Introduction
Over the past years, gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy has pivoted from standard white light endoscopy (WLE) toward a more specified and specialized type of endoscopy using different types of enhancement techniques to optimize optical diagnosis. These advanced endoscopic imaging technologies, denoted as virtual chromoendoscopy (VCE), improve visualization of mucosal abnormalities and enhance subtle structural and microvascular features facilitating decisions for management of GI diseases. Next to (virtual) chromoendoscopy, evolution from using standard white light endoscopes toward high-definition (HD) resolution scopes and magnification endoscopy has also contributed to better detection and characterization of mucosal lesions like colorectal polyps, colorectal cancer, dysplasia, etc. [1, 2]. This review however focuses on the commercially available and emerging VCE technologies. The aim was to provide an overview of the available imaging technologies, their clinical applicability, and added value.
VCE Technologies
Flexible GI endoscopy has known an important evolution in the last decades with the development of a series of so-called push-button VCE technologies to make advanced endoscopic imaging more widely available. These new technologies rely on the use of a narrowed part of the available spectral bandwidth. In contrast to dye-based chromoendoscopy (DCE), currently available VCE uses a combination of optical and digital (pre- or post-pro-cessing) filtering to enhance contrast. Next to optimal mucosal visualization, a high-quality bowel preparation, and well-trained experienced operators, HD imaging is a prerequisite for optimal application of these techniques. Nowadays, the commercially available systems are brand-dependent and the most recently available techniques include (1) narrowband imaging (NBI) (Olympus Medical Systems, Japan); (2) blue light imaging (BLI) and linked color imaging (LCI) (Fujifilm, Japan), and (3) i-scan optical enhancement (i-scan OE) (Pentax, Japan). Table 1 provides a summary of the endoscopic imaging methods discussed in this review.
Narrowband Imaging
NBI was the first commercially available type of VCE and relies on the preprocessing technique of the optical filtering of the illumination light. First of all, it discards the standard red, green, and blue filters and second re-duces the spectral bandwidth to a concentered wave-length of 415 nm for blue and 540 nm for green light [3]. The narrowed band blue light excites hemoglobin which has an absorption peak of 415 nm and therefore absorbs the blue light, allowing structures containing high levels of hemoglobin (e.g., capillaries, veins) to appear darker, providing a positive contrast to the surrounding mucosa. The 540 nm light corresponds to a secondary hemoglobin absorption peak, enlightening the deeper mucosal and submucosal blood vessels. Hence, the final composite NBI image improves visualization of predominantly mucosal and vascular structures [4].
BLI and LCI
Previously, the Fuji Intelligent Chromo Endoscopy (Fujifilm Corporate, Tokyo, Japan) was a post-processing technology enhancing the visualization of mucosal structures and microcirculation. This has now been replaced by BLI, a preprocessing technology like NBI enhancing the mucosal surface by using blue light that superficially penetrates the mucosa and excites hemoglobin [5]. BLI is based on an unfiltered emission of short-wavelength blue light generated by adaptation of a four-light-emitting diode (LED) multi-light technology, providing an innovative visualization of the intestinal mucosa. This technology is based on the combination of four types of light as source emitters: blue-violet, blue, green, and red. LCI is a recent development (Fujifilm Corporate) in imaging technology created by a short-wavelength narrowband laser light in combination with a white laser light, enabling a brighter light in distant areas with a higher contrast between white and red spots [6]. BLI and LCI are two of the observation modes of the four-LED multilight technology that allows enhanced visualization of hemoglobin by, respectively, intensifying the blue or red light spectrum, improving delineation and detection [7-9].
I-Scan Digital Contrast
A third narrow spectrum technology is i-scan. It originally consisted of a post-processing digital contrast technology comprising three enhancement features, involving post-processing algorithms applied on WLE images. The surface enhancement sharpens the image by recognition of edges; contrast enhancement reflects differences between structures and depressed areas (darker spots) via presentation of low-density areas (more blue color); tone enhancement improves individual organ appearance by digital narrowed spectrum imaging [4].
Further developments lead to the i-scan OE system. That, like NBI and BLI, is a preprocessing technique and combines optical and digital enhancement chromoendoscopy [10]. It uses three types of algorithms combining aspects of the original i-scan post-processing system and the new preprocessing filtering technique. The three available modes include surface enhancement (i-scan 1) for the detection of abnormalities in the GI tract; tone enhancement (i-scan 2) for pattern characterization; and optical enhancement (i-scan 3) for characterization of blood vessels, glandular ducts, and mucosa. Each of these algorithms can be selected by pressing a pre-assigned button on the handpiece of the scope. The newly added optical enhancement i-scan 3 function employs band-limited light to achieve higher overall transmittance by connect-ing the peaks of the hemoglobin absorption spectrum (415, 540, and 570 nm), thus creating a continuous wave-length spectrum, like NBI.
The Clinical Role of Enhanced Endoscopy
The Role of VCE in Detection and Characterization of Upper GI Diseases
Barrett’s Esophagus
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) is diagnosed when columnar intestinal mucosa replaces the normal stratified squamous mucosa, so the z-line no longer corresponds to the gastroesophageal junction and is histologically confirmed by the presence of intestinal metaplasia (IM). The presence and extent of BE should be described as suggested by the Prague classification, by assessing the circumference and the maximum extent of the endoscopically visualized BE segment proximal of the gastroesophageal junction [11].
Screening and Surveillance. Nowadays, standard of care in BE surveillance remains endoscopic evaluation using the Seattle biopsy protocol. This includes targeted biopsies of visible lesions, but since neoplasia can be patchy, also random biopsies are taken every 1-2 cm in every quadrant over the entire extent of the BE segment [12-14]. Advanced imaging may facilitate lesion detection and improve surveillance accuracy (Fig. 1) [12].
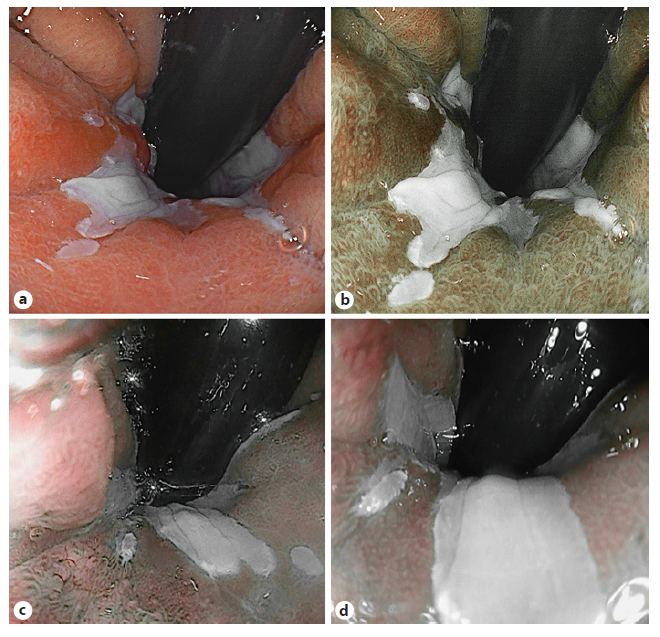
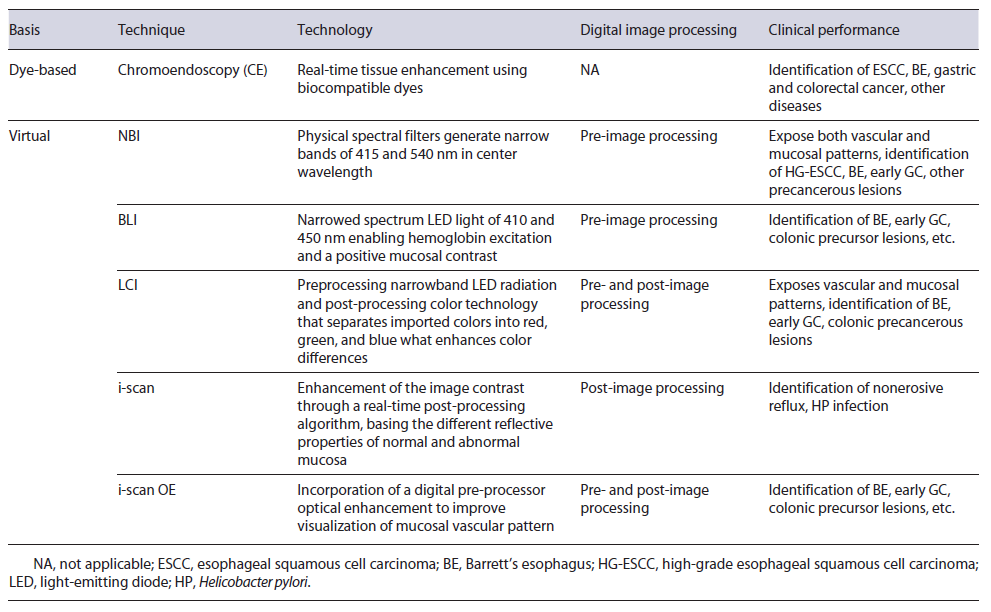
Fig. 1 Virtual chromoendoscopy image of Barrett’s esophagus. White light imaging (a); blue light imaging (b); i-scan 2 imaging (c); and i-scan OE imaging (d).
NBI plus targeted biopsies has not proven to be superior to WLE with random biopsies in detection of dysplasia (92% vs. 92%) but is able to detect a larger amount of dysplastic areas (30% vs. 21%, p < 0.0001) leading to fewer biopsies per patient (3.6 vs. 7.6, p < 0.0001) [15]. Multiple meta-analyses confirm a high sensitivity of 95-96% and high specificity of 94-95% for the detection of high-grade dysplasia (HGD) using NBI [12, 15].
Several VCE-based classification systems have been developed and validated (Table 2) [16-18]. Overall, they all suggest that an irregular mucosal and vascular pattern is predictive for dysplasia, and a ridged/villous pattern guides toward a specialized IM (SIM) lesion [4]. When comparing the three commercially available VCE classification systems head-to-head, their diagnostic accuracy for SIM and dysplasia detection was low (SIM: 57% [Nottingham and Kansas] and 63% [Amsterdam]; dysplasia: 75% [irrespective of the classification systems]) [19]. The newer Barrett’s International NBI Group (BING) criteria were validated to be used to discriminate between non-neoplastic and neoplastic BE [20]. This classification is also based on simple surface and vascular patterns, and a regular pattern is predictive for non-neoplastic BE and an irregular pattern for neoplastic BE (Table 2) [20].
BLI and i-scan have been studied for characterization of BE lesions and showed comparable performances as NBI when combined with magnification and conventional acetic acid (ACA) application (Fig. 1) [21, 22]. With inter-rater variability remaining a hurdle, LCI improves visibility with 44.4% in a group of 5 expert and 5 trainee endoscopists when compared to WLE resulting in moderate-substantial interrater reliability scores [23]. In parallel with the BING criteria, the Blue Light Imaging for Barrett’s Neoplasia Classification (BLINC) was validated as a promising tool with high sensitivity for detection [24]. The authors added an easy to identify additional feature, the dark color of neoplastic lesions, that is highlighted by BLI. Furthermore, a multicenter trial validated the use of the BING with the i-scan technology using an international group of expert endoscopists viewing videos collected from several European centers. Addition of ACA significantly increased the accuracy of the classification system using i-scan, from 69% to 79% (p = 0.01) (Table 2) [22].
Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the most common type of esophageal cancer worldwide and has a poor 5-year prognosis due to late recognition and diagnosis [25]. Timely and accurate diagnosis of early ESCC is crucial to improve patient prognosis and out-come. Lugol staining is currently standard of care but struggles with long procedural time, possible esophageal spasm, and potential allergic complications [26-28]. Compared to Lugol, NBI showed to be as efficient in terms of detection of HGD and ESCC lesions in high-risk patients [29]. When compared to WLE-only, a Japanese multicenter randomized controlled trial (RCT) demonstrated that NBI detected superficial ESCC (SESCC) more frequently (97% v 55%, p < 0.001) [30]. A meta-analysis based on 12 studies with expert centers demonstrated NBI to be as adequate as Lugol staining for diagnosis of HGD and ESCC [31]. On a per-lesion level, the sensitivity and specificity for Lugol chromoendoscopy were 92% and 98% versus 88% and 94% for NBI sensitivity and specificity, respectively. Recently, a French group investigated the use of NBI in nonexpert setting on 334 patients with a history of ESCC and demonstrated on a per-patient level a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 66% for Lugol staining and a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 77% for NBI, the latter being significantly superior to Lugol [28]. As previously demonstrated in expert hands, NBI has now proven to be more specific than Lugol staining in normal gastroenterology practice [28].
Hence, the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endos-copy (ESGE) recommends the use of at least HD-WLE in combination with a VCE modality like NBI next to Lugol staining for esophageal cancer screening and lesion assessment [32].
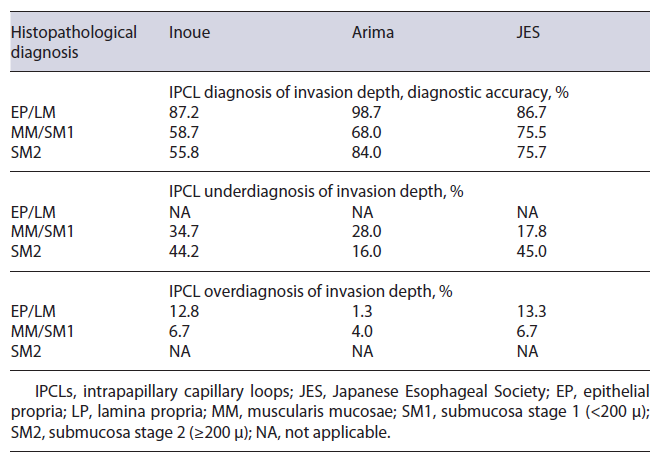
Screening and Surveillance. Intrapapillary capillary loops (IPCLs) are known optical markers for the assess-ment of SESCC. Several IPCL classifications have been investigated with no superior one. Fan et al. [33] conducted a meta-analysis for the comparison of three IPCL classifications for SESCC staging. This group compared the Inoue, the Arima, and the Japanese Esophageal Society (JES) IPCL classification and assessed impact of IPCL on diagnostic accuracy (Fig. 2). IPCL showed a high diagnostic accuracy for differentiation between epithelial (EP)/lamina propria (LP) and muscularis mucosae (MM) tumors with a pooled sensitivity of 0.91. IPCL showed a rather low sensitivity of 0.72 for diagnosing MM/submucosa stage 1 (<200 μ) (SM1) and submucosa stage 2 (≥200 μ) (SM2) staging. For EP/LP tumors, all three IPCL classifications had high diagnostic accuracy (Inoue 87.2%, Arima 98.7%, and JES 86.7%). When differentiating MM/SM1 staging tumors from EP/LP and ≥SM2 tumors, IPCL scored worse than pathology with 23.1% of the lesions underestimated and 6.3% of the lesions overestimated. When concerned to the different classifications, JES classification outperformed Inoue and Arima but underesti-mated 17.8% of the MM/SM1 lesions. For ≥SM2 staging with IPCL, an underestimation of 38.9% was shown and Arima classification outperformed the other two (Arima vs. Inoue vs. JES: 84.0% vs. 55.84% vs. 55.0%, p < 0.005) (Table 3). Hatta et al. [34] compared the diagnostic ability of magnifying endoscopy with BLI and NBI for the determination of invasion depth of SESCC by application of the JES IPCL classification. The overall accuracies did not significantly differ, and the sensitivity and predictive values in MM and ≥SM2 tumors were low. Therefore, the authors concluded that diagnosis by magnifying endoscopy alone might be unsatisfactory.
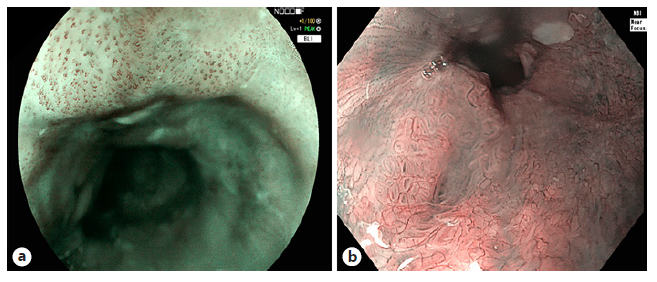
Fig. 2 Different types following the Japa-nese classification of intrapapillary capil-lary loops (IPCLs) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. IPCL type B1 in flat squamous lesion, visualized with BLI (a), IPCL type B2 squamous esophageal lesion, visu-alized in NBI with near focus (b). BLI, blue light imaging; NBI, narrowband imaging.
Table 3 Relationship between histopathological diagnosis and diagnostic accuracy of IPCL for invasion depth estimation [28]
Gastric IM/Dysplasia
Gastric IM (GIM) and dysplasia are precursor lesions of gastric cancer (GC). It can occur both in longstanding atrophic and nonatrophic gastritis. A genetic basis is currently still unknown [35, 36]. High prevalence regions of GC and/or Helicobacter pylori infection also tend to have a higher prevalence of GIM [35].
Screening and Surveillance. The mucosal and vascular pattern assessed by NBI is predictive for the presence of GIM and dysplasia (Fig. 3). Ridged or villous patterns suggest the presence of metaplasia, whereas regular patterns suggest the absence of dysplasia [4]. An indicative endoscopic diagnostic sign with a specificity of 93% is the “light blue crest” sign, although its absence does not exclude GIM given its positive predictive value of 91% [37]. A variable density of the vascular pattern is indicative for a H. pylori infection [4, 38]. In the same multicenter validation study, the authors showed a high diagnostic accuracy of NBI (>90%) allowing to take only targeted biopsies instead of random biopsies when using NBI [38]. Histological scoring systems like operative link on gastric assessment (OLGA) and operative link on GIM are based on the severity and topographic distribution of gastric atrophy and GIM, respectively. Both systems stratify gastric atrophy/GIM in a four-stage model, and a stage III or IV has shown to be associated with a high risk for GC [39, 40]. The endoscopic grading of GIM (EGGIM) classification using HD VCE with NBI was recently validated [41]. This classification assesses the entire gastric mucosa and rates according to the presence and extent of GIM from 0 to 10. An EGGIM score of ≥5 was found to be the optimal cut-off for the identification of patients with OLGA/operative link on GIM III or IV that are selected for further follow-up surveillance endoscopy. It is the first endoscopic scoring system that showed to be a direct and indepen-dent predictor for GC [41]. Therefore, it may replace the histological scoring systems in the future and help to directly select patients that need endoscopic surveillance.
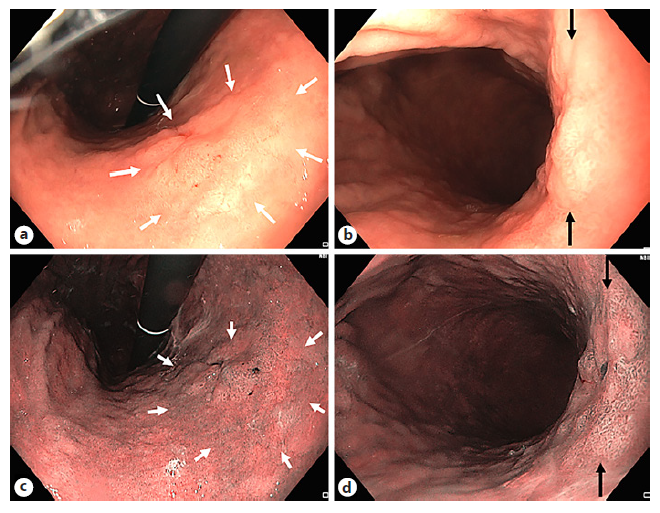
Fig. 3 Zone of gastric intestinal metaplasia (GIM) within gastric atrophy. GIM (white arrows) visualized in WLE (a), NBI (b). Close-up pictures of zone of GIM (between black arrows) in WLE (c) and NBI (d).
Both BLI and LCI have demonstrated improvement of gastric neoplasia detection. A Japanese group reported that the color difference between GC and the surrounding mucosa using LCI was significantly improved compared to WLE [42-44]. The most pronounced color difference was shown when a GC was surrounded by IM [42-44]. However, detection remains difficult, especially in nonexpert hands. Artificial intelligence (AI) based on LCI images is brought forward as possible solution [45]. Similarly, NBI has been reported to increase neoplasia detection in patients at risk [46]. In patients with previously detected GIM or gastric dysplasia, the overall sensitivity for detection of premalignancy (both GIM or dysplasia) was 71% for NBI versus 51% for WLE [46]. One of the limitations of this first-generation NBI (1G-NBI) is the too dark images, explaining the moderate clinical performances and making 1G-NBI unsuitable for GC screening in high-risk patients. The brightness and resolution obtained using NBI have been improved markedly since the introduction of the Olympus 290 series (EVIS LUCERA ELITE; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) and 190 series (EVIS EXERA III) endoscopy systems, in comparison with the previous 260 and 180 series, respectively. Recently, a Japanese group investigated the use of second-generation NBI (2G-NBI) for GC screening in high-risk patients, resulting in a sensitivity of 75% for premalignancy detection, comparable to 1G-NBI [47]. Although the positive predictive value was better for 2G-NBI (20.9%) in comparison with WLE (13.5%) (p = 0.015), the GC detection rate was not significantly improved over WLE.
Duodenal Pathology
NBI combined with magnification, on the one hand, can be helpful in the diagnosis, classification, and deter-mination of remission in patients with gluten enteropa-thy and on the other hand in the diagnosis of ampullary tumors or mucosal changes in lymphomas [48].
The Role of VCE in Imaging of the Lower GI Tract
Colorectal Polyps and Neoplasia
Initially, 1G-NBI did not show significant differences in colonic polyp detection rate (PDR) and adenoma detection rate (ADR) when compared to both conventional and tandem colonoscopy [49, 50]. After the introduction of the improved 2G-NBI, Horimatsu et al. [51] showed that the mean number of polyps detected per patient was significantly higher in the HD-NBI group than the HD-WLE group (2.01 vs. 1.56; p = 0.032). A prospective RCT comparing ADR and PDR between HD-NBI and HD-WLE colonoscopy using the 190 series Olympus endoscopy system found that both rates were significantly higher for NBI than for WL (adenoma: 48.3% vs. 34.4%, p = 0.01; polyps: 61.1% vs. 48.3%, p = 0.02) [52]. However, in a more recent observational trial in four academic and four community hospitals, 2G-NBI could not improve ADR (43.5% for NBI vs. 44.4% for WLE, p = 0.71) nor the mean number of adenomas detected (0.90 ± 1.38 vs. 0.91 ± 1.40, p = 0.95) [53]. However, ADR was higher with NBI in the academic group, whereas ADR was higher in the WLE group in community hospitals. NBI did significantly improve the mean number of flat and depressed lesions (0.62 ± 1.34 vs. 0.44 ± 1.01, p = 0.035). For sessile serrated polyp (SSP), attracting more and more attention as CRC precursor, the same research group found significantly more SSPs per patient in the HD-NBI group versus the HD-WLE group (0.05 vs. 0.01; p = 0.036) [51]. In a more recent RCT (randomization to colon inspection with NBI vs. WLE colonoscopy), the number of sessile serrated lesion (SSL) in the right colon (SSP plus hyperplastic polyps) was higher in the NBI group (204) compared to the WLE group (158), without reaching statistical significance (p = 0.085) [54]. Similar results were recently shown in a multicenter prospective RCT comparing the SSL detection rate between NBI and HD-WLE in expert hands. SSL detection rate was 7.5% in the NBI group and 8.0% in the WLE group (p = 0.852) [55]. Both ADR and PDR were not statistically significantly different between NBI and WLE colonoscopy.
In 2004, NBI visualization of the microvascular pattern was identified as a distinct manner of differentiation between non-neoplastic and neoplastic colonic lesions [56]. Even more, NBI vascular thickness showed to be related to the histological grade and depth of invasion of colonic neoplasms [57]. In addition, NBI microvascular density measurements improve accurate characterization similar to magnified chromoendoscopic assessments based on Kudo pit pattern classification [4, 58-60]. The NICE classification uses color, vessels, and surface pattern criteria for the endoscopic diagnosis of colonic polyps classifying them in three types (Fig. 4a) [3, 4, 61]. This new classification system was validated with a real-time sensitivity of 98% and a negative predictive value of 95% [62]. A more specified classification, based on the NICE classification, is the Japanese NBI Expert Team (JNET) classification, subdividing adenomatous lesions (NICE type 2 lesions) in type 2A or low-grade adenomas and type 2B or high-grade adenomas including shallow sub-mucosally invasive carcinomas [63]. Currently, an international multicenter validation trial is ongoing validating the JNET classification in clinical practice and therapeutic decision-making, and results are to be awaited. An important disadvantage of both the NICE and JNET classifications is that SSLs are not incorporated, although they have been identified as important precursor lesions of colonic cancer and thereby cannot be discarded [4, 64]. Ijspeert et al. [65] developed and validated the “Work-group serrAted polypS and Polyposis” (WASP) classification, combining the NICE criteria and four of the Haze-winkel criteria: (1) clouded surface, (2) indistinct border, (3) irregular shape, and (4) dark spots inside the crypts [4, 64]. A holistic and feasible stepwise approach of endoscopic polyp differentiation has been proposed including hyperplastic polyps, adenoma, and sessile serrated adeno-ma/SSP (Fig. 4b).
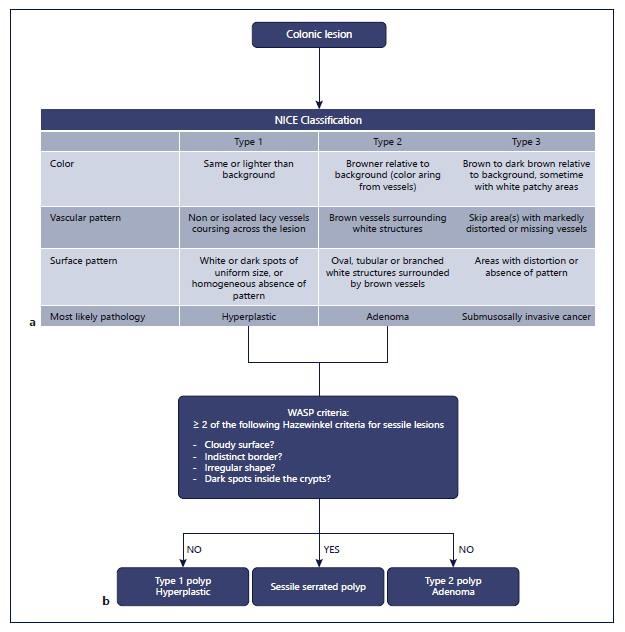
Fig. 4 a The NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic (NICE) classification system. b With integration of the Workgroup serrAted polypS and Polyposis’ (WASP) classification based on NICE and four Hazewinkel criteria [65, 67, 114].
The potential cost saving of optical diagnosis of diminutive polyps is clear. The initial DISCARD trial showed a promising overall accuracy of 93% for optical diagnosis and characterization of polyps <10 mm with NBI and a good prediction of surveillance interval [66]. However, the consecutive multicentric DISCARD 2 trial demonstrated only moderate sensitivities for optical diagnosis (83.9%) far below the 95% the study was powered to detect [67]. On a polyp level, test sensitivity (presence of adenoma, n = 1,620 polyps) was 76.1%. This result could be augmented to 99.4% in a fully adjusted analysis if at least 2 NICE characteristics were present. Hence, NBI-assisted optical diagnosis cannot be routinely recommended and should be preserved for expert hands, as recommended by the ESGE [68]. The optical effect of NBI can be appreciated in Figure 5.
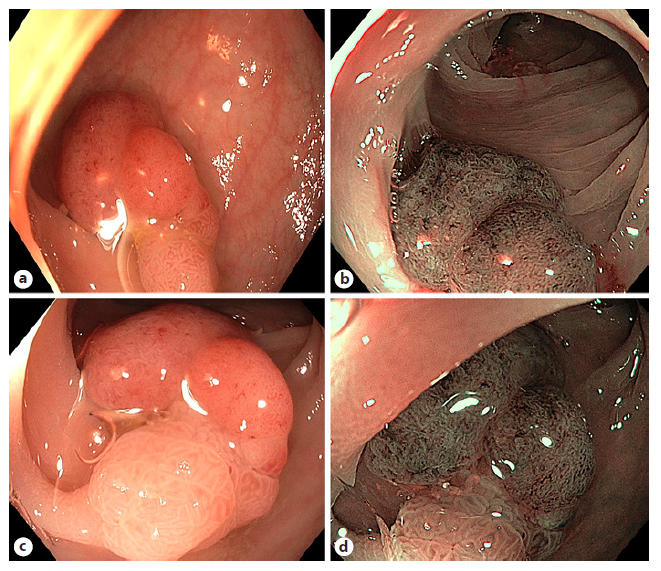
Fig. 5 Visualization of a colorectal polyp with white light versus narrowband imaging with or without magnification endoscopy. White light without near focus (a), NBI without near focus (b), white light with near focus (c), and NBI with near focus (d).
I-scan has also been tested as application for polyp detection and characterization using pit pattern and vascular pattern. Bouwens et al. [69] showed a sensitivity of 79%, a specificity of 86%, and an accuracy of 81% for non-expert endoscopist trained in a single session with i-scan and applying their own developed i-scan classification for endoscopic diagnosis. In terms of adenoma detection, a meta-analysis could not withhold a significant difference n adenoma detection between i-scan and WLE nor i-scan and HD-WLE [70]. However, a RCT published after this meta-analysis showed a significantly higher ADR in the i-scan group compared to the HD-WLE colonoscopy group (47.2% vs. 37.7%, p = 0.01). This outcome could mainly be attributed to an increased detection rate of diminutive, flat, and right-sided adenomas [71]. Recently, the SIMPLE classification, developed as a novel endo-scopic optical diagnostic classification system using i-scan, was validated [72]. In a cohort of 399 patients, the investigators assessed the agreement of surveillance intervals determined by optical diagnosis compared with pathology-based results and the diagnostic performances for diminutive polyps. For patients with at least one polyp ≤5 mm, agreement was 93.5% (95% confidence interval [CI] 91.4-95.6), and for polyps ≤10 mm 92.7% (95% CI: 98.7-95.1). The NPV for rectosigmoid adenomas ≤5 mm and ≤10 mm was 86.7% and 85.1%, respectively, too low for clinical implementation.
More recently, the mean number of adenomas per patient was reported to be significantly higher in the BLI group compared with that in the HD-WLE group, but with-out significantly higher ADR [73]. Furthermore, a BLI classification (BLI Adenoma Serrated International Classification (BASIC)) was developed to enable characterization of colorectal polyps. BASIC significantly improved the pre-training accuracy from 87% to 94% and significantly increased sensitivity and NPV of adenoma [74].
In a multicenter RCT, LCI showed to significantly augment the PDR compared to WLE without prolongation of the procedure time [75]. In terms of miss rate, a recent tandem colonoscopy RCT of the right colon (LCI-WLE vs. WLE-LCI) demonstrated in the LCI-first group a significantly lower adenoma miss rate in the right colon (11.8% vs. 30.6%, p < 0.001) [76]. Moreover, when tested for SSP/SSA detection, LCI showed to be superior to WLE and a lower SSA miss rate [77, 78]. In a recent meta-analysis, LCI significantly increased the number of adenomas detected per patient versus WLE (difference 0.22, 95% CI: 0.08-0.36, p < 0.002) [7]. The number of flat polyps per patient and the additional PDR were both significantly higher with LCI.
The current ESGE guidelines do not yet recommend VCE for routine practice. VCE can be used in average risk patients to increase ADR. However, the routine use must be balanced against costs and practical considerations. ESGE also suggests as weak recommendation that VCE and DCE can be used, under strictly controlled conditions, for real-time optical diagnosis of diminutive (≤5 mm) colorectal polyps, and can replace histopathological diagnosis [68].
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel diseases, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (UC), result in chronic inflammation of the ileal and/or colonic mucosa and if uncontrolled may lead to intra-epithelial neoplastic (IN) changes and colitisassociated dysplasia or cancer [79]. Colonoscopy surveillance is therefore recommended to detect the IN in curable stages [80, 81].
HD-WLE has shown to improve dysplasia detection when compared to standard WLE with an adjusted prevalence ratio of detecting dysplasia of 2.21 (95% CI 1.09-4.45) [82]. Although the SCENIC guidelines recommend the combination of DCE and targeted biopsies, hard evidence is currently lacking. However, a systematic review including 4 RCTs concluded that DCE is superior (RR: 1.38; 95% CI: 1.02-1.88) [83]. This latter conclusion is supported by more recent research (n = 305) showing a significantly better detection of dysplasia in the HD-CE group (n = 17) versus the HD-WLE group (n = 7) (p = 0,032) [84].
The use of VCE for dysplasia detection has recently been accepted by the ESGE [68, 85]. For NBI, the per-lesion analysis resulted in a significantly inferior false-positive biopsy rate (p < 0.001) and a similar true-positive rate as well as more missed IN lesions with NBI, albeit without reaching statistical significance [86]. Additionally, two Dutch groups could not demonstrate a significant improvement of detection of dysplasia when compared to HD-WLE [49, 59]. However, as stated in recent research, NBI in longstanding UC may not be significantly different from DCE for neoplasia detection (21.2% for DCE vs. 21.5% for NBI), but since it significantly shortens the procedural duration and is easier to apply, it could serve as a possible alternative for classical DCE [115].
With the ESGE shifting toward targeted biopsies, the collection of random biopsies during WLE surveillance examination is no longer recommended [85]. For patients with longstanding UC in remission, advanced imaging technologies are useful in identifying areas for targeted biopsies to assess histological disease activity. In UC, colonic mucosal erythema visualized by LCI correlates well with histological inflammation, and the LCI classification can predict relapse rates [87].
Endoscopic assessment of disease activity in both Crohn’s disease and UC has shown to be important in terms of patient treatment and prognostication. The Mayo endoscopic subscore (MES) is the most widely used endoscopic scoring system. Despite its simplicity, the MES was never formally validated and is strongly limited by inter- and intra-observer variability. So, more detailed and specific scoring systems like the Ulcerative Colitis Endoscopic Index of Severity (UCEIS) and Ulcerative Colitis Colonoscopic Index of Severity were developed and showed superiority in their operating characteristics over the MES, but remained limited by large observer-dependency [88, 89]. In 2017, a new and more comprehensive VCE score, the Paddington International Virtual Chromoendoscopy (PICaSSO) score, was developed and validated, including details of subtle vascular and mucosal changes reflecting acute or chronic inflammatory changes [90]. Eight assessors were trained with a 60-min training module outlining 3 different i-scan modes of the vascular and mucosal changes in every stage of disease activity in UC. The assessors’ performance was evaluated on 20 i-scan videoclips used both before and after the training module. The interobserver agreement for MES was high in both test phases (pre: k = 0 0.85; 95% CI: 0.78-0.90; post: k = 0.85; 95% CI: 0.77-0.90), and the same goes for the UCEIS (pre: k = 0.86; 95% CI: 0.77-0.92; post: k = 0 0.84; 95% CI: 0.75-0.91). The interobserver agreement of the PICaSSO endoscopic score was very high in both the pre- and post-test (k = 0.92; 95% CI: 0.86-0.96 and k = 0.89; 95% CI: 0.84-0.94, respectively), with an accuracy of predicting histological disease activity by the Robarts Histological Index of 72% (95% CI: 64-79%). Hence, the author’s conclusion that the PICaS-SO score may be used to define the endoscopic findings of mucosal and vascular healing in UC and reflects well the entire spectrum of histological changes.
Prospects and Future Directions
Several enhancement techniques for GI endoscopy have found their way into clinical practice and have proven to be helpful in several situations. All the abovementioned types of VCE increase the detection of neoplasia in both upper and lower GI tracts. Meta-analyses described the positive impact of VCE on the detection and diagnosis of ESCC, GC, and ESCC [31, 91, 92]. Similar meta-analyses have been conducted in the lower GI tract showing comparable positive trends for polyp detection [7, 70]. By improving the characterization of dysplasia in IBD and BE, colorectal polyps, and cancer, VCE has an impact on therapeutic decision-making and patient care. Augmentation of the dysplasia detection rate and less false-positive detections in dysplasia screening in BE and UC has pivoted the current practice toward targeted bi-opsies rather than random biopsies, what was endorsed by the ESGE for UC [82, 85, 86]. In colorectal cancer prevention, a similar path has been taken with improving characterization and ADR, and a discard strategy has been proposed and approved by the ESGE for diminutive hyperplastic polyps in the rectosigmoid in expert hands [68]. In parallel with the guidelines, novel classifications have been developed and validated, using VCE for both detection and characterization of GI lesions. Classifications like the JNET, WASP, SIMPLE, and BASIC have altered the field of colorectal polyps using VCE, more specific NBI, i-scan, and BLI, respectively [65, 72, 74, 93]. In the field of upper GI endoscopy, the BING/BLINC, the EGGIM score, and the use of JES classification for IPCL for BE, GC, and ESCC, respectively, have been validated [24, 33, 41].
VCE with NBI, BLI, LCI, and i-scan has recently been expanded by Olympus Corporation (Tokyo, Japan) with the introduction of texture and color enhancement imag-ing (TXI), the extended depth of field technology, and red dichromatic imaging technology, as part of the new EVIS X1 video system. Results are to be awaited, although a recent RCT comparing TXI to WLE, NBI, and DCE with indigo carmine staining for the visualization of serrated colorectal lesions (hyperplastic and SSL) showed that TXI had a significantly superior visibility score to WLE but inferior to NBI and DCE for hyperplastic polyps and SSL detection [94]. On a case-based level, red dichromatic imaging may improve the visualization of cryptogenic gastric bleeds since it improves redness and depth imaging [95]. The same suggestions have been made for the estimation of disease activity in UC and mucosal depth during endoscopic submucosal dissections [96, 97].
The use of VCE requires a certain experience and can reach its optimal impact in expert hands. Both DCE and VCE have their own learning curve and equipment to be controlled [98, 99]. Good training programs in a secured and standardized environment with direct feedback are needed to meet the required skills for optimal results [100]. For example, in case of optical diagnosis with NBI new evidence suggests that by changing the way of introducing this into community-based practice with periodically audited training and immediate feedback, the accuracy is sufficient to avoid post-polypectomy histological examination or to leave hyperplastic lesions in the rectosigmoid [101]. As suggested by the ESGE, before one can perform a qualitative optical diagnosis, the endoscopist should have a personal experience of at least 300 upper and 300 lower GI endoscopies and meeting the ESGE quality measures [102]. In addition, ESGE suggests that every endoscopist should be able and competent to per-form UGI/LGI endoscopy with HD white light combined with VCE and/or DCE before commencing training in optical diagnosis. The required number of DCE and DCE endoscopies is however not specified.
VCE has proven to significantly reduce the procedural duration as a push-on-the-button option. So, one could speculate that this may result in better time management and may increase cost-effectiveness by fewer random biopsies. However, their clinical applicability remains operator dependent and therefore is directly linked to training skills of the performing endoscopist. To overcome human interfering factors, AI has been proposed. Recently developed AI detection tools have shown their positive impact on polyp and adenoma detection [103]. In the field of IBD, Takenaka et al. [104], Bossuyt et al. [105], and Stidham et al. [106] developed an automated AI system for estimation of disease activity and severity in UC patients. The ARGOS project had the first automated system for BE dysplasia detection on WLE images with high accuracy of 92% for detecting and localizing BE dysplasia [107]. Currently, the system is further developed for real-time assessment. Hashimoto et al. [108] developed a similar CADe system which was now trained based on images (dysplastic and nondysplastic) illuminated with WL and NBI, near focus, and non-near focus, resulting in high accuracies for correctly detecting early neoplasia. A real-time deep learning (DL) system for classification and segmentation, differentiating between BE and early adenocarcinoma, has recently been developed. While an expert endoscopist conducts the endoscopic assessment of BE, the DL system captures real-time random images. The diagnostic and classifying accuracy of this DL system was 89.9% on 14 cases with neoplastic BE [109].
Based on the promising results in detection of lesions, there is currently a growing interest for characterization by AI. As well described in a recent systematic review and meta-analysis, most conducted studies are based on retrospective data with still images in WL and NBI [110]. To date, only three research groups used prospectively col-lected data with NBI. The first compared their computer-based algorithm with experts and nonexperts in terms of classification between neoplastic and non-neoplastic colorectal polyp and achieved a comparable diagnostic performance (expert group: 93.4% sensitivity, 91.8% specificity, and 92.7% accuracy; computer-based algorithm: 95.0% sensitivity, 90.3% specificity, and 93.1% ac-curacy) [111]. Both are significantly superior to the non-expert group (86.0% sensitivity, 87.8% specificity, and 86.8% accuracy). Second, a Taiwanese group developed a DL computer-aided diagnostic tool for the identification of neoplastic versus hyperplastic diminutive polyps [112].
This system classified polyps with similar clinical perfor-mances in a shorter time than the endoscopists. Third, the first single-center open label study was conducted assessing the real-time performance of a support vector machine with endocytoscopes after application of the NBI and methylene blue staining modes, respectively, for classification of diminutive (<5 mm) polyps in neoplastic and non-neoplastic [113]. The system showed performances allowing a resect and discard strategy of diminutive hyperplastic polyps. The CAD NPV was 96.5% (CI: 92.1-98.9%) (best-case scenario) and 95.2% (CI: 90.3-98.0%) (worst-case scenario) with NBI. Hence, the combination of higher detection with a better characterization by VCE and the objectivity and steady reproducibility of an AI system may be golden, based on the preliminary available data. Further investigation of this approach is currently subject of ongoing clinical research.
To conclude, an early endoscopic diagnosis of GI pathology is primordial for high-quality patient management enabling early treatment, a better prognosis, and patient care. WLE is still the first step in the detection of GI diseases, although evidence increases that VCE improves detection. Further characterization by CE, dye-based or virtual, can be applied as an add-on diagnostic tool to yield more details for a definite diagnosis based on targeted biopsies.
With increasing data on the potential of VCE, international guidelines are shifting toward the use of these techniques in specific situations. With the new era of AI in GI endoscopy, a brighter future is probably to be expected since AI can overcome the human limitations of these techniques improving early diagnosis, treatment, prognosis, and overall quality of daily endoscopy.