Introduction
Metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is now considered the most prevalent chronic liver disease, affecting a quarter of the world population and up to 46% of the Western adult population [1, 2]. It is characterized by an excessive liver fat accumulation (steatosis in more than 5% of the hepatocytes), as a result of insulin resistance on hepatic metabolism [2]. MAFLD can also result, in a minority of cases, from other causes unrelated to insulin resistance, as inborn metabolic diseases [3]. The spectrum of presentation of MAFLD is wide ranging, from simple steatosis to steatohepatitis and related fibro-sis, cirrhosis, and its complications [2].
Dorfman-Chanarin syndrome (DCS; Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man [OMIM] 275630) is a rare multi-systemic autosomal recessive inborn metabolic disease, first described by Dorfman et al. [4] in 1974 and Chanarin Case Description
A 61-year-old Caucasian male with a long-established diagnosis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis/MAFLD related cirrhosis was referred to the liver transplantation outpatient clinic in 2016 due to suspicion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Back to 1986, while having mild alcohol consumption and a body mass index of 26.6, he was diagnosed with fatty liver disease based on histological findings. Alcohol consumption was stopped by that time. In 2014, he was diagnosed with liver cirrhosis. Another percutaneous liver biopsy was done, documenting a cirrhotic liver with signs of macrovesicular steatosis, necroinflammatory lesions and ballooning degeneration of hepatocytes, compatible with MAFLD. The follow-up of the patient included a 6-month ultrasound screening of hepatocellular carcinoma and, in this context, he was referred to our institution, to be evaluated for liver transplantation.
A “scaly” rash most evident on his trunk since birth and hearing loss since the 1980s, for which he had had surgery 16 years later, were documented. Neither blood transfusions nor intravenous drugs use were reported. No other cardiovascular risk factors besides a recently diagnosed arterial hypertension and a body mass index in the overweight category (29.8) were perceived. Concerning his family history, he was born of a consanguineous marriage between two first cousins. Thyroid disease is prevalent in his family, but no one else had history of liver disease, abnormal skin rashes, nor progressive deafness at a young age, although two of his siblings complained of tinnitus. None of his four brothers and sisters shared clinical features compatible with DCS. On physical ex-amination, he had a good overall appearance. His skin was dry and scaly (fish scale-like; Fig. 1), especially on the trunk, hard to fold; a Dermatology consultant confirmed ichthyosis. His abdomen did not show any signs of collateral circulation and his liver was palpable 2 cm below the rib cage; neither splenomegaly nor ascites were identified. He presented with a Model for End-stage Liver Disease score of 9 and a Child-Pugh score of 5 points (class A).
Alpha-fetoprotein was within the normal range (1.9 µg/L). Liver analytical profile revealed aspartate transaminase (AST) 101 U/L, alanine transaminase (ALT) 109 U/L, total bilirubin 1.56 mg/dL, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) 130 U/L, γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT) 270 U/L. Lipid profile was normal. A raised creatine kinase (CK) was also found (539 U/L), even though there were no muscular complaints. In spite of MAFLD related cirrhosis previously assumed, based on histological findings, and in the context of con-genital ichthyosis, deafness, and elevated muscular enzymes, a DCS diagnosis was proposed. Viral hepatitis, hemochromatosis, Wilson’s disease, autoimmune liver disease, and α-1 antitrypsin deficiency were excluded. A peripheral blood smear was immediately performed, showing multiple vacuoles on the cytoplasm of polymorphonuclear cells, eosinophils, basophils, and monocytes (Fig. 2), a common finding of lipid storage diseases named Jordans’ anomaly. In light of these findings, his previous liver biopsy, done in 2014, was reviewed, being also compatible with DCS diagnosis, motivating the molecular study of the ABHD5 gene.
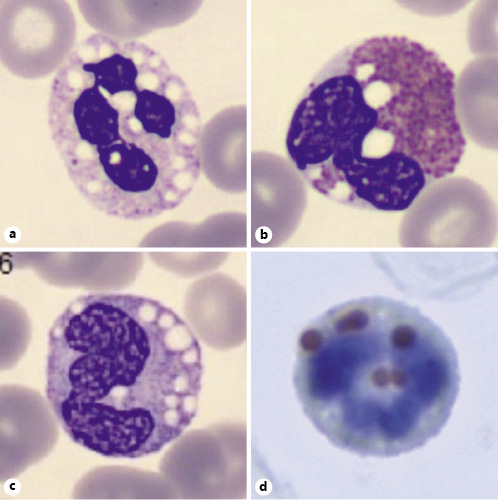
Fig. 2 Jordans’ anomaly in a neutrophil (a), an eosinophil (b), and a monocyte (c; peripheral blood smear stained in Leish-man’s stain, ×1,000). Lipid vacuoles were confirmed by using oil red staining (×1,000; d).
Specific primers were designed for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for amplification of the coding regions, as well as the surrounding zones, using the software PrimerBlast (www.ncbi.nlm. nih.gov/tools/primer-blast/). The PCR products were purified by the illustraTM ExoProStarTM (GE Healthcare Life Sciences) and used for direct sequencing with BigDyeTM Terminator version 3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and ran on ABI PRISM® 3100 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems). All the obtained sequences were compared with the reference sequence (NM_016006.4), using the SeqScape® Software version 2.5 (Applied Biosystems). A nonsense mutation c.934C>T (p.R312*), first described by Pujol et al. [8] in 2005, was found in exon 6, in apparent homozygosity. Since both of his parents were deceased, their genetic study was unavailable, but the hypothesis of “true” homozygosity was considered very likely because of their consanguinity. Therefore, the patient was labeled as a homozygous for this particular mutation, which confirmed the proposed diagnosis.
The patient was started on ursodeoxycholic acid, which slightly improved his biochemical profile (AST 62 U/L, ALT 57 U/L, ALP 101 U/L, GGT 60 U/L, total bilirubin 1.56 mg/dL). Large esophageal and gastric varices were found on his last upper endoscopy and non-selective beta-blockers were started. Abdominal magnetic resonance found a 17-mm nodule between segments IV and VIII, suggestive of hepatocellular carcinoma, treated with microwave thermal ablation. The patient was successfully submitted to liver transplant in January 2019 and remains, to date, with a completely normal liver profile and no signs of hepatocellular carcinoma relapse.
Discussion
Histological compatible MAFLD features have a multitude of etiologies, so when the most common causes are excluded and other non-explained clinical findings are observed, rare causes should be looked for. Here we present a case of a rare cause of histological findings compatible with MAFLD, but without any other clinical features besides overweight and a recently diagnosed systemic ar-terial hypertension. Importantly, diagnosis of DCS remained unnoticed till significant findings in the clinical past history and physical examination were considered, and whose clinical course and evolution culminated in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma that led to liver transplantation.
The ABHD5 gene (MIM*604780) is located on chromosome 3p21 and is comprised of seven exons that encompass about 28 kb of genomic DNA, generating a 349-amino acid protein (ABHD5). This enzyme serves as a cofactor for ATGL, enhancing its enzymatic activity up to twenty-fold; when a mutation alters the amino acid sequence of this protein, the intracellular accumulation of triglycerides ensues, causing DCS. Less than one hundred cases have been reported worldwide, with the majority of them coming from Mediterranean and Middle-East countries, especially Turkey. The first report on the sequence analysis of the ABHD5 protein in DCS patients [9] documented eight distinct mutations; the spectrum of gene variants included insertion, deletion, splicesite and point mutations. Since then, more variants have been described, most of them involving truncation mutations in ABHD5, but large deletions were also found [10].
As far as we know, this is the first known case of homozygosity of the nonsense mutation c.934C>T (p. R312*), first described in 2005 in a 4-year-old compound heterozygote [8]. This nonsense mutation in exon 6, inherited from the patient’s consanguineous parents, led to the replacement of arginine for a stop codon, originating a truncated 312-amino acid protein. Although our patient’s diagnosis was made several years later than most of the published reports [11-14], we do not have enough information regarding his past medical history to be able to consider any causative relation between this mutation and his clinical phenotype. In fact, several authors have reported conflicting evidence regarding a genotype-phenotype correlation [10, 15-17]. Redaelli et al. [10] identified a mutation that conserved >90% of the native protein, but was associated with severe clinical manifestations, and also a mutation that caused precocious truncation of the protein, which was associated with severe steatohepatitis, but a relatively mild phenotype concerning other clinical DCS features. The authors hypothesized that the accumulation of non-functional ABHD5 proteins may have a more deleterious consequence for cellular lipid droplets metabolism in some tissues than total loss of the protein expression [10].
ABHD5 is expressed in multiple tissues (including skin, muscle, liver, gastrointestinal epithelium, central nervous system, and blood leukocytes), thus explaining the multisystemic but also very heterogeneous manifestations associated with DCS. The most frequent and characteristic features are ichthyosis, liver steatosis/hepatomegaly, and mild myopathy, but ataxia, neurosensory hearing loss, sub-capsular cataracts, nystagmus, strabismus, mental retardation, short stature, microcephaly, and intestinal and renal involvement have also been de-scribed [4, 5, 18-22]. Our patient presented with MAFLD histological features (which evolved into liver cirrhosis with portal hypertension and hepatocellular carcinoma), ichthyosis, altered muscle enzymes, and unilateral neuro-sensory hearing loss at different stages of his life, which, altogether, suggest a typical DCS presentation.
Liver involvement is present in about 64% of patients with DCS [21], but the severity of steatohepatitis is variable, with cirrhosis being present in approximately 15% of patients [13, 23-25]. Our patient was first diagnosed with chronic liver disease back in 1986 with MAFLD histological features, while clinical findings compatible with cirrhosis only showed up more than 28 years later. There are cases of presentation with cirrhosis both in children [23-26] as in adults [12, 13, 27], but no correlation between genotype and phenotype has been uncovered. While not resolving or im-proving other manifestations of DCS, liver transplantation has been performed in an adult with this syndrome, with no relapse of steatosis or fibrosis in the control liver biopsy per-formed at 1 year of follow-up [28]. Our patient was successfully transplanted due to hepatocellular carcinoma that developed in an already cirrhotic liver after a bridging therapy with microwave thermal ablation in January 2019. One year and a half later, he presents a completely normal liver profile and no signs of hepatocellular carcinoma relapse. In the absence of an abnormal liver profile, no liver biopsy of the explant was performed to date.
Cutaneous involvement in DCS is a constant feature and ichthyosis usually corresponds to non-bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma [20], as observed in our patient, but other dermatologic manifestations have been reported [4, 8, 21]. Nevertheless, there is no correlation between the severity of the skin condition and the microscopic findings [20], which is supported by ABHD5’s ATGL-independent role in epidermal lipid metabolism [29, 30]. A mild myopathy was suspected because of elevated CK, but we did not perform a muscle biopsy to confirm. In DCS, opposite to neutral lipid storage disease with myopathy, there is no cardiomyopathy simultaneous to skeletal muscle disease, presumably be-cause even a low amount of lipase activity may preserve cardiac function [31]. This issue is important when considering evaluation of patients to liver transplantation. Our patient also had unilateral neurosensorial deafness, but no other symptoms or signs of nervous system, intestinal, or renal involvement.
The most common and characteristic laboratory finding is May-Grünwald-Giemsa-negative lipid droplets (Jordans’ anomaly) in otherwise normal peripheral blood leukocytes [18], which was seen in our patient (Fig. 2). Before a clinical suspicion of DCS, a blood smear for screening for lipid inclusions in neutrophils must be made. Muscular and liver enzymes can be mild to moderately elevated (two- to three-fold), consequent to muscle and liver involvement, but serum lipids, as most of the other common biochemical blood tests, are usually nor-mal [9]. Our patient presented with abnormal liver tests, as expected, and with CK elevation, possibly predicting some skeletal muscle involvement.
There is no standardized treatment for DCS. Restriction of long chain fatty acids in the diet and promoting middle chain fatty acid intake are supposed to benefit the skin by reducing ichthyosis and alter the lipid accumulation in other organs, but no randomized controlled trials have been done. Acitretin showed a beneficial effect in reducing ichthyosis in two infants, even in the presence of compromised liver function [32, 33], but there are no studies regarding the long-term effect on DCS patients. Ursodeoxycholic acid has been investigated in several randomized controlled trials for MAFLD, at different doses and for up to 2 years, but only showed some bio-chemical but no histological improvements [34-36]; the improvement on our patient’s laboratory data also demonstrated this effect.
DCS is a rare congenital disorder with overlapping liver histological features with MAFLD, which may lead to misdiagnosis. Evolution of the chronic liver disease related to DCS does not reflect the type of mutation nor is it predictive of the outcome. Yet, once cirrhosis is established, common complications including hepatocellular carcinoma may arise and whose conduct is similar to that of cirrhosis of other etiologies. In this setting, liver trans-plantation may be successfully performed and indications are the same as for patients with other etiologies of liver disease, as it may resolve cirrhosis complications but not extrahepatic manifestations of DCS.
















