain [1,4]. Treatment failure should be considered in case of leak increase. Preoperative radiotherapy, lack of protective stoma, development of complications, and male sex are associated with EVT failure [4]. The long duration of therapy is still a limitation. In challenging cases with suboptimal response to EVT, FG may complete leak closure.














